File - Varsity Field
... Heterogametic sex: sex that produces two different types of gametes with respect to the sex chromosomes. ...
... Heterogametic sex: sex that produces two different types of gametes with respect to the sex chromosomes. ...
Genetics Terms
... • Allele – different copies or forms of a gene controlling a certain trait (eye, hair color) • Dominant – the observed or expressed trait (prevents the expression of a recessive allele) ...
... • Allele – different copies or forms of a gene controlling a certain trait (eye, hair color) • Dominant – the observed or expressed trait (prevents the expression of a recessive allele) ...
1 - TeacherWeb
... _____ birds are more closely related to reptiles than mammals _____ amphibians produce an amniotic egg _____ hair evolved in an ancestor shared by mammals, birds, and reptiles _____ birds would be most similar to mammals when comparing DNA nucleotide or amino acid sequences ...
... _____ birds are more closely related to reptiles than mammals _____ amphibians produce an amniotic egg _____ hair evolved in an ancestor shared by mammals, birds, and reptiles _____ birds would be most similar to mammals when comparing DNA nucleotide or amino acid sequences ...
Genetic Disorders Mendelian Disorders
... The hereditary material of all multi-cellular organisms is the famous double helix of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which contains all of our genes. DNA, in turn, is made up of four chemical bases, pairs of which form the "rungs" of the twisted, laddershaped DNA molecules. All genes are made up of st ...
... The hereditary material of all multi-cellular organisms is the famous double helix of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which contains all of our genes. DNA, in turn, is made up of four chemical bases, pairs of which form the "rungs" of the twisted, laddershaped DNA molecules. All genes are made up of st ...
If there are “CUES” listed within the question, please USE them and
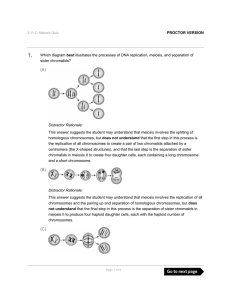
... 2) Use Figure 13.7 & 13.8 to summarize the major steps in meiosis. Be sure to differentiate between homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids. 3) The somatic cells of a mosquito contain three pairs of chromosomes—two large ones, two medium-sized ones, and two small ones. One large chromosome bear ...
... 2) Use Figure 13.7 & 13.8 to summarize the major steps in meiosis. Be sure to differentiate between homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids. 3) The somatic cells of a mosquito contain three pairs of chromosomes—two large ones, two medium-sized ones, and two small ones. One large chromosome bear ...
Based on the study of probability
... – Metaphase I- homologous chromosomes side by side – Anaphase I- ho. chrom. separate (not chromatids) – Telophase I- 2 cells with 2 chromatids of every chromos. ...
... – Metaphase I- homologous chromosomes side by side – Anaphase I- ho. chrom. separate (not chromatids) – Telophase I- 2 cells with 2 chromatids of every chromos. ...
KS4 Chromosomes, Genes and DNA
... DNA’s ability to copy itself means that all the genetic information is passed on to new cells. How does a DNA helix make a copy of itself? ...
... DNA’s ability to copy itself means that all the genetic information is passed on to new cells. How does a DNA helix make a copy of itself? ...
NAME_________________________________ CLASS:______
... _____________: the passing of physical characteristics from parent to offspring. _____________: the scientific study of heredity. Mendel started his experiments with ________________ plants. _____________: an organism that is the offspring of many generations that have the same trait. (purebred shor ...
... _____________: the passing of physical characteristics from parent to offspring. _____________: the scientific study of heredity. Mendel started his experiments with ________________ plants. _____________: an organism that is the offspring of many generations that have the same trait. (purebred shor ...
(A) (B) (C)
... This answer suggests the student may understand that recessive traits can be difficult to trace in families since carriers do not show the trait, but does not understand that this would not be an issue with a genetic marker because markers are traced using molecular biology techniques, and even if a ...
... This answer suggests the student may understand that recessive traits can be difficult to trace in families since carriers do not show the trait, but does not understand that this would not be an issue with a genetic marker because markers are traced using molecular biology techniques, and even if a ...
1 Genetics (BIL-250) Review Questions #1 (2
... (2-4) How does RNA differ from DNA? (2-1) What is the relationship between cellular DNA content and the structural or organizational complexity of the organism? (2-2) Arrange the following in increasing order of eukaryotic chromosome condensation, beginning with the simplest level of organization (1 ...
... (2-4) How does RNA differ from DNA? (2-1) What is the relationship between cellular DNA content and the structural or organizational complexity of the organism? (2-2) Arrange the following in increasing order of eukaryotic chromosome condensation, beginning with the simplest level of organization (1 ...
Anaphase I
... • In animals, meiosis produces gametes, which undergo no further cell division before fertilization • Gametes are the only haploid cells in animals • Gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote that divides by mitosis to develop into a multicellular organism • In some plants and most fungi, haploid cells ...
... • In animals, meiosis produces gametes, which undergo no further cell division before fertilization • Gametes are the only haploid cells in animals • Gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote that divides by mitosis to develop into a multicellular organism • In some plants and most fungi, haploid cells ...
Notes april 16 and 17 - Salmon River High School
... plant cells in culture will sometimes ________________ take up DNA on their ...
... plant cells in culture will sometimes ________________ take up DNA on their ...
