Biological Diversity Review Questions
... inbreeding may be a result of calves from the same genes mating. 25. Identify at least four different ways that human activity affects ...
... inbreeding may be a result of calves from the same genes mating. 25. Identify at least four different ways that human activity affects ...
This examination paper consists of 4 pages
... occur in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes transpose conservatively code for a transposase enzyme ...
... occur in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes transpose conservatively code for a transposase enzyme ...
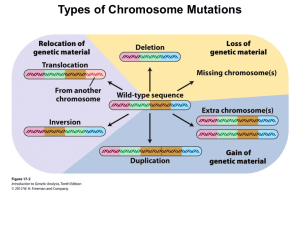
Chapter 8: Chromosomes and Chromosomal Anomalies
... means than controls on spatial-perceptual tasks (e.g., the ability to mentally rotate a three dimensional image) and slightly lower averages on quantitative skills. Verbal intelligence is normal, and indeed there have been reports that women with TS may actually have higher than average vocabulary a ...
... means than controls on spatial-perceptual tasks (e.g., the ability to mentally rotate a three dimensional image) and slightly lower averages on quantitative skills. Verbal intelligence is normal, and indeed there have been reports that women with TS may actually have higher than average vocabulary a ...
Chromosomal Abnormalities
... 1. You should have two copies of the chromosome sheet to represent your genetic makeup. One sheet represents the chromosomes of your mother's egg and the other sheet represents the chromosomes from your father's sperm. You should use one pencil color for your mother and another color for your father ...
... 1. You should have two copies of the chromosome sheet to represent your genetic makeup. One sheet represents the chromosomes of your mother's egg and the other sheet represents the chromosomes from your father's sperm. You should use one pencil color for your mother and another color for your father ...
Chapter 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... • Sex-linked genes are genes on the sex chromosomes • Sex chromosomes determine the gender in some species • In humans, XX is female and XY is male. • The Y chromosome is much smaller and does not contain all of the genes that the X does. • Males determine the sex of a child. • Sex-linked recessive ...
... • Sex-linked genes are genes on the sex chromosomes • Sex chromosomes determine the gender in some species • In humans, XX is female and XY is male. • The Y chromosome is much smaller and does not contain all of the genes that the X does. • Males determine the sex of a child. • Sex-linked recessive ...
Chromosomal Theory 1.
... In female mammals, only one X chromosome is active. a. Therefore, males and females have the same number of copies of the genes on the X chromosome. ...
... In female mammals, only one X chromosome is active. a. Therefore, males and females have the same number of copies of the genes on the X chromosome. ...
GeneticsNotes08
... – occurs during ______________________ of meiosis I – results in _______________________________ of genes – The farther apart two genes are located on a chromosome, the more likely they are to be separated by crossing over. ...
... – occurs during ______________________ of meiosis I – results in _______________________________ of genes – The farther apart two genes are located on a chromosome, the more likely they are to be separated by crossing over. ...
(Barr Body).
... Chromosomes are the rod-shaped, filamentous bodies present in the nucleus, which become visible during cell division. They are the carriers of the gene or unit of heredity. Chromosome are not visible in active nucleus due to their high water content, but are clearly seen during cell division. ...
... Chromosomes are the rod-shaped, filamentous bodies present in the nucleus, which become visible during cell division. They are the carriers of the gene or unit of heredity. Chromosome are not visible in active nucleus due to their high water content, but are clearly seen during cell division. ...
Mammalian X Chromosome Inactivation
... Rarely do fetuses go to term. Rarely do babies survive. Symptoms include: ...
... Rarely do fetuses go to term. Rarely do babies survive. Symptoms include: ...
DNA Recombination
... In order to remove a gene from one cell and insert it into another cell, the gene must be cut from the original chromosome and implanted into the one in the recipient cell. This is accomplished by using special chemicals called restriction enzymes. These enzymes recognize a specific sequence of nucl ...
