Chapter 11 Notes – Fill In
... At the end of meiosis 1 there are two daughter cells - Each has 1 set of chromosomes (is haploid) - Chromosomes do not replicate before Meiosis II Meiosis II __________________ II - Chromosomes become visible __________________ II - Chromosomes line up at the center of the cell _______________ ...
... At the end of meiosis 1 there are two daughter cells - Each has 1 set of chromosomes (is haploid) - Chromosomes do not replicate before Meiosis II Meiosis II __________________ II - Chromosomes become visible __________________ II - Chromosomes line up at the center of the cell _______________ ...
Chapter 14 Human Genetics - Hollidaysburg Area School
... Scientists know much less about human inheritance than they do about other organisms. Model organisms are the fruit fly and mice. With this new understanding, scientists must study genetics carefully. WHY? ...
... Scientists know much less about human inheritance than they do about other organisms. Model organisms are the fruit fly and mice. With this new understanding, scientists must study genetics carefully. WHY? ...
genes - Brookwood High School
... 1. Used to see chromosomal abnormalities or genetic disorders. 2. 44 or 22 pairs of chromosomes are autosomes. ...
... 1. Used to see chromosomal abnormalities or genetic disorders. 2. 44 or 22 pairs of chromosomes are autosomes. ...
Mendelian Genetics - Mrs. Cindy Williams Biology website
... – Genes on the same chromosome are not always linked. – Crossing-over sometimes separates linked genes to form new allele combinations. – This allows for greater genetic diversity. ...
... – Genes on the same chromosome are not always linked. – Crossing-over sometimes separates linked genes to form new allele combinations. – This allows for greater genetic diversity. ...
Spring Exam Study Guide 2015 answers
... 67. Two plants with the genotypes TT and Tt would have the same ___________________. Phenotype 68. What is independent assortment? When two or more characteristics are inherited, they are inherited independently of one another 69. Situations in which one allele for a gene is not completely domin ...
... 67. Two plants with the genotypes TT and Tt would have the same ___________________. Phenotype 68. What is independent assortment? When two or more characteristics are inherited, they are inherited independently of one another 69. Situations in which one allele for a gene is not completely domin ...
Chromosomal Abnormalities
... There are a number of physical characteristics associated with Down syndrome, although each person with Down syndrome may display only a few of these. The most common physical characteristics include: Eyes – nearly all people with Down syndrome have a slight upward slant of the eyes. There can also ...
... There are a number of physical characteristics associated with Down syndrome, although each person with Down syndrome may display only a few of these. The most common physical characteristics include: Eyes – nearly all people with Down syndrome have a slight upward slant of the eyes. There can also ...
chapter 3: biological beginnings
... Methods Used by Behavior Genetics – genetic influence on behavior. Identical twins – monozygotic – single fertilized egg Fraternal twins – dizygotic – separate eggs Twin studies help establish heredity’s effect on behavior. Adoption studies reveal more strength for the inheritedbehavior theory. Mol ...
... Methods Used by Behavior Genetics – genetic influence on behavior. Identical twins – monozygotic – single fertilized egg Fraternal twins – dizygotic – separate eggs Twin studies help establish heredity’s effect on behavior. Adoption studies reveal more strength for the inheritedbehavior theory. Mol ...
Human genetic L.Saba Abood
... • VARIATION: similarities and differences. The genetic information of an individual is contained in the chromosomes. Every human cell contains 23 pair of chromosomes. One pair is called sex chromosomes Male: XY, Female: XX, other 22 pairs of homologous chromosomes are called autosomes (each chromoso ...
... • VARIATION: similarities and differences. The genetic information of an individual is contained in the chromosomes. Every human cell contains 23 pair of chromosomes. One pair is called sex chromosomes Male: XY, Female: XX, other 22 pairs of homologous chromosomes are called autosomes (each chromoso ...