Genetic_Meiosis Review_15
... 10. _______________ Different forms of the same gene (ex. Blue, green, brown eye color) 11. _______________ Sex cells. 12. _______________ The process of joining male and female reproductive cells during sexual reproduction. 13. _______________ The passing on of genes from parent to offspring. 14. N ...
... 10. _______________ Different forms of the same gene (ex. Blue, green, brown eye color) 11. _______________ Sex cells. 12. _______________ The process of joining male and female reproductive cells during sexual reproduction. 13. _______________ The passing on of genes from parent to offspring. 14. N ...
04BIO201 Exam 1 key
... a. Label the homologous chromosomes by indicating which belong in the same pair. b. Label the sister chromatids. c. How many individual molecules of DNA are present in the cell at prophase of mitosis? 8 homologous chromosomes ...
... a. Label the homologous chromosomes by indicating which belong in the same pair. b. Label the sister chromatids. c. How many individual molecules of DNA are present in the cell at prophase of mitosis? 8 homologous chromosomes ...
Speed Dating Review
... Ants collect food on the forest floor. Sometimes, an ant will pick up fungus cells while scavenging. The fungus grows inside the ants, releases chemical signals, and eventually takes over the ant's behavior. The ant climbs onto the underside of a leaf and latches on. As the ant dies, the fungus prod ...
... Ants collect food on the forest floor. Sometimes, an ant will pick up fungus cells while scavenging. The fungus grows inside the ants, releases chemical signals, and eventually takes over the ant's behavior. The ant climbs onto the underside of a leaf and latches on. As the ant dies, the fungus prod ...
Title Screening candidate genes required for CENP
... Centromere is the specialized chromosomal region where the assembly of a large protein complex called the kinetochore takes place. The kinetochore functions in mediating the attachment of spindle fibres to sister chromatids during cell division. Successful formation of a complete kinetochore ensures ...
... Centromere is the specialized chromosomal region where the assembly of a large protein complex called the kinetochore takes place. The kinetochore functions in mediating the attachment of spindle fibres to sister chromatids during cell division. Successful formation of a complete kinetochore ensures ...
Sex Linked Inheritance
... What does “sex-linked” or “X-linked” mean? How are sex-linked conditions inherited? How do you solve sex-linked problems? ...
... What does “sex-linked” or “X-linked” mean? How are sex-linked conditions inherited? How do you solve sex-linked problems? ...
Genetics final exam honors 2010
... ______________________________ 8. The final stage of cell division where the cytoplasm divides and cells become separate from one another. _______________________________ 9. A change in a gene or chromosome. _______________________________ 10. Condensed DNA typically found in the shape of an X. ____ ...
... ______________________________ 8. The final stage of cell division where the cytoplasm divides and cells become separate from one another. _______________________________ 9. A change in a gene or chromosome. _______________________________ 10. Condensed DNA typically found in the shape of an X. ____ ...
Study Island
... Development of the cell theory was made possible by advances in _______. A. physics B. chemistry C. microscopy D. anatomy 2. All living organisms use energy. They also grow and reproduce. What is another characteristic of all living organisms? A. All living organisms must consume food in order to ac ...
... Development of the cell theory was made possible by advances in _______. A. physics B. chemistry C. microscopy D. anatomy 2. All living organisms use energy. They also grow and reproduce. What is another characteristic of all living organisms? A. All living organisms must consume food in order to ac ...
Chromosome
A chromosome (chromo- + -some) is a packaged and organized structure containing most of the DNA of a living organism. It is not usually found on its own, but rather is complexed with many structural proteins called histones as well as associated transcription (copying of genetic sequences) factors and several other macromolecules. Two ""sister"" chromatids (half a chromosome) join together at a protein junction called a centromere. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only when the cell is undergoing mitosis. Even then, the full chromosome containing both joined sister chromatids becomes visible only during a sequence of mitosis known as metaphase (when chromosomes align together, attached to the mitotic spindle and prepare to divide). This DNA and its associated proteins and macromolecules is collectively known as chromatin, which is further packaged along with its associated molecules into a discrete structure called a nucleosome. Chromatin is present in most cells, with a few exceptions - erythrocytes for example. Occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, chromatin composes the vast majority of all DNA, except for a small amount inherited maternally which is found in mitochondria. In prokaryotic cells, chromatin occurs free-floating in cytoplasm, as these cells lack organelles and a defined nucleus. The main information-carrying macromolecule is a single piece of coiled double-stranded DNA, containing many genes, regulatory elements and other noncoding DNA. The DNA-bound macromolecules are proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions. Chromosomes vary widely between different organisms. Some species such as certain bacteria also contain plasmids or other extrachromosomal DNA. These are circular structures in the cytoplasm which contain cellular DNA and play a role in horizontal gene transfer.Compaction of the duplicated chromosomes during cell division (mitosis or meiosis) results either in a four-arm structure (pictured to the right) if the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome or a two-arm structure if the centromere is located near one of the ends. Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a vital role in genetic diversity. If these structures are manipulated incorrectly, through processes known as chromosomal instability and translocation, the cell may undergo mitotic catastrophe and die, or it may unexpectedly evade apoptosis leading to the progression of cancer.In prokaryotes (see nucleoids) and viruses, the DNA is often densely packed and organized. In the case of archaea by homologs to eukaryotic histones, in the case of bacteria by histone-like proteins. Small circular genomes called plasmids are often found in bacteria and also in mitochondria and chloroplasts, reflecting their bacterial origins.