... In order to remove a gene from one cell and insert it into another cell, the gene must be cut from the original chromosome and implanted into the one in the recipient cell. This is accomplished by using special chemicals called restriction enzymes. These enzymes recognize a specific sequence of nucl ...
Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics
... • Similarities to Mitosis: – Same basic stages, except occur twice ...
... • Similarities to Mitosis: – Same basic stages, except occur twice ...
Genetic Disorders
... • Some genetic disorders are caused by alleles that are located on the sex chromosomes, i.e. Hemophilia and redgreen color blindness. • The X sex chromosome is larger than the Y and therefore carries many alleles that have little to do with gender. • The inheritance of X-linked genes follow special ...
... • Some genetic disorders are caused by alleles that are located on the sex chromosomes, i.e. Hemophilia and redgreen color blindness. • The X sex chromosome is larger than the Y and therefore carries many alleles that have little to do with gender. • The inheritance of X-linked genes follow special ...
DNA Structure and Function
... form a large complex • Complex anchors to nuclear matrix • DNA moves through enzymes ...
... form a large complex • Complex anchors to nuclear matrix • DNA moves through enzymes ...
WEEK 1 PROBLEMS Problems From Chapter 1
... determined, 37.5 percent of the bases were found to be cytosine. The DNA of this organism is known to be double-stranded. What is the percentage of adenine in this DNA? 1.3 DNA extracted from a certain virus has the following base composition: 20 percent adenine, 40 percent thymine, 25 percent guani ...
... determined, 37.5 percent of the bases were found to be cytosine. The DNA of this organism is known to be double-stranded. What is the percentage of adenine in this DNA? 1.3 DNA extracted from a certain virus has the following base composition: 20 percent adenine, 40 percent thymine, 25 percent guani ...
CHAPTER 12 CHROMOSOMAL PATTERNS OF INHERITANCE
... 3. Sex chromosomes in the human female are XX; those of the male are XY. 4. Males produce X-containing and Y-containing gametes; therefore males determine the sex of offspring. 5. Besides genes that determine sex, sex chromosomes carry many genes for traits unrelated to sex. 6. An X-linked gene is a ...
... 3. Sex chromosomes in the human female are XX; those of the male are XY. 4. Males produce X-containing and Y-containing gametes; therefore males determine the sex of offspring. 5. Besides genes that determine sex, sex chromosomes carry many genes for traits unrelated to sex. 6. An X-linked gene is a ...
Cure/Treatment
... Human somatic cells contain…. 46 individual chromosomes or 23 chromosome pairs Of these 23 pairs… SEX CHROMOSOMES (1 pair) • determine the sex of an individual AUTOSOMES (22 pairs) • do not determine the sex of an individual ...
... Human somatic cells contain…. 46 individual chromosomes or 23 chromosome pairs Of these 23 pairs… SEX CHROMOSOMES (1 pair) • determine the sex of an individual AUTOSOMES (22 pairs) • do not determine the sex of an individual ...
Bio 102 Practice Problems Cell Cycle and Cell Division
... 7. Genetic analysis of cancer cells shows that they are usually aneuploid (have more or fewer chromosomes than normal). In addition to dividing rapidly, they also very often have mutations which affect the checkpoints of the cell cycle. Suppose a cell acquires a mutation so that the checkpoint at th ...
... 7. Genetic analysis of cancer cells shows that they are usually aneuploid (have more or fewer chromosomes than normal). In addition to dividing rapidly, they also very often have mutations which affect the checkpoints of the cell cycle. Suppose a cell acquires a mutation so that the checkpoint at th ...
Final Review Sheet 2
... energy from sunlight. D It contains a green pigment, which helps an animal capture energy from sunlight. 4. Even on a windy day, most plants can remain upright. Which structure plays the greatest role in providing a plant with this type of support? A nucleus B mitochondrion C cell wall D skeleton ...
