Datasheet
... The R100PX-48V/100A is a switched mode rectifier (SMR) module designed to provide up to 100A of output current into a 48V nominal system. This rectifier has been especially designed to be used in conjunction with a battery to provide an uninterruptible DC power system. The low noise and high reliabi ...
... The R100PX-48V/100A is a switched mode rectifier (SMR) module designed to provide up to 100A of output current into a 48V nominal system. This rectifier has been especially designed to be used in conjunction with a battery to provide an uninterruptible DC power system. The low noise and high reliabi ...
click here
... the specifications are nearly identical for the two vendors. Our main interest was in gain and noise figure for this experiment. ...
... the specifications are nearly identical for the two vendors. Our main interest was in gain and noise figure for this experiment. ...
How do series and parallel circuits work?
... 2. Each device in the circuit may be turned off independently without stopping the current flowing to other devices in the circuit. ...
... 2. Each device in the circuit may be turned off independently without stopping the current flowing to other devices in the circuit. ...
IXI848 - IXYS Power
... The VOUT output is a current source driving a 33kΩ resistance to ground for a gain of 10, or a 165kΩ resistance to ground for a gain of 50. Output gain is reduced by resistive loading of the VOUT terminal. The impedance of the external monitor load (ZM) should be chosen high enough to maintain the d ...
... The VOUT output is a current source driving a 33kΩ resistance to ground for a gain of 10, or a 165kΩ resistance to ground for a gain of 50. Output gain is reduced by resistive loading of the VOUT terminal. The impedance of the external monitor load (ZM) should be chosen high enough to maintain the d ...
Resistance does not vary with the applied voltage
... Two wires having different resistivities ρ1 and ρ2 and equal cross sections, a, are connected end to end. Their lengths are l1 and l2. If a battery is connected to this system such that a potential difference of V is maintained between the ends, a) What will be the current densities in the wires? b) ...
... Two wires having different resistivities ρ1 and ρ2 and equal cross sections, a, are connected end to end. Their lengths are l1 and l2. If a battery is connected to this system such that a potential difference of V is maintained between the ends, a) What will be the current densities in the wires? b) ...
t6_transformers
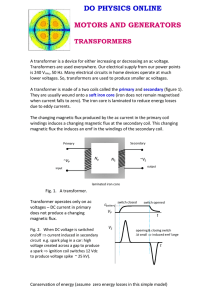
... TRANSFORMERS A transformer is a device for either increasing or decreasing an ac voltage. Transformers are used everywhere. Our electrical supply from our power points is 240 Vrms, 50 Hz. Many electrical circuits in home devices operate at much lower voltages. So, transformers are used to produce sm ...
... TRANSFORMERS A transformer is a device for either increasing or decreasing an ac voltage. Transformers are used everywhere. Our electrical supply from our power points is 240 Vrms, 50 Hz. Many electrical circuits in home devices operate at much lower voltages. So, transformers are used to produce sm ...
Impedance and Ohm`s Law
... and currents in a circuit when impedance or admittance are used. A resistor’s voltage and current are in phase. Voltage leads current through an inductor by 90o. Current leads voltage through a capacitor by 90o. ...
... and currents in a circuit when impedance or admittance are used. A resistor’s voltage and current are in phase. Voltage leads current through an inductor by 90o. Current leads voltage through a capacitor by 90o. ...
Testing tool for sensor manufacturing
... Introduction In today’s business environment, the US sensor market is ...
... Introduction In today’s business environment, the US sensor market is ...
electrical circuits - Riverside Rebel Science
... • Primary Cells – electric cells that can not be recharged because the chemical reaction is not reversible. • Secondary Cells – electric cells that can be recharged by forcing the chemical reaction in the reverse direction. • Fuel Cells – electric cells that require a continuous supply of chemicals ...