Midterm Exam: 2000-2001
... first within the observed organelle? A. Light to chemical C. Heat to electrical B. ATP to light D. Chemical to chemical 26. A protein in the cell membrane changed its shape to move sodium and potassium ions against their concentration gradients. Which molecule was most likely used by the protein as ...
... first within the observed organelle? A. Light to chemical C. Heat to electrical B. ATP to light D. Chemical to chemical 26. A protein in the cell membrane changed its shape to move sodium and potassium ions against their concentration gradients. Which molecule was most likely used by the protein as ...
Notes
... and laid end to end, they would make a very thin thread that would be approximately 3 meters long ...
... and laid end to end, they would make a very thin thread that would be approximately 3 meters long ...
ESSENTIAL CONCEPTS CLASS ACTIVITY 1: Polygenic Inheritance
... State that some traits result from more than two alleles (Reardon: most traits….are polygenic) (4.3.3) Describe ABO blood types as an example of codominance and multiple alleles (4.3.4) ...
... State that some traits result from more than two alleles (Reardon: most traits….are polygenic) (4.3.3) Describe ABO blood types as an example of codominance and multiple alleles (4.3.4) ...
BL 414 Genetics Spring 2006 Study Guide for Test 3
... for X-inactivation, and heavy methylation occurs along the chromosome ...
... for X-inactivation, and heavy methylation occurs along the chromosome ...
File - Mrs. Riggs Online
... law of independent assortment: many traits inherited independently of one another; segregation of one gene does not influence segregation of another linkage: two genes located on same chromosome which may be inherited together; do not follow law of independent assortment (Hemophilia A + colorblindne ...
... law of independent assortment: many traits inherited independently of one another; segregation of one gene does not influence segregation of another linkage: two genes located on same chromosome which may be inherited together; do not follow law of independent assortment (Hemophilia A + colorblindne ...
Gen 305, presentation 6′, 16
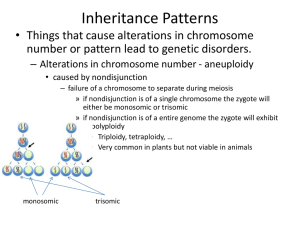
... • Chromosome numbers can vary in two main ways – Euploidy • Variation in the number of complete sets of chromosome ...
... • Chromosome numbers can vary in two main ways – Euploidy • Variation in the number of complete sets of chromosome ...
Chapter 7 – Linkage, Recombination, and
... (differentially from one type) – Human chromosomes usually lost, only a few remain – Human genes expressed in hybrid cell lines must be located on retained chromosomes • deletion studies can give more specific location on chromosome ...
... (differentially from one type) – Human chromosomes usually lost, only a few remain – Human genes expressed in hybrid cell lines must be located on retained chromosomes • deletion studies can give more specific location on chromosome ...
Pierce chapter 7
... (differentially from one type) – Human chromosomes usually lost, only a few remain – Human genes expressed in hybrid cell lines must be located on retained chromosomes • deletion studies can give more specific location on chromosome ...
... (differentially from one type) – Human chromosomes usually lost, only a few remain – Human genes expressed in hybrid cell lines must be located on retained chromosomes • deletion studies can give more specific location on chromosome ...
Chapter 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... ______ ______ – used to determine the probability that crossing over between genes will occur - genes that split up due to crossing over 1% of the time are said to be ______ ______ ______ part ...
... ______ ______ – used to determine the probability that crossing over between genes will occur - genes that split up due to crossing over 1% of the time are said to be ______ ______ ______ part ...
Meiosis/ Genetics Study Guide*Test Wednesday 2/ 22/12
... selection of a particular gene in the gene pair for one trait to be passed to the offspring has nothing to do with the selection of the gene for any other trait. More precisely the law states that alleles of different genes assort independently of one another during gamete formation. 16. What is the ...
... selection of a particular gene in the gene pair for one trait to be passed to the offspring has nothing to do with the selection of the gene for any other trait. More precisely the law states that alleles of different genes assort independently of one another during gamete formation. 16. What is the ...
