Noise in Analog Circuits
... prevalent the noise is at different frequencies. Noise is typically described in terms of the noise power. However, in this respect the jargon makes somewhat sloppy use of terminology, and what is called “noise power” is often in units of V2. There are several types of noise. a) White noise: White n ...
... prevalent the noise is at different frequencies. Noise is typically described in terms of the noise power. However, in this respect the jargon makes somewhat sloppy use of terminology, and what is called “noise power” is often in units of V2. There are several types of noise. a) White noise: White n ...
PT-6008-GeneratorReactances-en
... 3. the impedance to the point of the fault, mostly cable impedance, 4. and the impedance of the fault, if arcing. The generator internal voltage and generator impedance determines the current that flows when the terminals of a generator are shorted. The effect of armature reaction on the generator a ...
... 3. the impedance to the point of the fault, mostly cable impedance, 4. and the impedance of the fault, if arcing. The generator internal voltage and generator impedance determines the current that flows when the terminals of a generator are shorted. The effect of armature reaction on the generator a ...
SHOCK VALUE
... • Competition must have at least one task or question from each of the five areas. • Competition must consist of both hands-on tasks and questions. • 50% of the score must be from hands-on tasks and 50% must be from the theoretical portion. • The event supervisor may provide some ...
... • Competition must have at least one task or question from each of the five areas. • Competition must consist of both hands-on tasks and questions. • 50% of the score must be from hands-on tasks and 50% must be from the theoretical portion. • The event supervisor may provide some ...
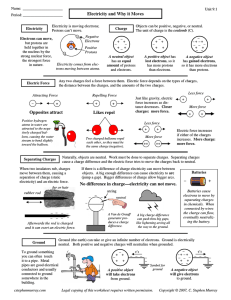
Physics notes - Electricity
... (1) The same current flows through each conductor, i.e. I1 = I 2 = ........ = I 6 = I . (2) The sum of the potential difference across each conductor equals the potential difference between the two ends of the series connection, i.e. V1 + V2 + ..... + V6 = V XY . (3) The total resistance equals the ...
... (1) The same current flows through each conductor, i.e. I1 = I 2 = ........ = I 6 = I . (2) The sum of the potential difference across each conductor equals the potential difference between the two ends of the series connection, i.e. V1 + V2 + ..... + V6 = V XY . (3) The total resistance equals the ...
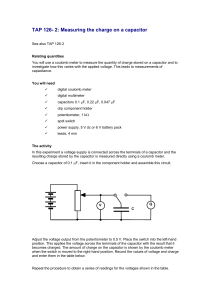
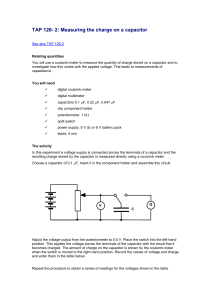
TAP 126- 2: Measuring the charge on a capacitor
... The coulomb meter is a useful instrument for measuring the charge stored on small-value capacitors. A typical coulomb meter can measure up to 2 mC. For voltages of up to 6 V this implies that it can be used with capacitors up to a maximum value of 0.3 mF. The use of the coulomb meter described here ...
... The coulomb meter is a useful instrument for measuring the charge stored on small-value capacitors. A typical coulomb meter can measure up to 2 mC. For voltages of up to 6 V this implies that it can be used with capacitors up to a maximum value of 0.3 mF. The use of the coulomb meter described here ...
Tech Short 16 - Detectors and Discriminators
... rather briefly outline the various forms of detector used in valve receivers, when and why they are used, discuss typical detector circuits used in Eddystone valve receivers of the post-WWII era, and provide some commentary on their performance and faults that may develop in them. Detector circuits ...
... rather briefly outline the various forms of detector used in valve receivers, when and why they are used, discuss typical detector circuits used in Eddystone valve receivers of the post-WWII era, and provide some commentary on their performance and faults that may develop in them. Detector circuits ...
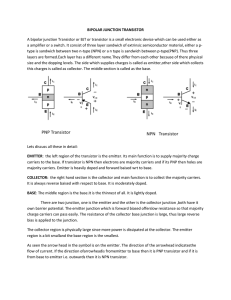
Bipolar Junction Transistor
... The transistor is a current controlled device. The output voltage power and current are controlled by the input current. Since there are two type of charge carriers: majority and minority hence it is called as Bi-Polar. In layman terms,transistor is a regulator. As the speed of the fan can be contr ...
... The transistor is a current controlled device. The output voltage power and current are controlled by the input current. Since there are two type of charge carriers: majority and minority hence it is called as Bi-Polar. In layman terms,transistor is a regulator. As the speed of the fan can be contr ...
AC TRANSMISSION
... transmitted at two different values of VR. The normal operation is at the upper value, within narrow limits around 1.0 pu. At the lower voltage, the current is higher and may exceed thermal limits. The feasibility of operation at the lower voltage also depends on load characteristics, and may lead t ...
