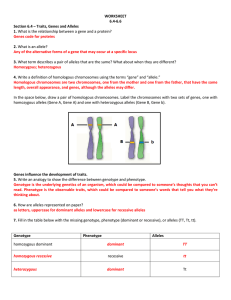
WORKSHEET 6.4-6.6 Section 6.4 – Traits, Genes and Alleles 1
... Yes. The chromosomes carrying those genes will line up randomly and separate randomly during meiosis. 8. If genes A and B are located at opposite ends on the same chromosome, are they likely to follow Mendel’s law of independent assortment? Explain. Yes. The genes will be far enough from each other ...
... Yes. The chromosomes carrying those genes will line up randomly and separate randomly during meiosis. 8. If genes A and B are located at opposite ends on the same chromosome, are they likely to follow Mendel’s law of independent assortment? Explain. Yes. The genes will be far enough from each other ...
7.014 Genetics Section Problems
... iii) To be type B, individual 3 must have gotten an io ALK- chromosome from Dad and an I B ALK+ chromosome from Mom. iv) Individual 4 got an IA ALK- chromosome from Mom and an io ALK- chromosome from Dad. If no recombination occurred, then for this impending child the chance of getting I B ALK+ chro ...
... iii) To be type B, individual 3 must have gotten an io ALK- chromosome from Dad and an I B ALK+ chromosome from Mom. iv) Individual 4 got an IA ALK- chromosome from Mom and an io ALK- chromosome from Dad. If no recombination occurred, then for this impending child the chance of getting I B ALK+ chro ...
Organization of chromosomes in the interphase cell - UvA-DARE
... that separates chromosome territories, dispersed chromatin of neighboring chromosomes can interact. Chromosomes are not always separated by non-chromatin space. Regularly, condensed regions of chromosome territories or chromosomal domains were so closely apposed that they appeared to form a single c ...
... that separates chromosome territories, dispersed chromatin of neighboring chromosomes can interact. Chromosomes are not always separated by non-chromatin space. Regularly, condensed regions of chromosome territories or chromosomal domains were so closely apposed that they appeared to form a single c ...
Powerpoint - Colorado FFA
... determined by three alleles, IA, IB, and i. The letters A and B refer to two carbohydrates on the surface of red blood cells. The i allele means that neither carbohydrate is present. The IA and IB alleles are both dominant over i, which is recessive. But neither IA or IB is dominant over the other. ...
... determined by three alleles, IA, IB, and i. The letters A and B refer to two carbohydrates on the surface of red blood cells. The i allele means that neither carbohydrate is present. The IA and IB alleles are both dominant over i, which is recessive. But neither IA or IB is dominant over the other. ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... There are many other types of inheritance patterns other than simple dominant or recessive inheritance. Incomplete Dominance and Codominance Incomplete dominance occurs when the heterozygote is intermediate between the two homozygotes. Codominance occurs when alleles are equally expressed in a heter ...
... There are many other types of inheritance patterns other than simple dominant or recessive inheritance. Incomplete Dominance and Codominance Incomplete dominance occurs when the heterozygote is intermediate between the two homozygotes. Codominance occurs when alleles are equally expressed in a heter ...
Genes & Development
... Boveri’s support for nuclear control Polyspermy in sea urchins • Embryos developing with multiple sets of chromosomes had defects • Chromosome number (nucleus) important ...
... Boveri’s support for nuclear control Polyspermy in sea urchins • Embryos developing with multiple sets of chromosomes had defects • Chromosome number (nucleus) important ...
Genetic Notes review page (blanks filled in except for
... 6. Four types of asexual reproduction: __Binary fission_____, __runners (also called Vegetative Propagation) ____, __budding____, ___fragmentation (also called regeneration)______. ((There is one we do not learn about in 7th grade called: Parthenogenesis -Though most of the organisms that use asexua ...
... 6. Four types of asexual reproduction: __Binary fission_____, __runners (also called Vegetative Propagation) ____, __budding____, ___fragmentation (also called regeneration)______. ((There is one we do not learn about in 7th grade called: Parthenogenesis -Though most of the organisms that use asexua ...
Reebops: A "Model" Organism for Teaching Genetic Concepts
... Gametes are formed through a special process, known as meiosis. Meiosis reduces, by half, the number of chromosomes in each cell that is finally produced. For this reason, meiosis also is known as reduction division. (It should be noted that meiosis differs from the normal process of cell division ...