Genetics - Tomball FFA
... Chromosomes There are 2 sex chromosomes included in the diploid number of the chromosomes. All of the other chromosomes are referred to as autosomes. In mammals if the sex chromosomes are alike, XX it results in a female. If the sex chromosomes are different, XY it results in a male. ...
... Chromosomes There are 2 sex chromosomes included in the diploid number of the chromosomes. All of the other chromosomes are referred to as autosomes. In mammals if the sex chromosomes are alike, XX it results in a female. If the sex chromosomes are different, XY it results in a male. ...
Genes Chromosomes and DNA
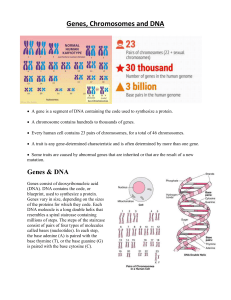
... A gene is a segment of DNA containing the code used to synthesize a protein. A chromosome contains hundreds to thousands of genes. Every human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more t ...
... A gene is a segment of DNA containing the code used to synthesize a protein. A chromosome contains hundreds to thousands of genes. Every human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more t ...
Date
... A) Do all cells grow and divide at the same rate? ________________________________ B) What cells live for a very short period of time? _______________________________ C) What cells live for a very long period of time? _______________________________ ...
... A) Do all cells grow and divide at the same rate? ________________________________ B) What cells live for a very short period of time? _______________________________ C) What cells live for a very long period of time? _______________________________ ...
Reproduction Review
... The critical features of meiosis: a) Another name for meiosis is sexual reproduction b) How many chromosomes does a normal human body cell have? 23 pairs c) Are they in pairs or single? pairs d) In the first stage of meiosis, what happens to the number of chromosomes? doubles e) In the last stage of ...
... The critical features of meiosis: a) Another name for meiosis is sexual reproduction b) How many chromosomes does a normal human body cell have? 23 pairs c) Are they in pairs or single? pairs d) In the first stage of meiosis, what happens to the number of chromosomes? doubles e) In the last stage of ...
Faithful meiotic chromosome segregation in Caenorhabditis elegans
... We use the genetic model system C. elegans to identify genes that are essential for proper meiotic prophase cell cycle progression and faithful meiotic chromosome segregation. Characterization of the encoded factors, their interaction partners and identification of mammalian (human) homologues will ...
... We use the genetic model system C. elegans to identify genes that are essential for proper meiotic prophase cell cycle progression and faithful meiotic chromosome segregation. Characterization of the encoded factors, their interaction partners and identification of mammalian (human) homologues will ...
Karyotype

A karyotype (from Greek κάρυον karyon, ""kernel"", ""seed"", or ""nucleus"", and τύπος typos, ""general form"") is the number and appearance of chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The term is also used for the complete set of chromosomes in a species, or an individual organism.Karyotypes describe the chromosome count of an organism, and what these chromosomes look like under a light microscope. Attention is paid to their length, the position of the centromeres, banding pattern, any differences between the sex chromosomes, and any other physical characteristics. The preparation and study of karyotypes is part of cytogenetics. The study of whole sets of chromosomes is sometimes known as karyology. The chromosomes are depicted (by rearranging a photomicrograph) in a standard format known as a karyogram or idiogram: in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size.The basic number of chromosomes in the somatic cells of an individual or a species is called the somatic number and is designated 2n. Thus, in humans 2n = 46. In the germ-line (the sex cells) the chromosome number is n (humans: n = 23).p28So, in normal diploid organisms, autosomal chromosomes are present in two copies. There may, or may not, be sex chromosomes. Polyploid cells have multiple copies of chromosomes and haploid cells have single copies.The study of karyotypes is important for cell biology and genetics, and the results may be used in evolutionary biology (karyosystematics) and medicine. Karyotypes can be used for many purposes; such as to study chromosomal aberrations, cellular function, taxonomic relationships, and to gather information about past evolutionary events.