... energy from sunlight. D It contains a green pigment, which helps an animal capture energy from sunlight. 4. Even on a windy day, most plants can remain upright. Which structure plays the greatest role in providing a plant with this type of support? A nucleus B mitochondrion C cell wall D skeleton ...
Biology 105
... • Principle of segregation • Before sexual reproduction occurs, the two alleles carried by an individual parent must separate. Each sex cell carries only one allele for each trait. ...
... • Principle of segregation • Before sexual reproduction occurs, the two alleles carried by an individual parent must separate. Each sex cell carries only one allele for each trait. ...
Slide 1
... • Each cell of our body contains 46 chromosomes • They are made of DNA our genetic material • A gene is a segment of DNA along the length of ...
... • Each cell of our body contains 46 chromosomes • They are made of DNA our genetic material • A gene is a segment of DNA along the length of ...
Review questions to go with the powerpoint
... 55.The Human Genome Project ______________ all of human ______. This information has been used for ________ therapy. 56.DNA put together from 2 different species is called _________________ DNA. 57.A ________ is an organism made from one cell of another organism and is a genetically ______________ c ...
... 55.The Human Genome Project ______________ all of human ______. This information has been used for ________ therapy. 56.DNA put together from 2 different species is called _________________ DNA. 57.A ________ is an organism made from one cell of another organism and is a genetically ______________ c ...
Pre – AP Biology
... • Extra copies of genes on the X chromosome interfere with male sexual development, often preventing the testes from functioning normally and reducing the levels of testosterone. • A shortage of testosterone can lead to delayed or incomplete puberty, breast enlargement (gynecomastia), reduced facial ...
... • Extra copies of genes on the X chromosome interfere with male sexual development, often preventing the testes from functioning normally and reducing the levels of testosterone. • A shortage of testosterone can lead to delayed or incomplete puberty, breast enlargement (gynecomastia), reduced facial ...
Chromosome
A chromosome (chromo- + -some) is a packaged and organized structure containing most of the DNA of a living organism. It is not usually found on its own, but rather is complexed with many structural proteins called histones as well as associated transcription (copying of genetic sequences) factors and several other macromolecules. Two ""sister"" chromatids (half a chromosome) join together at a protein junction called a centromere. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only when the cell is undergoing mitosis. Even then, the full chromosome containing both joined sister chromatids becomes visible only during a sequence of mitosis known as metaphase (when chromosomes align together, attached to the mitotic spindle and prepare to divide). This DNA and its associated proteins and macromolecules is collectively known as chromatin, which is further packaged along with its associated molecules into a discrete structure called a nucleosome. Chromatin is present in most cells, with a few exceptions - erythrocytes for example. Occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, chromatin composes the vast majority of all DNA, except for a small amount inherited maternally which is found in mitochondria. In prokaryotic cells, chromatin occurs free-floating in cytoplasm, as these cells lack organelles and a defined nucleus. The main information-carrying macromolecule is a single piece of coiled double-stranded DNA, containing many genes, regulatory elements and other noncoding DNA. The DNA-bound macromolecules are proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions. Chromosomes vary widely between different organisms. Some species such as certain bacteria also contain plasmids or other extrachromosomal DNA. These are circular structures in the cytoplasm which contain cellular DNA and play a role in horizontal gene transfer.Compaction of the duplicated chromosomes during cell division (mitosis or meiosis) results either in a four-arm structure (pictured to the right) if the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome or a two-arm structure if the centromere is located near one of the ends. Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a vital role in genetic diversity. If these structures are manipulated incorrectly, through processes known as chromosomal instability and translocation, the cell may undergo mitotic catastrophe and die, or it may unexpectedly evade apoptosis leading to the progression of cancer.In prokaryotes (see nucleoids) and viruses, the DNA is often densely packed and organized. In the case of archaea by homologs to eukaryotic histones, in the case of bacteria by histone-like proteins. Small circular genomes called plasmids are often found in bacteria and also in mitochondria and chloroplasts, reflecting their bacterial origins.