Electromagnetics
... 1. Please derive (from Maxwell’s eqs.) impedance Zo of free space and express it in terms of the constants of free space o and o . Prove that E wave and H wave are in phase in the free space. Also prove that the energy densities of E and H waves are equal. (15%) 2. Please give the equations of D ...
... 1. Please derive (from Maxwell’s eqs.) impedance Zo of free space and express it in terms of the constants of free space o and o . Prove that E wave and H wave are in phase in the free space. Also prove that the energy densities of E and H waves are equal. (15%) 2. Please give the equations of D ...
Ch33 - Siena College
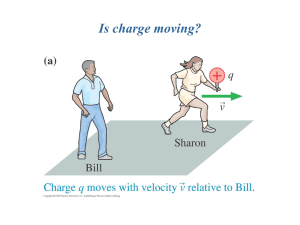
... where V is the velocity of frame S' relative to frame S and where the fields are measured at the same point in space by experimenters at rest in each reference frame. NOTE: These equations are only valid if V << c. ...
... where V is the velocity of frame S' relative to frame S and where the fields are measured at the same point in space by experimenters at rest in each reference frame. NOTE: These equations are only valid if V << c. ...
PHYS-2100 Introduction to Methods of Theoretical Physics Fall 1998 1) 2)
... these are called “left” and “right”-handed circularly polarized waves. 3) This problem desribes a simple waveguide. It is similar to Nettel, Problem 4.13. An electromagnetic wave propagates in a TE mode between a waveguide made of two parallel plates of infinite extent. The plates are made of perfec ...
... these are called “left” and “right”-handed circularly polarized waves. 3) This problem desribes a simple waveguide. It is similar to Nettel, Problem 4.13. An electromagnetic wave propagates in a TE mode between a waveguide made of two parallel plates of infinite extent. The plates are made of perfec ...
... Calculate the charge density and current as seen by an observer in S' moving with a speed v along the z axis. Calculate the electric and magnetic fields seen by this observer. Transform these fields to find the fields in the original frame. Check that these agree with a direct calculation in the ori ...
... Calculate the charge density and current as seen by an observer in S' moving with a speed v along the z axis. Calculate the electric and magnetic fields seen by this observer. Transform these fields to find the fields in the original frame. Check that these agree with a direct calculation in the ori ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... E y 2 iˆ (2 xy z ) ˆj 2 z kˆ is a 01. Check whether the field given by possible electrostatic field or not 02. Distinguish between polar and non-polar dielectrics 03. Outline the characteristics of para magnetic materials 04. How are the bound and free charges related to each other in linear ...
... E y 2 iˆ (2 xy z ) ˆj 2 z kˆ is a 01. Check whether the field given by possible electrostatic field or not 02. Distinguish between polar and non-polar dielectrics 03. Outline the characteristics of para magnetic materials 04. How are the bound and free charges related to each other in linear ...
Finding the Equation of a Line Given Two Points: Name Algebra 1
... A system of equations is a collection of two or more equations with a same set of unknowns. In solving a system of equations, we try to find values for each of the unknowns that will satisfy every equation in the system. When solving a system containing two linear equations there will be one ordered ...
... A system of equations is a collection of two or more equations with a same set of unknowns. In solving a system of equations, we try to find values for each of the unknowns that will satisfy every equation in the system. When solving a system containing two linear equations there will be one ordered ...
ASPDEN`S EARLY LAW OF ELECTRODYNAMICS
... [2]) which consisted of introducing a new term in the familiar empirically derived formula. This new term integrates to zero when ~losed circuital currents are involved. Thus, since Maxwell, Ampere, and Biot and Savart relied on closed circuits in their experiments it is understandable that such a t ...
... [2]) which consisted of introducing a new term in the familiar empirically derived formula. This new term integrates to zero when ~losed circuital currents are involved. Thus, since Maxwell, Ampere, and Biot and Savart relied on closed circuits in their experiments it is understandable that such a t ...
EEE 431 Computational methods in Electrodynamics
... H: Magnetic field intensity (A/ m) D: Electric flux density (C/ m2 ) B: Magnetic flux density (Weber/ m2 ) J: Electric current density (A/ m2 ) Jc :Conduction electric current density (A/ m2 ) Jd :Displacement electric current density(A/m2) :Volume charge density (C/m3) ...
... H: Magnetic field intensity (A/ m) D: Electric flux density (C/ m2 ) B: Magnetic flux density (Weber/ m2 ) J: Electric current density (A/ m2 ) Jc :Conduction electric current density (A/ m2 ) Jd :Displacement electric current density(A/m2) :Volume charge density (C/m3) ...
19.- Modeling Electromagnetic Fields in Induction Heating
... The objective of modeling is to produce a mathematical representation of the induction heating process by first determining the induced current distribution in the component. Ultimately, one would like to produce a predictive capability capable of assisting in process optimization and new process de ...
... The objective of modeling is to produce a mathematical representation of the induction heating process by first determining the induced current distribution in the component. Ultimately, one would like to produce a predictive capability capable of assisting in process optimization and new process de ...
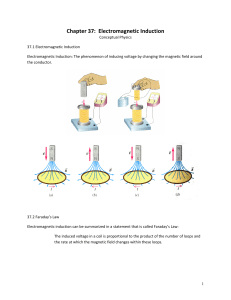
Chapter 37: Electromagnetic Induction
... Chapter 37: Electromagnetic Induction Conceptual Physics 37.1 Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Induction: The phenomenon of inducing voltage by changing the magnetic field around the conductor. ...
... Chapter 37: Electromagnetic Induction Conceptual Physics 37.1 Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Induction: The phenomenon of inducing voltage by changing the magnetic field around the conductor. ...
Discussion Note #28
... varying electric field to induce a magnetic field in a manner analogous to Faraday Induction, where a changing magnetic field induces an electric field. This process is now called Maxwell Induction. Once the displacement current is included, the two induction equations become symmetric and imply tha ...
... varying electric field to induce a magnetic field in a manner analogous to Faraday Induction, where a changing magnetic field induces an electric field. This process is now called Maxwell Induction. Once the displacement current is included, the two induction equations become symmetric and imply tha ...