Congenital Nystagmus
... Support for location of an X-linked ICN gene, with respect to three chromosome Xp markers. Likelihood estimates are given in log10. Distances between marker loci, in centimorgans, are shown along the X-axis. The maximum location score for NYS1 is between DXS8015 and DXS1003, over the locus DXS993. P ...
... Support for location of an X-linked ICN gene, with respect to three chromosome Xp markers. Likelihood estimates are given in log10. Distances between marker loci, in centimorgans, are shown along the X-axis. The maximum location score for NYS1 is between DXS8015 and DXS1003, over the locus DXS993. P ...
DNA & Heredity PowerPoint
... Explain why a trait inherited by incomplete dominance, such as the color of Appaloosa horses, is not a blend of two alleled. Describe two genetic disorders and discuss how they are inherited. Draw a Punnett square on the board explaining why males are affected more than females by sex-linked inherit ...
... Explain why a trait inherited by incomplete dominance, such as the color of Appaloosa horses, is not a blend of two alleled. Describe two genetic disorders and discuss how they are inherited. Draw a Punnett square on the board explaining why males are affected more than females by sex-linked inherit ...
BioSc 231 Exam 2 2003
... Bonus Question (4 pts) An Arabidopsis thaliana flowering mutation has been generated in the Columbia (Col) line. The mutant line was then crossed with a wild-type Landsberg erectus (Ler) line to generate the F1 generation. The F1 generation was allowed to self to produce the F2 generation. F2 plant ...
... Bonus Question (4 pts) An Arabidopsis thaliana flowering mutation has been generated in the Columbia (Col) line. The mutant line was then crossed with a wild-type Landsberg erectus (Ler) line to generate the F1 generation. The F1 generation was allowed to self to produce the F2 generation. F2 plant ...
Meiosis packet
... maternal and paternal homologs (therefore each cell produced in meiosis is genetically different), while mitosis produces cells that are diploid, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (therefore genetically identical). The final difference is that meiosis produces gametes and m ...
... maternal and paternal homologs (therefore each cell produced in meiosis is genetically different), while mitosis produces cells that are diploid, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (therefore genetically identical). The final difference is that meiosis produces gametes and m ...
Meiosis Information Sheet
... maternal and paternal homologs (therefore each cell produced in meiosis is genetically different), while mitosis produces cells that are diploid, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (therefore genetically identical). The final difference is that meiosis produces gametes and m ...
... maternal and paternal homologs (therefore each cell produced in meiosis is genetically different), while mitosis produces cells that are diploid, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (therefore genetically identical). The final difference is that meiosis produces gametes and m ...
Ch. 11 The Control of Gene Expression (Lecture Notes)
... lung cancer cases among men and 79% among women - about 87% altogether. Smokeless tobacco (chewing tobacco or snuff) increases the risk of cancers of the mouth, larynx, throat, and esophagus. Don’t Sunbathe Almost all cases of basal and squamous cell skin cancers are considered to be sun related. Fu ...
... lung cancer cases among men and 79% among women - about 87% altogether. Smokeless tobacco (chewing tobacco or snuff) increases the risk of cancers of the mouth, larynx, throat, and esophagus. Don’t Sunbathe Almost all cases of basal and squamous cell skin cancers are considered to be sun related. Fu ...
Genetics
... characteristics is determined by individual units called genes. Genes are passed from parents to offspring. • In cases in which two or more forms of the genes for a single trait exist, some forms of the gene may be dominant and others many be recessive. ...
... characteristics is determined by individual units called genes. Genes are passed from parents to offspring. • In cases in which two or more forms of the genes for a single trait exist, some forms of the gene may be dominant and others many be recessive. ...
3 Meiosis
... and animals to produce individuals with traits that they liked. This is known as selective breeding. Breeders may choose a plant or animal with traits they would like to see in the offspring. They breed that individual with another that also has those traits. For example, farmers might breed fruit t ...
... and animals to produce individuals with traits that they liked. This is known as selective breeding. Breeders may choose a plant or animal with traits they would like to see in the offspring. They breed that individual with another that also has those traits. For example, farmers might breed fruit t ...
V. How virusES cause cancer
... a) The twelfth codon normally codes for a valine amino acid, but the mutation results in a glycine amino acid at that position in the G-protein b) Once activated, the mutant G-protein will be stuck on 3. Twenty percent of tumors have mutated ras gene B. Some proto-oncogenes are normal, but over exp ...
... a) The twelfth codon normally codes for a valine amino acid, but the mutation results in a glycine amino acid at that position in the G-protein b) Once activated, the mutant G-protein will be stuck on 3. Twenty percent of tumors have mutated ras gene B. Some proto-oncogenes are normal, but over exp ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... chromosomal complement of 46 chromosomes plus one extra chromosome #21. While there is impaired fertility of both sexes, females are more likely to be fertile than males. Assume that children are born to a female with Down syndrome and a normal 46chromosome male. What proportion of the offspring wou ...
... chromosomal complement of 46 chromosomes plus one extra chromosome #21. While there is impaired fertility of both sexes, females are more likely to be fertile than males. Assume that children are born to a female with Down syndrome and a normal 46chromosome male. What proportion of the offspring wou ...
Chap 11 – Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
... DNA Packaging and chemical modifications can affect gene expression Methylation of DNA – Certain enzymes can add a methyl group to DNA bases, without changing the sequence of the bases. – Methylation generally inhibits gene expression ...
