Print this page
... membrane reappears and two identical cells have been formed. Only one of the new cells is shown here. ...
... membrane reappears and two identical cells have been formed. Only one of the new cells is shown here. ...
WARNING:
... Chromosome – a threadlike strand inside the nucleus that is made up of DNA Mitosis – the process of cell division Asexual Reproduction – reproduction by simple cell division Sexual Reproduction – the form of reproduction in which cells from two parents unite to form a zygote Meiosis – the process th ...
... Chromosome – a threadlike strand inside the nucleus that is made up of DNA Mitosis – the process of cell division Asexual Reproduction – reproduction by simple cell division Sexual Reproduction – the form of reproduction in which cells from two parents unite to form a zygote Meiosis – the process th ...
Ch 16 Genetics Review
... • They don't divide up the DNA between the new cells • Each daughter cell will get one-half of the DNA • The cell membrane begins to pinch. When it's all over, you are left with four haploid cells that are called gametes. The eventual purpose of the gametes will be to find other gametes with which t ...
... • They don't divide up the DNA between the new cells • Each daughter cell will get one-half of the DNA • The cell membrane begins to pinch. When it's all over, you are left with four haploid cells that are called gametes. The eventual purpose of the gametes will be to find other gametes with which t ...
4.2 Sources of DNA
... meaning that is does not transribe into protein Eukaryotes have a lack of operators in their DNA, meaning that gene expression is controlled differently ...
... meaning that is does not transribe into protein Eukaryotes have a lack of operators in their DNA, meaning that gene expression is controlled differently ...
DNA, chromosomes and Genes
... Interestingly, the Human Genome Project reveled we all have mutations in our DNA sequence which do not affect the phenotype!! Occurs at a very low rate: about 1 in 1mil bases. UV radiation and some chemicals can increase the rate – These agents are linked to cancer - cancer arises when there is a ch ...
... Interestingly, the Human Genome Project reveled we all have mutations in our DNA sequence which do not affect the phenotype!! Occurs at a very low rate: about 1 in 1mil bases. UV radiation and some chemicals can increase the rate – These agents are linked to cancer - cancer arises when there is a ch ...
Objectives 8 - u.arizona.edu
... relationship to carrier status in X-linked disorders. The Lyon hypothesis explains dosage compensation, variable expression in female heterozygotes, and mosaicism. Dosage compensation refers to the finding that females only express one allele of Xlinked genes even though they have two, so that they ...
... relationship to carrier status in X-linked disorders. The Lyon hypothesis explains dosage compensation, variable expression in female heterozygotes, and mosaicism. Dosage compensation refers to the finding that females only express one allele of Xlinked genes even though they have two, so that they ...
Cell Division and Differentiation
... A cell’s chromosomes are usually long, thin strands. Just before the cell divides, however, the chromosomes become shorter, thicker and more visible. They are said to condense. Each chromosome duplicates and becomes two strands, each one called a chromatid. The two chromatids are joined at the ...
... A cell’s chromosomes are usually long, thin strands. Just before the cell divides, however, the chromosomes become shorter, thicker and more visible. They are said to condense. Each chromosome duplicates and becomes two strands, each one called a chromatid. The two chromatids are joined at the ...
Inheritance Patterns in Dragons
... consist of a variety of different forms, but only two forms are ever present per gene (one from the mother, the other from the father). The two different gene forms on the pair of chromosomes may be identical or different. The different forms that comprise a gene are called alleles. ...
... consist of a variety of different forms, but only two forms are ever present per gene (one from the mother, the other from the father). The two different gene forms on the pair of chromosomes may be identical or different. The different forms that comprise a gene are called alleles. ...
Genetics
... Genes exists in more than 2 allelis forms in the same locus of given pair of homologous chromosomes. Each allele produces a distinctive phenotype. For example: ANO blood group system ~ the human blood groups are controlled by three alleles IA, IB, I ...
... Genes exists in more than 2 allelis forms in the same locus of given pair of homologous chromosomes. Each allele produces a distinctive phenotype. For example: ANO blood group system ~ the human blood groups are controlled by three alleles IA, IB, I ...
Lecture Chpt. 15 Genetics.errors
... Also known as Trisomy 18 Almost every organ system is affected. 1:10,000 live births. Children with full Trisomy 18 generally do not live more than a few months. • Characteristics: small jaw, low-set ears, and a strawberry-shaped head. ...
... Also known as Trisomy 18 Almost every organ system is affected. 1:10,000 live births. Children with full Trisomy 18 generally do not live more than a few months. • Characteristics: small jaw, low-set ears, and a strawberry-shaped head. ...
Biotechnology Unit Test Review
... 3. Gene cloning – A gene is inserted into a bacteria. Then, many copies of the gene are made when the bacteria divide. 4. DNA ligase – Enzyme used to join the “sticky ends” of a recombinant DNA 5. Gel electrophoresis – Technique used to separate DNA or protein fragments based on size 6. Polymerase c ...
... 3. Gene cloning – A gene is inserted into a bacteria. Then, many copies of the gene are made when the bacteria divide. 4. DNA ligase – Enzyme used to join the “sticky ends” of a recombinant DNA 5. Gel electrophoresis – Technique used to separate DNA or protein fragments based on size 6. Polymerase c ...
