SBI3U genetics review
... 21. What is a disorder and a disease that are related to translocation? - Down syndrome is related to translocation between chromosomes 14 and 21. Also cancer could occur if part of chromosome 8 exchanges places with chromosome 14. 22. What is amniocentesis used for? - Amniocentesis is a medical pr ...
... 21. What is a disorder and a disease that are related to translocation? - Down syndrome is related to translocation between chromosomes 14 and 21. Also cancer could occur if part of chromosome 8 exchanges places with chromosome 14. 22. What is amniocentesis used for? - Amniocentesis is a medical pr ...
ENVI 30 Environmental Issues
... Down’s syndrome may be caused not by trisomy but by extra material from chromosome 21 attached to other, large chromosome Reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22 can increase likelihood of developing chronic ...
... Down’s syndrome may be caused not by trisomy but by extra material from chromosome 21 attached to other, large chromosome Reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22 can increase likelihood of developing chronic ...
The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
... •Breakage of a chromosome can lead to four types of changes in chromosome structure ...
... •Breakage of a chromosome can lead to four types of changes in chromosome structure ...
Chi-Square Analysis
... codes for a protein that directs the development of male anatomical features ...
... codes for a protein that directs the development of male anatomical features ...
Genetics Unit final
... has been turned off. White is just the absence of any color on hair. This results in three different colors. – Male calico cats only have one X either orange and white or black and white… depending on which color is turned off in the X inactivationmales cannot be all three colors. ...
... has been turned off. White is just the absence of any color on hair. This results in three different colors. – Male calico cats only have one X either orange and white or black and white… depending on which color is turned off in the X inactivationmales cannot be all three colors. ...
7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype
... 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype Males and females can differ in sex-linked traits. • Genes on sex chromosomes are called sex-linked genes. – Y chromosome genes in mammals are responsible for male characteristics. – X chromosome genes in mammals affect many traits. ...
... 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype Males and females can differ in sex-linked traits. • Genes on sex chromosomes are called sex-linked genes. – Y chromosome genes in mammals are responsible for male characteristics. – X chromosome genes in mammals affect many traits. ...
Sex Linked Inheritance
... contribute to male characteristics. (About 87 genes total.) – The X carries a lot more genetic information. (About 2000!) ...
... contribute to male characteristics. (About 87 genes total.) – The X carries a lot more genetic information. (About 2000!) ...
Sex Linked Inheritance
... contribute to male characteristics. (About 87 genes total.) – The X carries a lot more genetic information. (About 2000!) ...
... contribute to male characteristics. (About 87 genes total.) – The X carries a lot more genetic information. (About 2000!) ...
File
... All plants and animals inherit traits from their parents. Mendel used peas when he discovered how traits are passed. Eye color, height, and intelligence are all inherited. Punnett squares are used to predict the outcome of crossed traits. A female is produced if an egg unites with a sperm containing ...
... All plants and animals inherit traits from their parents. Mendel used peas when he discovered how traits are passed. Eye color, height, and intelligence are all inherited. Punnett squares are used to predict the outcome of crossed traits. A female is produced if an egg unites with a sperm containing ...
File - Ruggiero Science
... b. always causes the same X chromosome in a female’s cells to be switched off. c. switches on the Y chromosome in a male cell. d. none of the above ____ 29. A cat that has spots of only one color a. has no Barr bodies. c. must be a female. b. must be a male. d. may be a male or a female. ____ 30. Th ...
... b. always causes the same X chromosome in a female’s cells to be switched off. c. switches on the Y chromosome in a male cell. d. none of the above ____ 29. A cat that has spots of only one color a. has no Barr bodies. c. must be a female. b. must be a male. d. may be a male or a female. ____ 30. Th ...
DNA Connection (pgs.101-106)
... Along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. ...
... Along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. ...
Characteristics of linked genes
... • If a male inherits a recessive allele from his mom he will express the trait • Chance of a female inheriting a double dose is much less • It is rare for X & Y to cross over ...
... • If a male inherits a recessive allele from his mom he will express the trait • Chance of a female inheriting a double dose is much less • It is rare for X & Y to cross over ...
Chapter 24 Genetics and Genomics Genotype and
... • each son with one recessive allele will have the disease • each son has no allele on the Y chromosome to mask the recessive allele • each daughter has a 50% chance of receiving the recessive allele from the ...
