What is DNA?
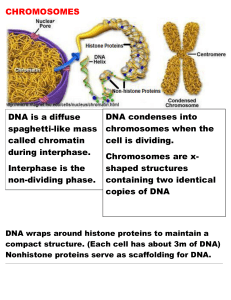
... • Fine thread like structures located in a cell’s nucleus. • Chromosomes control heredity • Chromosomes are made of chromatin, which are very long thin strands of DNA • Chromatin is wrapped tightly together around a protein in an X shape ...
... • Fine thread like structures located in a cell’s nucleus. • Chromosomes control heredity • Chromosomes are made of chromatin, which are very long thin strands of DNA • Chromatin is wrapped tightly together around a protein in an X shape ...
The Process of Cell Division
... In eukaryotic cells, DNA is packaged into multiple chromosomes. DNA double helix ...
... In eukaryotic cells, DNA is packaged into multiple chromosomes. DNA double helix ...
Document
... Below are the topic sentences for the essential question paragraphs. You must write a paragraph explaining each answer and have a colored picture for each paragraph. EQ 6 What role do chromosomes play in inheritance? According to the chromosome theory of inheritance, genes are carried from parents t ...
... Below are the topic sentences for the essential question paragraphs. You must write a paragraph explaining each answer and have a colored picture for each paragraph. EQ 6 What role do chromosomes play in inheritance? According to the chromosome theory of inheritance, genes are carried from parents t ...
Keystone Vocabulary 61-70
... 63. Homologous Structure: A physical characteristic in different organisms that is similar because it was inherited from a common ancestor. 64. Interphase: The longest lasting phase of the cell cycle in which a cell performs the majority of its functions, such as preparing for nuclear division and c ...
... 63. Homologous Structure: A physical characteristic in different organisms that is similar because it was inherited from a common ancestor. 64. Interphase: The longest lasting phase of the cell cycle in which a cell performs the majority of its functions, such as preparing for nuclear division and c ...
Intro to DNA
... Intro to DNA • NOTE: • “matching pairs” of chromosomes • = “homologous pairs”. • In every human somatic cell, there are 23 homologous pairs of chromosomes. ...
... Intro to DNA • NOTE: • “matching pairs” of chromosomes • = “homologous pairs”. • In every human somatic cell, there are 23 homologous pairs of chromosomes. ...
Mitosis and Meiosis Crossword
... 1 - These are not visible in the cell during interphase 3 - An Egg has 23 chromosomes. Is it haploid or diploid? 5 - This is when the cell breaks into two 8 - This term describes when genetic segments of information are swapped when the chromosomes are next to each other. 11 - Spindle fiber ...
... 1 - These are not visible in the cell during interphase 3 - An Egg has 23 chromosomes. Is it haploid or diploid? 5 - This is when the cell breaks into two 8 - This term describes when genetic segments of information are swapped when the chromosomes are next to each other. 11 - Spindle fiber ...
Genetics Vocabulary Week 3
... Asexual Reproduction – one parent producing offspring identical to parent and to other offspring. Buzz words are one, identical, fission, regenerate, mitosis (Example: bacteria – binary fission; fungi (yeast) – budding Mitosis – the stage of the cell cycle when a cell’s chromosomes are copied exactl ...
... Asexual Reproduction – one parent producing offspring identical to parent and to other offspring. Buzz words are one, identical, fission, regenerate, mitosis (Example: bacteria – binary fission; fungi (yeast) – budding Mitosis – the stage of the cell cycle when a cell’s chromosomes are copied exactl ...
Cloze passage 3
... o) The twisted shape of a DNA molecule p) A biologist who worked with fruit fly to identify sex-linkage q) The features or traits of an organism are controlled by both genes and the ……………. r) The base complementary to thymine s) A model we used to represent chromosomes t) A biological name for a fam ...
... o) The twisted shape of a DNA molecule p) A biologist who worked with fruit fly to identify sex-linkage q) The features or traits of an organism are controlled by both genes and the ……………. r) The base complementary to thymine s) A model we used to represent chromosomes t) A biological name for a fam ...
Meiosis = nuclear division that reduces chromosome
... Meiosis = nuclear division that reduces chromosome number by half sex cell division gametes = sperm & egg (ovum) (plural = ova) results in 4 haploid cells sperm (23) + egg (23) zygote (46) = fertilized egg you have exactly ½ of your Dad’s chromosomes and ½ of your Mom’s puberty = stage ...
... Meiosis = nuclear division that reduces chromosome number by half sex cell division gametes = sperm & egg (ovum) (plural = ova) results in 4 haploid cells sperm (23) + egg (23) zygote (46) = fertilized egg you have exactly ½ of your Dad’s chromosomes and ½ of your Mom’s puberty = stage ...
Honors Genetics Chapter 2: Mitosis and Meiosis INTRODUCTION
... genetics information. Chromosomes are only visible during mitosis and meiosis. During Interphase, when the cell’s nucleus is not dividing, DNA is organized as chromatin (spaghetti on a plate). Mitosis: leads to the production of two new cells, each with the same number of cells as the original paren ...
... genetics information. Chromosomes are only visible during mitosis and meiosis. During Interphase, when the cell’s nucleus is not dividing, DNA is organized as chromatin (spaghetti on a plate). Mitosis: leads to the production of two new cells, each with the same number of cells as the original paren ...
DNA Glossary - FutureLearn
... DNA is located in the chromosomes present in the nucleus of the cell. The DNA of an individual is the same in every one of his or her cells (but is not present in red blood cells because these cells have no nuclei) and different from everyone else’s other than identical twins. The DNA molecule resem ...