... transmitted at two different values of VR. The normal operation is at the upper value, within narrow limits around 1.0 pu. At the lower voltage, the current is higher and may exceed thermal limits. The feasibility of operation at the lower voltage also depends on load characteristics, and may lead t ...
Revision Essentials - The Random Information Bureau
... VCC1 and bottom transistor pulls down towards VCC2. Much more efficient (no bias and no quiescent current), but suffers from crossover distortion due to 0.6v switch-on requirement for each transistor. Gain is 0 at crossover point. Class AB amplifiers: Using class B circuit but with small quiescent c ...
... VCC1 and bottom transistor pulls down towards VCC2. Much more efficient (no bias and no quiescent current), but suffers from crossover distortion due to 0.6v switch-on requirement for each transistor. Gain is 0 at crossover point. Class AB amplifiers: Using class B circuit but with small quiescent c ...
MAX4923–MAX4926 Overvoltage Protectors with External pFET General Description
... pFET. When the input voltage exceeds the OVLO threshold, these devices turn off the external pFET to prevent damage to protected components. The typical overvoltage trip level is set to 7.18V (MAX4923), 6.16V (MAX4924), 5.65V (MAX4925), and 4.46V (MAX4926). When the supply drops below the UVLO thres ...
... pFET. When the input voltage exceeds the OVLO threshold, these devices turn off the external pFET to prevent damage to protected components. The typical overvoltage trip level is set to 7.18V (MAX4923), 6.16V (MAX4924), 5.65V (MAX4925), and 4.46V (MAX4926). When the supply drops below the UVLO thres ...
FSB50550A / FSB50550AT Motion SPM 5 Series ®
... Figure 3. Recommended MCU Interface and Bootstrap Circuit with Parameters 3rd Notes: 1. Parameters for bootstrap circuit elements are dependent on PWM algorithm. For 15 kHz of switching frequency, typical example of parameters is shown above. 2. RC-coupling (R5 and C5) and C4 at each input of Motion ...
... Figure 3. Recommended MCU Interface and Bootstrap Circuit with Parameters 3rd Notes: 1. Parameters for bootstrap circuit elements are dependent on PWM algorithm. For 15 kHz of switching frequency, typical example of parameters is shown above. 2. RC-coupling (R5 and C5) and C4 at each input of Motion ...
L12b_4345_Sp02
... CONTACT RESISTANCE THE RESISTANCE RC ADDED BY A SINGLE CONTACT HAVING WIDTH WC AND LENGTH LC EQUALS RC = (RS*C)1/2 COTH(LC *(RS/ C)1/2)/WC RS – SHEET RESISTANCE OF THE RESISTOR MATERIAL C – SPECIFIC CONTACT RESISTANCE ...
... CONTACT RESISTANCE THE RESISTANCE RC ADDED BY A SINGLE CONTACT HAVING WIDTH WC AND LENGTH LC EQUALS RC = (RS*C)1/2 COTH(LC *(RS/ C)1/2)/WC RS – SHEET RESISTANCE OF THE RESISTOR MATERIAL C – SPECIFIC CONTACT RESISTANCE ...
Evaluates: MAX1501 MAX1501 Evaluation Kit General Description Features
... In NiMH/NiCd charge mode, the MAX1501 charges 3cell NiMH/NiCd batteries using voltage, current, and thermal-control loops. When a 3-cell NiMH/NiCd battery pack with a voltage below 2.8V is inserted, the MAX1501 charger enters the prequalification stage where it precharges the battery pack with 10% o ...
... In NiMH/NiCd charge mode, the MAX1501 charges 3cell NiMH/NiCd batteries using voltage, current, and thermal-control loops. When a 3-cell NiMH/NiCd battery pack with a voltage below 2.8V is inserted, the MAX1501 charger enters the prequalification stage where it precharges the battery pack with 10% o ...
Simulation of a Cascaded Multilevel Inverter Topology with Reduced
... switches are depleted in the conduction path, so both the switching as well as conduction losses are reduced, lower input current distortion and electromagnetic interference are also reduced. Therefore it assists for the higher efficiency of the converter. The propound inverter focus extends the out ...
... switches are depleted in the conduction path, so both the switching as well as conduction losses are reduced, lower input current distortion and electromagnetic interference are also reduced. Therefore it assists for the higher efficiency of the converter. The propound inverter focus extends the out ...
Heating in Aluminum Electrolytic Strobe and Photoflash Capacitors
... Hz or higher, and the resulting AC voltage is small, foil etch structure and the electrolyte resistivity, generally less than 10% of the DC voltage rating which is in turn dependent on composition and temof the capacitor. For these applications, the capaci- perature. DFOX is approximately constant a ...
... Hz or higher, and the resulting AC voltage is small, foil etch structure and the electrolyte resistivity, generally less than 10% of the DC voltage rating which is in turn dependent on composition and temof the capacitor. For these applications, the capaci- perature. DFOX is approximately constant a ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.