Genetics Study Guide Key
... 14) Why is sickle cell disease also an example of codominance…what benefit do heterozygotes have? a. Heterozygotes have both normal hemoglobin and sickle hemoglobin 15) Which disease above is caused by a dominant allele? Huntingtons disease a. Why is it so easily passed on in families? Because symp ...
... 14) Why is sickle cell disease also an example of codominance…what benefit do heterozygotes have? a. Heterozygotes have both normal hemoglobin and sickle hemoglobin 15) Which disease above is caused by a dominant allele? Huntingtons disease a. Why is it so easily passed on in families? Because symp ...
Review Relationships between Vertebrate ZW and XY Sex
... The patchy distribution of different sex chromosome systems in fish suggests that numerous transitions between different ancestral modes (e.g. environmental, unisexuality, hermaphroditism, ZW, XY) have occurred during the course of evolution [21]. For instance, teleost fish display a haphazard distr ...
... The patchy distribution of different sex chromosome systems in fish suggests that numerous transitions between different ancestral modes (e.g. environmental, unisexuality, hermaphroditism, ZW, XY) have occurred during the course of evolution [21]. For instance, teleost fish display a haphazard distr ...
1 Hello, my name is Gary Cutting, and I`m going to speak on the
... which genetics is treated. And, of course, as one can see, this would be the ideal situation where there were four individuals observed so you could see that three out of four would be affected. Of course, in usual situations in medicine, not all families will have four children, for example, if the ...
... which genetics is treated. And, of course, as one can see, this would be the ideal situation where there were four individuals observed so you could see that three out of four would be affected. Of course, in usual situations in medicine, not all families will have four children, for example, if the ...
Genetics_Test_Regular_Bio
... 12. In primroses, the combined expression of the allele for white flowers and the allele for red flowers produces a new phenotype that is pink. This illustrates incomplete dominance. Which of the following would be the correct product from a cross between a white primrose and a heterozygous pink pr ...
... 12. In primroses, the combined expression of the allele for white flowers and the allele for red flowers produces a new phenotype that is pink. This illustrates incomplete dominance. Which of the following would be the correct product from a cross between a white primrose and a heterozygous pink pr ...
Question 1 The female gamete is the spore. sperm. egg. zygote
... 1. Cell geneticists have identified what type(s) of chromosome rearrangement? ...
... 1. Cell geneticists have identified what type(s) of chromosome rearrangement? ...
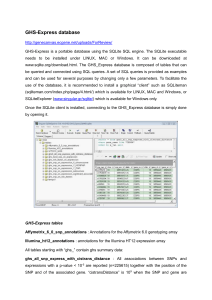
GHS-Express database http://genecanvas.ecgene.net/uploads/Fo
... expressions with a p-value < 10-5 are reported (n=225615) together with the position of the SNP and of the associated gene. “cistransDistance” is 109 when the SNP and gene are ...
... expressions with a p-value < 10-5 are reported (n=225615) together with the position of the SNP and of the associated gene. “cistransDistance” is 109 when the SNP and gene are ...
doc Sample midterm 2
... Answer b. Interactions between null mutations of two genes in this pathway will produce 9:7 ratio of wildtype:mutant. Use the information below to answer the next two questions: The recessive mutations vg (vestigial wings) and br (brown eyes) identify two autosomal genes on the second chromosome of ...
... Answer b. Interactions between null mutations of two genes in this pathway will produce 9:7 ratio of wildtype:mutant. Use the information below to answer the next two questions: The recessive mutations vg (vestigial wings) and br (brown eyes) identify two autosomal genes on the second chromosome of ...
Inheritance Problems
... (funky little toe & thumb) is dominant to normal and rough fur allele is dominant to normal. Pigs which are known to have both dominant alleles on one chromosome and both recessive alleles on the other chromosome are crossed with pigs that show the normal phenotypes. Their progeny fell into four phe ...
... (funky little toe & thumb) is dominant to normal and rough fur allele is dominant to normal. Pigs which are known to have both dominant alleles on one chromosome and both recessive alleles on the other chromosome are crossed with pigs that show the normal phenotypes. Their progeny fell into four phe ...