... • each son with one recessive allele will have the disease • each son has no allele on the Y chromosome to mask the recessive allele • each daughter has a 50% chance of receiving the recessive allele from the ...
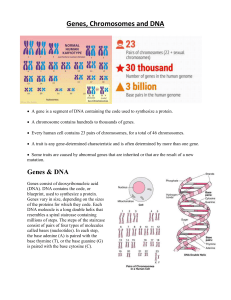
Genes Chromosomes and DNA
... A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or that are the result of a new mutation. ...
... A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or that are the result of a new mutation. ...
Genetics Since Mendel
... • Both parents have a recessive allele responsible for the disorder and pass it on to their child. • Because parents are heterozygous, they don’t show symptoms • Cystic Fibrosis is a homozygous recessive disorder ...
... • Both parents have a recessive allele responsible for the disorder and pass it on to their child. • Because parents are heterozygous, they don’t show symptoms • Cystic Fibrosis is a homozygous recessive disorder ...
Honors Genetics Chapter 2: Mitosis and Meiosis INTRODUCTION
... Chapter 2: Mitosis and Meiosis INTRODUCTION: Every living thing, except some viruses, contains DNA as the genetic material that houses the information to control the structure and function of the organism. A molecule of DNA is organized into units called genes, the products direct the metabolic acti ...
... Chapter 2: Mitosis and Meiosis INTRODUCTION: Every living thing, except some viruses, contains DNA as the genetic material that houses the information to control the structure and function of the organism. A molecule of DNA is organized into units called genes, the products direct the metabolic acti ...
Genes and Inheritance
... The result is a long, long strand of DNA and protein called a CHROMOSOME ...
... The result is a long, long strand of DNA and protein called a CHROMOSOME ...
Pedigrees - Cloudfront.net
... Pedigrees are used to: – Determine whether a trait is inherited – Show how a trait is passed from one generation to the next – To determine if an allele is dominant or recessive ...
... Pedigrees are used to: – Determine whether a trait is inherited – Show how a trait is passed from one generation to the next – To determine if an allele is dominant or recessive ...
Glossary of Terms - Liverpool Womens NHS Foundation Trust
... The total loss of one of a pair of chromosomes. This occurs, for example, in Turner syndrome where one X chromosome is lost leaving a total of 45 chromosomes. MONOZYGOTIC Two individuals (twins) born together from one sperm and one egg. MOSAICISM Where a genetic or chromosomal abnormality does not o ...
... The total loss of one of a pair of chromosomes. This occurs, for example, in Turner syndrome where one X chromosome is lost leaving a total of 45 chromosomes. MONOZYGOTIC Two individuals (twins) born together from one sperm and one egg. MOSAICISM Where a genetic or chromosomal abnormality does not o ...
Fundamentals of Lifespan Development
... Incomplete Dominance – A pattern of inheritance in which both alleles are expressed in the phenotype, resulting in a combined trait, or one that is intermediate between the two Genomic Imprinting – Alleles are imprinted, or chemically marked, so that one pair member (either mother’s or the father’s) ...
... Incomplete Dominance – A pattern of inheritance in which both alleles are expressed in the phenotype, resulting in a combined trait, or one that is intermediate between the two Genomic Imprinting – Alleles are imprinted, or chemically marked, so that one pair member (either mother’s or the father’s) ...
A population is a group of the same species living together in the
... Example of a congenital disorder caused by chromosomal mutation Cystic fibrosis is a mutation occurs on a single gene chromosome number 7 Down’s syndrome occurs when there are three number 21 chromosomes. ...
... Example of a congenital disorder caused by chromosomal mutation Cystic fibrosis is a mutation occurs on a single gene chromosome number 7 Down’s syndrome occurs when there are three number 21 chromosomes. ...
AG-BAS-02.471-05.4p d
... rod like segments called chromosomes • Chromosomes occurs in pairs in every cell of our body except in the sperm and ovum. • Chromosomes numbers are the same for each species. August 2008 ...
... rod like segments called chromosomes • Chromosomes occurs in pairs in every cell of our body except in the sperm and ovum. • Chromosomes numbers are the same for each species. August 2008 ...
What are multiple alleles
... nucleus of the organism to be cloned, and placing the egg cell with its new nucleus into a compatible or the same female for gestation. ...
... nucleus of the organism to be cloned, and placing the egg cell with its new nucleus into a compatible or the same female for gestation. ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.