... • Primary Cells – electric cells that can not be recharged because the chemical reaction is not reversible. • Secondary Cells – electric cells that can be recharged by forcing the chemical reaction in the reverse direction. • Fuel Cells – electric cells that require a continuous supply of chemicals ...
up11_educue_ch31 - University of Manchester
... A capacitor is connected across an ac source as shown. Which graph correctly shows the instantaneous current through the capacitor and the instantaneous voltage vab across the capacitor? (current in purple, voltage in blue) ...
... A capacitor is connected across an ac source as shown. Which graph correctly shows the instantaneous current through the capacitor and the instantaneous voltage vab across the capacitor? (current in purple, voltage in blue) ...
HW Lab 1 - HAW Hamburg
... Connect a load resistor to the terminals A and B of the circuit illustrated above. Measure the load voltage and the current for each of the following resistances: RL1 = 470 Ω RL2 = 4,7 kΩ RL3 = 10 kΩ Draw a characteristic diagram U = f(I) of the voltage source based on these three data points. Then ...
... Connect a load resistor to the terminals A and B of the circuit illustrated above. Measure the load voltage and the current for each of the following resistances: RL1 = 470 Ω RL2 = 4,7 kΩ RL3 = 10 kΩ Draw a characteristic diagram U = f(I) of the voltage source based on these three data points. Then ...
EET-225 Homework #1
... sentences when answering all questions. Where a problem involves a circuit, you must redraw the circuit as part of the solution, showing all indicated voltages and currents on the circuit diagram. Box or underline all final answers and show all work (see syllabus for example of homework standards). ...
... sentences when answering all questions. Where a problem involves a circuit, you must redraw the circuit as part of the solution, showing all indicated voltages and currents on the circuit diagram. Box or underline all final answers and show all work (see syllabus for example of homework standards). ...
DI-124 Design Idea LinkSwitch-TN
... When the internal MOSFET turns on, Q1 is also turned on, applying the input voltage across the transformer primary. Once the primary current reaches the internal current limit of U1, the MOSFET is turned off and the energy stored is delivered to the output. Regulation is maintained using ON/OFF cont ...
... When the internal MOSFET turns on, Q1 is also turned on, applying the input voltage across the transformer primary. Once the primary current reaches the internal current limit of U1, the MOSFET is turned off and the energy stored is delivered to the output. Regulation is maintained using ON/OFF cont ...
Elantec DC-DC Converter Solution for Virtex FPGAs How to use the
... and “power ground” pin connections. The goal is to localize the high current, high speed output noise into an “independent” loop which does not interfere with the more sensitive low level analog control functions. The layout is very important for the converter to function properly. Signal Ground (SG ...
... and “power ground” pin connections. The goal is to localize the high current, high speed output noise into an “independent” loop which does not interfere with the more sensitive low level analog control functions. The layout is very important for the converter to function properly. Signal Ground (SG ...
Module 3 – Networking media
... the screen moves higher or lower. The result is a representation of the signal (voltage) showing the level over time, like a wriggly piece of string laid on a desk. 3: A diagram of a flash light, it shows a battery connected to a light bulb via a switch. When the switch is open (off) no current can ...
... the screen moves higher or lower. The result is a representation of the signal (voltage) showing the level over time, like a wriggly piece of string laid on a desk. 3: A diagram of a flash light, it shows a battery connected to a light bulb via a switch. When the switch is open (off) no current can ...
MF60 0.6W 1% Metal Film Resistors Truohm – MF60
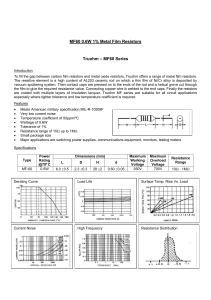
... To fill the gap between carbon film resistors and metal oxide resistors, Truohm offers a range of metal film resistors. The resistive element is a high content of AL203 ceramic rod on which a thin film of Ni/Cr alloy is deposited by vacuum sputtering system. Then contact caps are pressed on to the e ...
... To fill the gap between carbon film resistors and metal oxide resistors, Truohm offers a range of metal film resistors. The resistive element is a high content of AL203 ceramic rod on which a thin film of Ni/Cr alloy is deposited by vacuum sputtering system. Then contact caps are pressed on to the e ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.