Gene Tagging with Transposons
... • How can we prove Ty1 transposes as an RNA molecule? • Constructed Ty1 element with a galactose-inducible promoter and an intron • Used galactose to stimulate transcription, then found that all the new copies transposed had the intron spliced out ...
... • How can we prove Ty1 transposes as an RNA molecule? • Constructed Ty1 element with a galactose-inducible promoter and an intron • Used galactose to stimulate transcription, then found that all the new copies transposed had the intron spliced out ...
Punnett Square Practice Problems
... Vocabulary - Match the definitions on the left with the terms on the right: ____ 1. genotypes made of the same alleles ____ 2. different forms of genes for a single trait ____ 3. gene that is always expressed ____ 4. gene that is expressed only in the homozygous state ____ 5. genotypes made of two d ...
... Vocabulary - Match the definitions on the left with the terms on the right: ____ 1. genotypes made of the same alleles ____ 2. different forms of genes for a single trait ____ 3. gene that is always expressed ____ 4. gene that is expressed only in the homozygous state ____ 5. genotypes made of two d ...
Section 11-2
... offspring compare to the parents’ characteristics? All offspring had the same characteristic, which was like one of the parents’. The other characteristic seemed to have disappeared. 2. How do the characteristics of the second generation compare to the characteristics of the first generation? Both c ...
... offspring compare to the parents’ characteristics? All offspring had the same characteristic, which was like one of the parents’. The other characteristic seemed to have disappeared. 2. How do the characteristics of the second generation compare to the characteristics of the first generation? Both c ...
Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization S Sellers, B Gandolfi
... established into a recognized breed, called Munchkin, in 1994 (1). To date, the Munchkin breed has not been fully clinically and genetically characterized (Figure 1). In human achondroplasia, a mutation in the FGFR3 gene, is the most common form of human dwarfism that occurs 1 in 15,000 live births ...
... established into a recognized breed, called Munchkin, in 1994 (1). To date, the Munchkin breed has not been fully clinically and genetically characterized (Figure 1). In human achondroplasia, a mutation in the FGFR3 gene, is the most common form of human dwarfism that occurs 1 in 15,000 live births ...
Recessive
... would happen. (He found things like a tall and a short made 4 tall.. This led to the idea of dominant and recessive. ...
... would happen. (He found things like a tall and a short made 4 tall.. This led to the idea of dominant and recessive. ...
Functional monopolar spindles caused by
... figures are also found, with their chromosomes showing the typical configuration of this meiotic stage (Fig. 4H); these metaphases differ from wild type (Fig. 4G) in that they remain diploid, indicating that the reductional segregation failed during anaphase I. We have never observed normal anaphase ...
... figures are also found, with their chromosomes showing the typical configuration of this meiotic stage (Fig. 4H); these metaphases differ from wild type (Fig. 4G) in that they remain diploid, indicating that the reductional segregation failed during anaphase I. We have never observed normal anaphase ...
journals - the biopsychology research group
... removed during early germ cell development, re-established later in germ cell development or after fertilization, and maintained during embryonic development. ‘‘Imprinting’’ of the gene effectively tells the molecular machinery within the cell to express only one allele in the cell and its progeny. ...
... removed during early germ cell development, re-established later in germ cell development or after fertilization, and maintained during embryonic development. ‘‘Imprinting’’ of the gene effectively tells the molecular machinery within the cell to express only one allele in the cell and its progeny. ...
BSC 2011 MENDELIAN GENETICS PROBLEMS The following
... will be formed, and what will the proportions be? 13. In cattle, the gene for hornless (H) is dominant to the gene for horned (h), the gene for black (B) is dominant to that of red (b), and the gene for white face (or Hereford spotting) (S) is dominant to that for solid color (s). A cow with the gen ...
... will be formed, and what will the proportions be? 13. In cattle, the gene for hornless (H) is dominant to the gene for horned (h), the gene for black (B) is dominant to that of red (b), and the gene for white face (or Hereford spotting) (S) is dominant to that for solid color (s). A cow with the gen ...
mandelian genetics - study
... Differences between multiple alleles and polygenes Multiple Alleles Not influence by environmental factors ...