... DNA is located in the chromosomes present in the nucleus of the cell. The DNA of an individual is the same in every one of his or her cells (but is not present in red blood cells because these cells have no nuclei) and different from everyone else’s other than identical twins. The DNA molecule resem ...
Slide 1
... • mitochondria, chloroplast (the endosymbiont theory) • What form does DNA take in the nucleus? • chromosome • How do the 150 million base pairs that make up the human genome fit into the nucleus? • wrapped around histones • coiled and supercoiled chromatin condenses into chromosomes ...
... • mitochondria, chloroplast (the endosymbiont theory) • What form does DNA take in the nucleus? • chromosome • How do the 150 million base pairs that make up the human genome fit into the nucleus? • wrapped around histones • coiled and supercoiled chromatin condenses into chromosomes ...
Bio Ch 8-1 Notes
... Every cell of an organism produced by sexual reproduction has two copies of each autosome (one from each parent) ...
... Every cell of an organism produced by sexual reproduction has two copies of each autosome (one from each parent) ...
The DNA molecule exits for most of the cell cycle as
... The DNA molecule exists for most of the cell cycle as chromatin, a long, uncoiled single strand. Chromatin will coil around proteins called histones to form chromosomes. Chromosomes are packages of DNA which can be transferred to new daughter cells when the cell reproduces through mitosis. ...
... The DNA molecule exists for most of the cell cycle as chromatin, a long, uncoiled single strand. Chromatin will coil around proteins called histones to form chromosomes. Chromosomes are packages of DNA which can be transferred to new daughter cells when the cell reproduces through mitosis. ...
Mitosis Vocab
... function. 2. Chromatid – One part of a chromosome 3. Spindle fibers- protein filaments (part of cytoskeleton) that move the chromosomes apart during cell division. ...
... function. 2. Chromatid – One part of a chromosome 3. Spindle fibers- protein filaments (part of cytoskeleton) that move the chromosomes apart during cell division. ...
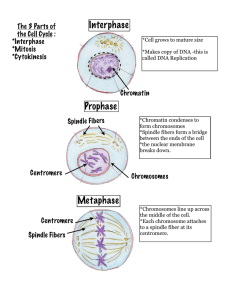
Interphase Prophase Metaphase
... *the centromeres split and the 2 chromatids separate. *the chromatids move along the spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell. * the cell is stretched out as the opposite ends pull apart. ...
... *the centromeres split and the 2 chromatids separate. *the chromatids move along the spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell. * the cell is stretched out as the opposite ends pull apart. ...
Genetic Birth Defects
... of two. It’s named after of John H.Edwards who first described it in 1960. ...
... of two. It’s named after of John H.Edwards who first described it in 1960. ...
Sex Chromosome Biology in the Mammalian Kingdom All biological
... million years ago, the X and Y chromosomes were very similar, but since then the Y chromosome has lost most of its genes, whereas the present X chromosome contains more than 1000 genes. Hence, the dosage of X-encoded genes needs to be equalized between female (XX) and male (XY) cells. This is achiev ...
... million years ago, the X and Y chromosomes were very similar, but since then the Y chromosome has lost most of its genes, whereas the present X chromosome contains more than 1000 genes. Hence, the dosage of X-encoded genes needs to be equalized between female (XX) and male (XY) cells. This is achiev ...
Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human
... 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
... 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
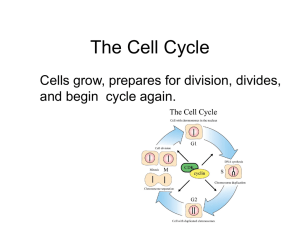
Stages of the cell cycle
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
Chromosome
A chromosome (chromo- + -some) is a packaged and organized structure containing most of the DNA of a living organism. It is not usually found on its own, but rather is complexed with many structural proteins called histones as well as associated transcription (copying of genetic sequences) factors and several other macromolecules. Two ""sister"" chromatids (half a chromosome) join together at a protein junction called a centromere. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only when the cell is undergoing mitosis. Even then, the full chromosome containing both joined sister chromatids becomes visible only during a sequence of mitosis known as metaphase (when chromosomes align together, attached to the mitotic spindle and prepare to divide). This DNA and its associated proteins and macromolecules is collectively known as chromatin, which is further packaged along with its associated molecules into a discrete structure called a nucleosome. Chromatin is present in most cells, with a few exceptions - erythrocytes for example. Occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, chromatin composes the vast majority of all DNA, except for a small amount inherited maternally which is found in mitochondria. In prokaryotic cells, chromatin occurs free-floating in cytoplasm, as these cells lack organelles and a defined nucleus. The main information-carrying macromolecule is a single piece of coiled double-stranded DNA, containing many genes, regulatory elements and other noncoding DNA. The DNA-bound macromolecules are proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions. Chromosomes vary widely between different organisms. Some species such as certain bacteria also contain plasmids or other extrachromosomal DNA. These are circular structures in the cytoplasm which contain cellular DNA and play a role in horizontal gene transfer.Compaction of the duplicated chromosomes during cell division (mitosis or meiosis) results either in a four-arm structure (pictured to the right) if the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome or a two-arm structure if the centromere is located near one of the ends. Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a vital role in genetic diversity. If these structures are manipulated incorrectly, through processes known as chromosomal instability and translocation, the cell may undergo mitotic catastrophe and die, or it may unexpectedly evade apoptosis leading to the progression of cancer.In prokaryotes (see nucleoids) and viruses, the DNA is often densely packed and organized. In the case of archaea by homologs to eukaryotic histones, in the case of bacteria by histone-like proteins. Small circular genomes called plasmids are often found in bacteria and also in mitochondria and chloroplasts, reflecting their bacterial origins.