... Gametes are formed through a special process, known as meiosis. Meiosis reduces, by half, the number of chromosomes in each cell that is finally produced. For this reason, meiosis also is known as reduction division. (It should be noted that meiosis differs from the normal process of cell division ...
Name
... All stages of the cell cycle not including mitosis (specifically G1, S, and G2) (3) Define carrier. A heterozygous individual for a recessive trait- passes on the gene and doesn't show a phenotype (3) Define cyclin. family of proteins that vary in their amount according to the cell cycle and regulat ...
... All stages of the cell cycle not including mitosis (specifically G1, S, and G2) (3) Define carrier. A heterozygous individual for a recessive trait- passes on the gene and doesn't show a phenotype (3) Define cyclin. family of proteins that vary in their amount according to the cell cycle and regulat ...
Biology Review for EOC
... Natural selection states that organisms with traits well suited to an environment are more likely to survive and produce more offspring than organisms without these favorable traits Biodiversity: Organisms become very different from each other as they evolve and become better suited to their env ...
... Natural selection states that organisms with traits well suited to an environment are more likely to survive and produce more offspring than organisms without these favorable traits Biodiversity: Organisms become very different from each other as they evolve and become better suited to their env ...
07Lab_MitoMei - Biology Learning Center at the University of
... Free earlobe: port is detached. Detached = dominant Swing hands, clasp together. If left thumb over right, you've got the dominant trait Bending your thumb away from your palm: INability to bend tip 60 degrees relative to thumb is dominant Hair on middle joint of finger is dominant Dimpled cheeks is ...
... Free earlobe: port is detached. Detached = dominant Swing hands, clasp together. If left thumb over right, you've got the dominant trait Bending your thumb away from your palm: INability to bend tip 60 degrees relative to thumb is dominant Hair on middle joint of finger is dominant Dimpled cheeks is ...
14-2 Human Chromosomes
... Autosomal vs Sex Linked Traits • Autosomes – All the chromosomes that do NOT play a role in sex determination • In humans, chromosomes 1 – 22 – Two copies » One from Mom » One from Dad » Same genes » Same location on chromosome » BUT may be different alleles (recipes) ...
... Autosomal vs Sex Linked Traits • Autosomes – All the chromosomes that do NOT play a role in sex determination • In humans, chromosomes 1 – 22 – Two copies » One from Mom » One from Dad » Same genes » Same location on chromosome » BUT may be different alleles (recipes) ...
Pedigree Chart Activity - Anderson School District One
... All living things have pedigrees. A pedigree is a diagram that shows the occurrence and appearance (phenotype) of a particular genetic trait, as it is passed from one generation to the next in a given family. From this information, along with an understanding of inheritance, genotypes of individuals ...
... All living things have pedigrees. A pedigree is a diagram that shows the occurrence and appearance (phenotype) of a particular genetic trait, as it is passed from one generation to the next in a given family. From this information, along with an understanding of inheritance, genotypes of individuals ...
Meiosis - cloudfront.net
... Makes 2 cells Makes 4 cells Genetically different cells Genetically identical cells Makes haploid cells Makes diploid cells A process of cell division Produces gametes Produces normal body cells Cells produced are used for growth Cells produced are used for reproduction ...
... Makes 2 cells Makes 4 cells Genetically different cells Genetically identical cells Makes haploid cells Makes diploid cells A process of cell division Produces gametes Produces normal body cells Cells produced are used for growth Cells produced are used for reproduction ...
RECIPROCAL CHROMOSOME TRANSLOCATIONS IN 437
... implicated in various forms of reproductive failure, ranging from defective gametogenesis (Crosignani, Rubin 1982) to recurrent spontaneous miscarriage (Campana et al. 1986). Autosomal balanced translocations have also been implicated in patients with infertility, particularly male infertility. In t ...
... implicated in various forms of reproductive failure, ranging from defective gametogenesis (Crosignani, Rubin 1982) to recurrent spontaneous miscarriage (Campana et al. 1986). Autosomal balanced translocations have also been implicated in patients with infertility, particularly male infertility. In t ...
Heredity and Genetics Study Guide
... o Be able to use a Punnett Square to show a cross involving incomplete dominance. o Be able to describe the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. o Know what sex cells are, and how they are different from normal body cells. o Be able to describe the process of meiosis, including the re ...
... o Be able to use a Punnett Square to show a cross involving incomplete dominance. o Be able to describe the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. o Know what sex cells are, and how they are different from normal body cells. o Be able to describe the process of meiosis, including the re ...