Sex linkage and Pedigrees
... rarely expressed in the female, and then usually only after menopause. ...
... rarely expressed in the female, and then usually only after menopause. ...
Cure/Treatment
... Amniocentesis - a small amount of amniotic fluid (containing fetal tissues and cells) is extracted from the amniotic sac surrounding the developing fetus - the DNA is examined for genetic abnormalities Chorionic Villi Sampling (CVS) - the removal of a small piece of the placenta (chorionic villi) d ...
... Amniocentesis - a small amount of amniotic fluid (containing fetal tissues and cells) is extracted from the amniotic sac surrounding the developing fetus - the DNA is examined for genetic abnormalities Chorionic Villi Sampling (CVS) - the removal of a small piece of the placenta (chorionic villi) d ...
Name - Mr. Spechts world of Science
... DNA and inserting it into bacterial DNA 2. A mutation occurs in a cell. Which sequence best represents the correct order of the events involved for this mutation to affect the traits expressed by this cell? (1) a change in the sequence of DNA bases joining amino acids in sequence appearance of chara ...
... DNA and inserting it into bacterial DNA 2. A mutation occurs in a cell. Which sequence best represents the correct order of the events involved for this mutation to affect the traits expressed by this cell? (1) a change in the sequence of DNA bases joining amino acids in sequence appearance of chara ...
Unit I: Genes, Nucleic A...d Chromosomes - BioWiki
... Chapter 2 covers the structures of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and methods for analyzing them biochemically. Methods for isolating genes, such as recombinant DNA technology and the polymerase chain reaction, are discussed in Chapter 3. In addition, this chapter explores some of the insights into gen ...
... Chapter 2 covers the structures of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and methods for analyzing them biochemically. Methods for isolating genes, such as recombinant DNA technology and the polymerase chain reaction, are discussed in Chapter 3. In addition, this chapter explores some of the insights into gen ...
HUMAN GENETICS
... 1. Polydactyly2. Huntington’s Disease a. Symptoms of Huntington’s usually do not develop until the person reaches their early 40’s. This disease is deadly. 3. Achondroplasia-rare form of dwarfism. Growth hormone production is shut down by a defective gene in this disorder. 4. Hutchinson-Gilford Prog ...
... 1. Polydactyly2. Huntington’s Disease a. Symptoms of Huntington’s usually do not develop until the person reaches their early 40’s. This disease is deadly. 3. Achondroplasia-rare form of dwarfism. Growth hormone production is shut down by a defective gene in this disorder. 4. Hutchinson-Gilford Prog ...
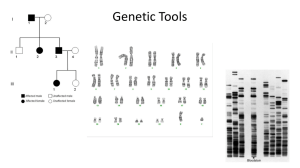
Genetic Tools
... called Sex-linked genes. • Traits determined by sex-linked genes are called sexlinked traits. • Because of this, sex-linked traits are most often seen in males who only have one copy of the X chromosome. ...
... called Sex-linked genes. • Traits determined by sex-linked genes are called sexlinked traits. • Because of this, sex-linked traits are most often seen in males who only have one copy of the X chromosome. ...
What is a TRAIT?
... What is a TRAIT? A specific characteristic that can be passed from parent to offspring. What is HEREDITY (inheritance)? Passing of traits from parent to offspring or from one generation to the next. Genes are the coded instructions that define our traits ...
... What is a TRAIT? A specific characteristic that can be passed from parent to offspring. What is HEREDITY (inheritance)? Passing of traits from parent to offspring or from one generation to the next. Genes are the coded instructions that define our traits ...
Genetics_notes
... influence the reproductive system and its related organs, – These hormones, however, also affect many other parts of the body ...
... influence the reproductive system and its related organs, – These hormones, however, also affect many other parts of the body ...
Linked Genes and Gene Mapping
... meiosis pairs line up on plate independent of pair above. – AND genes are on separate chromosomes ...
... meiosis pairs line up on plate independent of pair above. – AND genes are on separate chromosomes ...
Mendelian Genetics - Mill Creek High School
... pregnant again with ANOTHER baby that is Rh positive, then her body would see that fetus as a foreign invader and destroy it….basically destroys the baby’s RBC’s • Can take RoGam during 2nd and subsequent pregnancies to prevent problems with baby ...
... pregnant again with ANOTHER baby that is Rh positive, then her body would see that fetus as a foreign invader and destroy it….basically destroys the baby’s RBC’s • Can take RoGam during 2nd and subsequent pregnancies to prevent problems with baby ...
Meiosis - Grant County Schools
... Meiosis I Interphase – just like interphase of Mitosis the cell replicates its chromosomes (2 identical sister chromatids held together by a centromere) Prophase I – The chromosomes coil up and the spindles form. Each pair of homologous chromosomes come together, matched gene by gene (forms a four ...
... Meiosis I Interphase – just like interphase of Mitosis the cell replicates its chromosomes (2 identical sister chromatids held together by a centromere) Prophase I – The chromosomes coil up and the spindles form. Each pair of homologous chromosomes come together, matched gene by gene (forms a four ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.