Guass`s Law for magnetism
... • Straight Antenna – Electric field of EM wave produces a current in the electrons in the antenna • Loop Antenna – Magnetic field of EM wave induces a current • Tune in a station – uses the resonant frequency of ...
... • Straight Antenna – Electric field of EM wave produces a current in the electrons in the antenna • Loop Antenna – Magnetic field of EM wave induces a current • Tune in a station – uses the resonant frequency of ...
Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic (EM) Waves James Clerk
... • An electric field exerts a force on any charged particle • A magnetic field exerts a force on a moving charged particle ...
... • An electric field exerts a force on any charged particle • A magnetic field exerts a force on a moving charged particle ...
Time Varying Electric and Magnetic Fields
... equal to the time rate of decrease of the total magnetic flux linking the circuit. ...
... equal to the time rate of decrease of the total magnetic flux linking the circuit. ...
Class 8 , Physics 260 Electric Charge, Electric Field (3) 1. For a
... 4. In a uniform external electric field, a dipole experiences a torque given by τ =p×E 5. In a uniform external electric field, a dipole has potential energy U = −p · E ...
... 4. In a uniform external electric field, a dipole experiences a torque given by τ =p×E 5. In a uniform external electric field, a dipole has potential energy U = −p · E ...
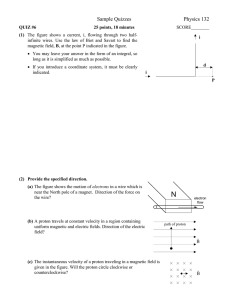
Sample Quizzes Physics 132
... (1) The figure shows a current, i, flowing through two halfinfinite wires. Use the law of Biot and Savart to find the magnetic field, B, at the point P indicated in the figure. ...
... (1) The figure shows a current, i, flowing through two halfinfinite wires. Use the law of Biot and Savart to find the magnetic field, B, at the point P indicated in the figure. ...
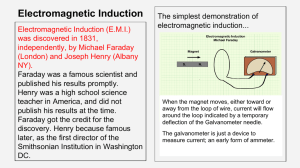
Electromagnetic Induction
... phenomenon, but Maxwell put it into mathematical terms. Consider a time-dependent magnetic field B(r,t); i.e., it changes in time t. The induced electric field E(r,t) circulates around the change of B. Picture: ...
... phenomenon, but Maxwell put it into mathematical terms. Consider a time-dependent magnetic field B(r,t); i.e., it changes in time t. The induced electric field E(r,t) circulates around the change of B. Picture: ...
Problem 1 and is oriented in such a y E
... Problem 1. A parallel-plate capacitor is stationary in frame K ′ and is oriented in such a way that the field inside it is parallel to the y ′ axis: E′ = (0, Ey′ , 0). The capacitor is moving with respect to the laboratory frame K along the x-axis with velocity V . Using Ampere’s law and Gauss’s law ...
... Problem 1. A parallel-plate capacitor is stationary in frame K ′ and is oriented in such a way that the field inside it is parallel to the y ′ axis: E′ = (0, Ey′ , 0). The capacitor is moving with respect to the laboratory frame K along the x-axis with velocity V . Using Ampere’s law and Gauss’s law ...
HW: practice 13
... Lesson 13-5: Elimination Using Multiplication p.572 - 577 Objective: to solve systems of equations by the elimination method using multiplication and addition/subtraction. ...
... Lesson 13-5: Elimination Using Multiplication p.572 - 577 Objective: to solve systems of equations by the elimination method using multiplication and addition/subtraction. ...
Chapter 29
... electric fields and added another term, called the displacement current, Id • This showed that magnetic fields are produced both by conduction currents and by time-varying electric fields ...
... electric fields and added another term, called the displacement current, Id • This showed that magnetic fields are produced both by conduction currents and by time-varying electric fields ...