2012 Genetics Vocab and Notes
... In the zygote, the fertilized egg, for the first time, the genes that make you YOU, came together. All of the billions of other cells in your body started with that one. Purebred = True Breeding – True-breeding- basically means the same as homozygous – having two dominant or two recessive alleles. W ...
... In the zygote, the fertilized egg, for the first time, the genes that make you YOU, came together. All of the billions of other cells in your body started with that one. Purebred = True Breeding – True-breeding- basically means the same as homozygous – having two dominant or two recessive alleles. W ...
Constructing A Human Lab
... freckles. Why does Katie look more like her mother than she does her father? F ...
... freckles. Why does Katie look more like her mother than she does her father? F ...
Chapters 12 through 16 Unit objective answers checked
... 11) What is reduction division – why is meiosis considered as such? In comparison, what is mitosis referred to as? Gametes end up with less chromosomes than they started with so reduction division. Mitosis is equation division. 12) Will the organism change from diploid to haploid after meiosis? Why ...
... 11) What is reduction division – why is meiosis considered as such? In comparison, what is mitosis referred to as? Gametes end up with less chromosomes than they started with so reduction division. Mitosis is equation division. 12) Will the organism change from diploid to haploid after meiosis? Why ...
Thesis-1959R-B751s
... from this study because it is likely that most individuals who read this report will have a basic knowledge of reproduction. Plan of Procedure Generally, this study has been based mostly upon elementary literature in this field. ...
... from this study because it is likely that most individuals who read this report will have a basic knowledge of reproduction. Plan of Procedure Generally, this study has been based mostly upon elementary literature in this field. ...
Supplemental Data Whorl-Specific Expression of
... Arabidopsis thaliana plants of the ecotype Landsberg erecta were transformed by using the vacuum infiltration method after placement of the plasmid into the Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain ASE. We recovered transgenic plants by selecting for kanamycin resistance. All plants were grown under continu ...
... Arabidopsis thaliana plants of the ecotype Landsberg erecta were transformed by using the vacuum infiltration method after placement of the plasmid into the Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain ASE. We recovered transgenic plants by selecting for kanamycin resistance. All plants were grown under continu ...
Comparative Genome Organization in plants: From Sequence and Markers to... and Chromosomes Summary
... fails to tell us about chromatin packaging and three-dimensional organization of the chromosomes. Repetitive DNA Sequence and the Large-Scale Organization of the chromosome: Before genomes of different organisms can be compared, the length of the sequence gaps must be determined, the homogeneity of ...
... fails to tell us about chromatin packaging and three-dimensional organization of the chromosomes. Repetitive DNA Sequence and the Large-Scale Organization of the chromosome: Before genomes of different organisms can be compared, the length of the sequence gaps must be determined, the homogeneity of ...
15C-ErorsExcptionChromoInh
... Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE
... Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Welcome Back to School - Glen Ridge Public Schools
... Hypothesis: 3:1 ration Gray/long:black/short Actual: neither 9:3:3:1, nor 3:1 Crossing-over ...
... Hypothesis: 3:1 ration Gray/long:black/short Actual: neither 9:3:3:1, nor 3:1 Crossing-over ...
Karyotype

A karyotype (from Greek κάρυον karyon, ""kernel"", ""seed"", or ""nucleus"", and τύπος typos, ""general form"") is the number and appearance of chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The term is also used for the complete set of chromosomes in a species, or an individual organism.Karyotypes describe the chromosome count of an organism, and what these chromosomes look like under a light microscope. Attention is paid to their length, the position of the centromeres, banding pattern, any differences between the sex chromosomes, and any other physical characteristics. The preparation and study of karyotypes is part of cytogenetics. The study of whole sets of chromosomes is sometimes known as karyology. The chromosomes are depicted (by rearranging a photomicrograph) in a standard format known as a karyogram or idiogram: in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size.The basic number of chromosomes in the somatic cells of an individual or a species is called the somatic number and is designated 2n. Thus, in humans 2n = 46. In the germ-line (the sex cells) the chromosome number is n (humans: n = 23).p28So, in normal diploid organisms, autosomal chromosomes are present in two copies. There may, or may not, be sex chromosomes. Polyploid cells have multiple copies of chromosomes and haploid cells have single copies.The study of karyotypes is important for cell biology and genetics, and the results may be used in evolutionary biology (karyosystematics) and medicine. Karyotypes can be used for many purposes; such as to study chromosomal aberrations, cellular function, taxonomic relationships, and to gather information about past evolutionary events.























