4-Sensor Glossary of Technical Definitions and Terminology
... The maximum current at which the proximity sensor can be continuously operated. Minimum Inrush Current: The maximum current level at which the proximity sensor can be operated for a short period of time. Minimum Load Current: The minimum amount of current required by the sensor to maintain reliable ...
... The maximum current at which the proximity sensor can be continuously operated. Minimum Inrush Current: The maximum current level at which the proximity sensor can be operated for a short period of time. Minimum Load Current: The minimum amount of current required by the sensor to maintain reliable ...
A Current-Feedback Instrumentation Amplifier With 5 V Offset for
... common ground. On the other hand, a high-side current-sense amplifier must be able to suppress a large input CM voltage, while also generating a ground-referred output voltage. Focusing on the specific application of monitoring load currents in laptops, a few specifications can be derived. Nowadays, ...
... common ground. On the other hand, a high-side current-sense amplifier must be able to suppress a large input CM voltage, while also generating a ground-referred output voltage. Focusing on the specific application of monitoring load currents in laptops, a few specifications can be derived. Nowadays, ...
TS1005 - Silicon Labs
... matched to each other as well as both resistors labeled R2 to ensure acceptable common-mode rejection performance. Resistor networks ensure the closest matching as well as matched drifts for good temperature stability. Capacitor C1 is included to limit the bandwidth and, therefore, the noise in sens ...
... matched to each other as well as both resistors labeled R2 to ensure acceptable common-mode rejection performance. Resistor networks ensure the closest matching as well as matched drifts for good temperature stability. Capacitor C1 is included to limit the bandwidth and, therefore, the noise in sens ...
Project synopsis on BLINKING LEDs USING 8051
... the transistor goes to cut off and the LED extinguishes. The transistor driver circuit for the LED can be avoided and the LED can be connected directly to the P1.0 pin with a series current limiting resistor(~1K). The time for which P1.o goes high and low (time period of the LED) is determined by th ...
... the transistor goes to cut off and the LED extinguishes. The transistor driver circuit for the LED can be avoided and the LED can be connected directly to the P1.0 pin with a series current limiting resistor(~1K). The time for which P1.o goes high and low (time period of the LED) is determined by th ...
STPMS1
... In order to enable proper operation of the switched capacitor (SC) section of AD converters, two DC buffers are added to the device. One is buffering the voltage reference level and the other is buffering the level of value equal to (VDD-VSS)/2. The AD converter block is further split into a voltage ...
... In order to enable proper operation of the switched capacitor (SC) section of AD converters, two DC buffers are added to the device. One is buffering the voltage reference level and the other is buffering the level of value equal to (VDD-VSS)/2. The AD converter block is further split into a voltage ...
Design and Simulation of Frequency Divider by Negative Differential
... Generally, in nonlinear systems which generate chaos, long-period behavior is also observed in some parameter regions. This is called the bifurcation phenomenon. In the bifurcation region, the system’s output period is the integer-multiple of the input period. It should be noted that the operation f ...
... Generally, in nonlinear systems which generate chaos, long-period behavior is also observed in some parameter regions. This is called the bifurcation phenomenon. In the bifurcation region, the system’s output period is the integer-multiple of the input period. It should be noted that the operation f ...
LT1795 - Dual 500mA/50MHz Current Feedback Line Driver Amplifier
... output current and excellent large signal characteristics. The combination of high slew rate, 500mA output drive and up to ±15V operation enables the device to deliver significant power at frequencies in the 1MHz to 2MHz range. Short-circuit protection and thermal shutdown insure the device’s rugged ...
... output current and excellent large signal characteristics. The combination of high slew rate, 500mA output drive and up to ±15V operation enables the device to deliver significant power at frequencies in the 1MHz to 2MHz range. Short-circuit protection and thermal shutdown insure the device’s rugged ...
CLWG Linear Potentiometer
... Measurement Specialties, TE Connectivity, TE Connectivity (logo) and EVERY CONNECTION COUNTS are trademarks. All other logos, products and/or company names referred to herein might be trademarks of their respective owners. The information given herein, including drawings, illustrations and schematic ...
... Measurement Specialties, TE Connectivity, TE Connectivity (logo) and EVERY CONNECTION COUNTS are trademarks. All other logos, products and/or company names referred to herein might be trademarks of their respective owners. The information given herein, including drawings, illustrations and schematic ...
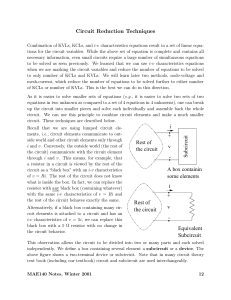
Circuit Reduction Techniques
... A typical Ohm-meter measures the resistance of a resistor by using the Ohm’s Law. It applies a known voltage of vs across the resistor, measures the current flowing through the resistor, and its dial are set to convert the measured value of current into the value of resistance by using R = vs /imeasu ...