... DNA Packaging and chemical modifications can affect gene expression Methylation of DNA – Certain enzymes can add a methyl group to DNA bases, without changing the sequence of the bases. – Methylation generally inhibits gene expression ...
Genetics 184 - Ronin Genetics
... among the female progeny.) Reversions to w1 were found as well as one female whose phenotype was scored as a partial reversion, i.e., the eye color was darker than wi but not normal eye color. The partial reversion was named white-crimson (wc). Since the exceptional attached X female had one wc and ...
... among the female progeny.) Reversions to w1 were found as well as one female whose phenotype was scored as a partial reversion, i.e., the eye color was darker than wi but not normal eye color. The partial reversion was named white-crimson (wc). Since the exceptional attached X female had one wc and ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS – CHAPTER 08
... The diploid state is the most common in eukaryotic organisms. Each cell contains pairs of homologous chromosomes (2n, where n is the number of homologous pairs of chromosomes, also known as the haploid number). Diploid cells have two copies of each gene, one on each chromosome of a homologous pair. ...
... The diploid state is the most common in eukaryotic organisms. Each cell contains pairs of homologous chromosomes (2n, where n is the number of homologous pairs of chromosomes, also known as the haploid number). Diploid cells have two copies of each gene, one on each chromosome of a homologous pair. ...
Document
... Nonsense mutation = converts a sense codon to a nonsense or stop codon, results in shortened polypeptide Frameshift mutation = arise from insertion or deletion of one or two bp within coding region of gene, results in the synthesis of nonfunctional protein ...
... Nonsense mutation = converts a sense codon to a nonsense or stop codon, results in shortened polypeptide Frameshift mutation = arise from insertion or deletion of one or two bp within coding region of gene, results in the synthesis of nonfunctional protein ...
AP Test Genetics Review
... Independent Assortment which says that each allele segregates independently from another (traits aren’t linked unless they are on the ...
... Independent Assortment which says that each allele segregates independently from another (traits aren’t linked unless they are on the ...
Genetics Mark Schedule 2010
... Somatic: Alterations in DNA that occur after conception/ Somatic mutations can occur in any of the cells of the body except the germ cells (sperm and egg) and therefore are not passed on to the offspring. Gametic: (may be called germline, which is acceptable) A heritable change in the DNA that occur ...
... Somatic: Alterations in DNA that occur after conception/ Somatic mutations can occur in any of the cells of the body except the germ cells (sperm and egg) and therefore are not passed on to the offspring. Gametic: (may be called germline, which is acceptable) A heritable change in the DNA that occur ...
File
... – Traits are inherited as discrete units. (alleles) – Organisms inherit two copies of each gene, one from each parent. – The two copies segregate during gamete formation. – The last two conclusions are called the law of segregation. ...
... – Traits are inherited as discrete units. (alleles) – Organisms inherit two copies of each gene, one from each parent. – The two copies segregate during gamete formation. – The last two conclusions are called the law of segregation. ...
Karyotype Lab Notes
... • To complete a karyotyping exercise to determine what type of genetic disorder a hypothetical baby would have. ...
... • To complete a karyotyping exercise to determine what type of genetic disorder a hypothetical baby would have. ...
Chapter 11 Notes
... a) So how does lactose turn on these genes b) all 3 controlled together as a unit 4. Promoter – There is a single promoter upstream from the genes 5. Operator – DNA sequence between the promoter and the genes – acts as a on/off switch 6. promoter + operator + genes = operon 7. Repressor – a protein ...
... a) So how does lactose turn on these genes b) all 3 controlled together as a unit 4. Promoter – There is a single promoter upstream from the genes 5. Operator – DNA sequence between the promoter and the genes – acts as a on/off switch 6. promoter + operator + genes = operon 7. Repressor – a protein ...
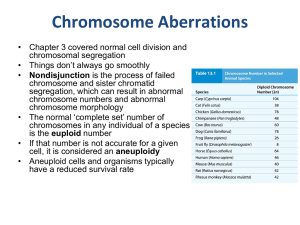
Chromosome Aberrations
... • They usually do not survive and are limited in number • If they do survive and the nondisjunction occurs early in embryogenesis, mosaicism can result • 25-30% of Turner syndrome cases are mosaics – some cells are 2n=45, some are 2n=46, some are 2n=47 ...
... • They usually do not survive and are limited in number • If they do survive and the nondisjunction occurs early in embryogenesis, mosaicism can result • 25-30% of Turner syndrome cases are mosaics – some cells are 2n=45, some are 2n=46, some are 2n=47 ...
Slide 1
... • A mutation is any change in the proper nucleic acid sequence of a specific gene in a cell’s genome. It may result from a single base pair mismatch during DNA replication. • Mutation can create genetic diversity within a population; either beneficial, neutral, bad, or lethal. • Mutation could resul ...
... • A mutation is any change in the proper nucleic acid sequence of a specific gene in a cell’s genome. It may result from a single base pair mismatch during DNA replication. • Mutation can create genetic diversity within a population; either beneficial, neutral, bad, or lethal. • Mutation could resul ...
tall
... 4. The father determines the gender of the child. t f 5. Each parent contributes half of a child’s genetic makeup. t f 6. Color blindness is more common in males than in females. t f 7. Parents can transmit to offspring characteristics that the parents themselves do not show. t f 8. Identica ...
... 4. The father determines the gender of the child. t f 5. Each parent contributes half of a child’s genetic makeup. t f 6. Color blindness is more common in males than in females. t f 7. Parents can transmit to offspring characteristics that the parents themselves do not show. t f 8. Identica ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.