5B39-02中文资料
... across the modules’ output terminals,. This approach should be used with caution because the output lacks the low impedance of a true voltage source. This means that the tolerance and size of the load impedance relative to the conversion resistor can introduce significant error. For example, a load ...
... across the modules’ output terminals,. This approach should be used with caution because the output lacks the low impedance of a true voltage source. This means that the tolerance and size of the load impedance relative to the conversion resistor can introduce significant error. For example, a load ...
ACS712: Fully Integrated, Hall Effect
... Sensitivity (Sens). The change in device output in response to a 1 A change through the primary conductor. The sensitivity is the product of the magnetic circuit sensitivity (G / A) and the linear IC amplifier gain (mV/G). The linear IC amplifier gain is programmed at the factory to optimize the sen ...
... Sensitivity (Sens). The change in device output in response to a 1 A change through the primary conductor. The sensitivity is the product of the magnetic circuit sensitivity (G / A) and the linear IC amplifier gain (mV/G). The linear IC amplifier gain is programmed at the factory to optimize the sen ...
AN703 Designing DC/DC Converters with the Si9110 Switchmode
... A buried zener with merged temperature compensating diode (patent pending) is used to achieve stability of 0.25 mV/°C. The Si9110 voltage reference is trimmed to 4 V plus or minus 1% with a bias current of 15 µA. This voltage varies by about 1% as IBIAS is varied from 5 to 50 µA. If 1% reference acc ...
... A buried zener with merged temperature compensating diode (patent pending) is used to achieve stability of 0.25 mV/°C. The Si9110 voltage reference is trimmed to 4 V plus or minus 1% with a bias current of 15 µA. This voltage varies by about 1% as IBIAS is varied from 5 to 50 µA. If 1% reference acc ...
Voltage source
... circuit). Such a theoretical device would have a zero ohm output impedance in series with the source. A real-world voltage source has a very low, but non-zero output impedance: often much less than 1 ohm. Conversely, a current source provides a constant current, as long as the load connected to the ...
... circuit). Such a theoretical device would have a zero ohm output impedance in series with the source. A real-world voltage source has a very low, but non-zero output impedance: often much less than 1 ohm. Conversely, a current source provides a constant current, as long as the load connected to the ...
current - Uplift Hampton
... DC power is provided at one voltage only There is energy lost in a power line due to dissipation of energy to heat throughout the length of the cable. So DC power plants must be close to users The major advantage of AC: AC voltages can be transformed to higher or lower voltages (can be stepped up or ...
... DC power is provided at one voltage only There is energy lost in a power line due to dissipation of energy to heat throughout the length of the cable. So DC power plants must be close to users The major advantage of AC: AC voltages can be transformed to higher or lower voltages (can be stepped up or ...
solving problems ch 14 ppt File
... flowing from the source is 4 amps. 2 amps flows through the upper branch of the circuit and 2 amps flows through the center branch of the circuit. b. 4 amps flowing through point P from bottom to top. The sum of the current in the branches is 4 amps. c. 2 amps are flowing through point P from left t ...
... flowing from the source is 4 amps. 2 amps flows through the upper branch of the circuit and 2 amps flows through the center branch of the circuit. b. 4 amps flowing through point P from bottom to top. The sum of the current in the branches is 4 amps. c. 2 amps are flowing through point P from left t ...
UT54ACS86 - Aeroflex Microelectronic Solutions
... 1. Functional tests are conducted in accordance with MIL-STD-883 with the following input test conditions: VIH = VIH(min) + 20%, - 0%; VIL = VIL(max) + 0%, 50%, as specified herein, for TTL, CMOS, or Schmitt compatible inputs. Devices may be tested using any input voltage within the above specified ...
... 1. Functional tests are conducted in accordance with MIL-STD-883 with the following input test conditions: VIH = VIH(min) + 20%, - 0%; VIL = VIL(max) + 0%, 50%, as specified herein, for TTL, CMOS, or Schmitt compatible inputs. Devices may be tested using any input voltage within the above specified ...
Sonic Fast Recovery Diode
... Data according to IEC 60747and per diode unless otherwise specified ...
... Data according to IEC 60747and per diode unless otherwise specified ...
A Test Oscillator For Ham Radio - Electrical and Information
... Depending on the applications, different oscillator models could be used. Hartley, Colpitts and Clapp are three of these models which are widely used. In the Hartley oscillator, an inductive feedback network and a capacitor are in parallel to set the oscillation frequency. The Colpitts oscillator is ...
... Depending on the applications, different oscillator models could be used. Hartley, Colpitts and Clapp are three of these models which are widely used. In the Hartley oscillator, an inductive feedback network and a capacitor are in parallel to set the oscillation frequency. The Colpitts oscillator is ...
Encoders Frequently Asked Questions
... arc welders, AC power lines, and transformers. Use twisted pair cabling when using the signal and its compliment, and shielded cabling when running any type of signal. Use the highest voltage available for the output voltage. For example, if the encoder will output 5 to 24 volts, then use 24 volts. ...
... arc welders, AC power lines, and transformers. Use twisted pair cabling when using the signal and its compliment, and shielded cabling when running any type of signal. Use the highest voltage available for the output voltage. For example, if the encoder will output 5 to 24 volts, then use 24 volts. ...
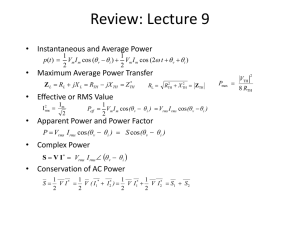
Review: Lecture 9
... Consider the circuit below. Determine the coupling coefficient. Calculate the energy stored in the coupled inductors at time t = 1s if v=60cos(4t +30°) V. ...
... Consider the circuit below. Determine the coupling coefficient. Calculate the energy stored in the coupled inductors at time t = 1s if v=60cos(4t +30°) V. ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.