... A typical Ohm-meter measures the resistance of a resistor by using the Ohm’s Law. It applies a known voltage of vs across the resistor, measures the current flowing through the resistor, and its dial are set to convert the measured value of current into the value of resistance by using R = vs /imeasu ...
Two-port network
... which are shown in Figure 1. These current and voltage variables are most useful at low-to-moderate frequencies. At high frequencies (e.g., microwave frequencies), the use of power and energy variables is more appropriate, and the two-port current–voltage approach that is discussed here is replaced ...
... which are shown in Figure 1. These current and voltage variables are most useful at low-to-moderate frequencies. At high frequencies (e.g., microwave frequencies), the use of power and energy variables is more appropriate, and the two-port current–voltage approach that is discussed here is replaced ...
Alternating Currents - Lagan College Physics
... A trigger pulse is sent from the oscilloscope to the transmitter. At the same time the spot is moved across the screen by the time base. When the receiver, which is connected to the Yinput, detects the pulse a deflection appears on the screen. If the time base had been set to 2 ms cm-1 then this pul ...
... A trigger pulse is sent from the oscilloscope to the transmitter. At the same time the spot is moved across the screen by the time base. When the receiver, which is connected to the Yinput, detects the pulse a deflection appears on the screen. If the time base had been set to 2 ms cm-1 then this pul ...
Alternating Currents
... A trigger pulse is sent from the oscilloscope to the transmitter. At the same time the spot is moved across the screen by the time base. When the receiver, which is connected to the Yinput, detects the pulse a deflection appears on the screen. If the time base had been set to 2 ms cm-1 then this pul ...
... A trigger pulse is sent from the oscilloscope to the transmitter. At the same time the spot is moved across the screen by the time base. When the receiver, which is connected to the Yinput, detects the pulse a deflection appears on the screen. If the time base had been set to 2 ms cm-1 then this pul ...
Lecture 03 Fundamental Electric Circuit Laws Full
... This essentially means that the total emf in a closed circuit, which may be the sum of a number of emfs at different locations and of different magnitudes and polarities, must equal the sum of the potential differences generated across all of the conducting elements due to the current circulating ar ...
... This essentially means that the total emf in a closed circuit, which may be the sum of a number of emfs at different locations and of different magnitudes and polarities, must equal the sum of the potential differences generated across all of the conducting elements due to the current circulating ar ...
AN-778 APPLICATION NOTE
... APPLICATION CIRCUIT FOR PRUP PIN The application circuit for the PRUP pin is shown in Figure 1. This circuit is used to condition the control signal for PRUP such that the device starts in the correct state. As described in the AD607 and AD61009 data sheets, there are instances when an improperly co ...
... APPLICATION CIRCUIT FOR PRUP PIN The application circuit for the PRUP pin is shown in Figure 1. This circuit is used to condition the control signal for PRUP such that the device starts in the correct state. As described in the AD607 and AD61009 data sheets, there are instances when an improperly co ...
PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRONICS It should be quite obvious to the
... Inductors. The purpose of an inductor, or inductance coil, is to insert inductance into a circuit. The effect of an inductance is to oppose any change 6 in the existing current flow in a circuit. The opposition to current flow in an a. c. circuit by an inductor is called inductive reactance and is m ...
... Inductors. The purpose of an inductor, or inductance coil, is to insert inductance into a circuit. The effect of an inductance is to oppose any change 6 in the existing current flow in a circuit. The opposition to current flow in an a. c. circuit by an inductor is called inductive reactance and is m ...
An undergraduate laboratory experiment for measuring the
... achieved only using a sophisticated automatic thermoregulator, equipped with a feedback-loop gain controlled by both the error signal and its time derivative(4). On the other hand the temperature errors introduced by non-equilibrium conditions can be accounted for in the data handling, as explained ...
... achieved only using a sophisticated automatic thermoregulator, equipped with a feedback-loop gain controlled by both the error signal and its time derivative(4). On the other hand the temperature errors introduced by non-equilibrium conditions can be accounted for in the data handling, as explained ...
Document
... An ac voltmeter using half-wave rectification is only approximatelv 45% as sensitive as a dc voltmeter. The circuit would probably be designed for full-scale deflection with a 10-V rms alternating current applied, which means the multiplier resistor would be only 45% of the value of the multiplier r ...
... An ac voltmeter using half-wave rectification is only approximatelv 45% as sensitive as a dc voltmeter. The circuit would probably be designed for full-scale deflection with a 10-V rms alternating current applied, which means the multiplier resistor would be only 45% of the value of the multiplier r ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.