... Differences between multiple alleles and polygenes Multiple Alleles Not influence by environmental factors ...
Autosomal monoallelic expression in the mouse
... throughout the genome, lacks chromosome-wide coordination, and varies between cell types. However, for some mouse genes, there appears to be skewing, in some ways resembling skewed X-inactivation, wherein one allele is more frequently active. Conclusions: These data suggest that autosomal random mon ...
... throughout the genome, lacks chromosome-wide coordination, and varies between cell types. However, for some mouse genes, there appears to be skewing, in some ways resembling skewed X-inactivation, wherein one allele is more frequently active. Conclusions: These data suggest that autosomal random mon ...
Mesoderm tissue development in Drosophila melanogaster Abstract
... regions for CG11148.7 In D. melanogaster, the dot chromosome has become mostly heterochromatin, which means the DNA has become tightly coiled and the information in these areas is not transcribed, in contrast to the high amount of euchromatin, or loosely coiled DNA that is transcribed actively into ...
... regions for CG11148.7 In D. melanogaster, the dot chromosome has become mostly heterochromatin, which means the DNA has become tightly coiled and the information in these areas is not transcribed, in contrast to the high amount of euchromatin, or loosely coiled DNA that is transcribed actively into ...
B - Computational Systems Biology Group
... Now: 23531 (NCBI 34 assembly 02/04) Recent estimations: 20.000 to 100.000. 50% mRNAs do not code for proteins (mouse) 50% display alternative splicing ...
... Now: 23531 (NCBI 34 assembly 02/04) Recent estimations: 20.000 to 100.000. 50% mRNAs do not code for proteins (mouse) 50% display alternative splicing ...
Biology Unit 7 Genetics 7:1 Genetics Gregor Mendel: • Austrian
... EPISTASIS: the interaction between two or more genes to control a single phenotype Example: Labrador retriever Coat Color, coat color is determined by two genes the E gene and B gene. Yellow furhomozygous recessive ee Black or Chocolate fur could be EE or Ee o BlackCould be BB or Bb because ...
... EPISTASIS: the interaction between two or more genes to control a single phenotype Example: Labrador retriever Coat Color, coat color is determined by two genes the E gene and B gene. Yellow furhomozygous recessive ee Black or Chocolate fur could be EE or Ee o BlackCould be BB or Bb because ...
BIO 101 Study Guide Exam 4 Patterns of Inheritance Chapter 9
... A) Explain why Mendel’s decision to work with peas was a good choice. B) Define and distinguish between true-breeding organisms, hybrids, the P generation, the F1 generation, and the F2 generation. C) Define and distinguish between the following pairs of terms: genotype and phenotype; dominant allel ...
... A) Explain why Mendel’s decision to work with peas was a good choice. B) Define and distinguish between true-breeding organisms, hybrids, the P generation, the F1 generation, and the F2 generation. C) Define and distinguish between the following pairs of terms: genotype and phenotype; dominant allel ...
1 A CAPS marker, FER-G8, for detection of Ty3 and Ty3a alleles
... gene in chromosome 6 (ca. 8 cM). LA1969 was also the source of resistance against Tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) for new lines developed in Cuba (Piňón et al., 2005). Scott and his team (Agrama and Scott, 2006; Scott, 2001; Scott et al., 1995) have used several accessions of S. chilense as so ...
... gene in chromosome 6 (ca. 8 cM). LA1969 was also the source of resistance against Tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) for new lines developed in Cuba (Piňón et al., 2005). Scott and his team (Agrama and Scott, 2006; Scott, 2001; Scott et al., 1995) have used several accessions of S. chilense as so ...
Lesson 3
... • When the defective gene is replaced with a normal one using the gene therapy, the cells with the new gene begin to make the missing substance. • The practice of placing fragments of DNA from one organism into another is called genetic engineering, and it is considered highly experimental. • Geneti ...
... • When the defective gene is replaced with a normal one using the gene therapy, the cells with the new gene begin to make the missing substance. • The practice of placing fragments of DNA from one organism into another is called genetic engineering, and it is considered highly experimental. • Geneti ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.