Chapter 21
... Millikan’s Oil-Drop Experiment – Robert A. Millikan in 1909 used the uniform electric field to determine the charge on a single electron. – He found experimentally that the changes in the charges of the oil drops were always multiples of 1.60 X 10-19 C. ...
... Millikan’s Oil-Drop Experiment – Robert A. Millikan in 1909 used the uniform electric field to determine the charge on a single electron. – He found experimentally that the changes in the charges of the oil drops were always multiples of 1.60 X 10-19 C. ...
2 electric-fields-good
... Electric field lines around a charged object can be mapped by imagining the direction that a POSITIVE test charge would move in that region of space 1. Place the test charge near the object 2. Decide which direction the charge will move 3. Draw a field vector in the direction of motion ...
... Electric field lines around a charged object can be mapped by imagining the direction that a POSITIVE test charge would move in that region of space 1. Place the test charge near the object 2. Decide which direction the charge will move 3. Draw a field vector in the direction of motion ...
ppt
... If you took an electrically charged ball and shook it up and down rapidly, charges in a nearby metal object would move in response. How far away could that metal object be and still respond? ...
... If you took an electrically charged ball and shook it up and down rapidly, charges in a nearby metal object would move in response. How far away could that metal object be and still respond? ...
Sample Question Paper
... (iii) Show that it is impossible to obtain a total non solenoidal current with non zero value of with the conditions in (c) (ii) above. ...
... (iii) Show that it is impossible to obtain a total non solenoidal current with non zero value of with the conditions in (c) (ii) above. ...
AC Circuits - San Jose State University
... We will use this law to obtain some useful results by choosing a simple path along which the magnitude of B is constant, (or independent of dl). That way, after taking the dot product, we can factor out |B| from under the integral sign and the integral will be very easy to do. ...
... We will use this law to obtain some useful results by choosing a simple path along which the magnitude of B is constant, (or independent of dl). That way, after taking the dot product, we can factor out |B| from under the integral sign and the integral will be very easy to do. ...
$doc.title
... “three-space” and when the solutions are graphed, the graph is a plane. (A quick note, you can think of solving for z and you would get z as a function of x and y, i.e. z = f ( x, y ) = 2x + 3y − 10 . This may help with the plane idea...) 2. Systems of Linear Equations in Three Variables: Consider t ...
... “three-space” and when the solutions are graphed, the graph is a plane. (A quick note, you can think of solving for z and you would get z as a function of x and y, i.e. z = f ( x, y ) = 2x + 3y − 10 . This may help with the plane idea...) 2. Systems of Linear Equations in Three Variables: Consider t ...
21-1 Creating and Measuring Electric Fields
... When there are two or more, the field is the vector sum from individual charges Lines ...
... When there are two or more, the field is the vector sum from individual charges Lines ...
L24_A2_2009_10_CoulombsLaw
... Two point charges Q1 is +6.3nC & Q2 is 2.7nC exerts a force of 3.2x10-5N when they are d metres apart a. Find d b. Find the force if d increases to 3d [69mm] [3.6 x 10-6N] e = -1.6 x 10-19 C 0 = 8.85 x 10-12 F/m ...
... Two point charges Q1 is +6.3nC & Q2 is 2.7nC exerts a force of 3.2x10-5N when they are d metres apart a. Find d b. Find the force if d increases to 3d [69mm] [3.6 x 10-6N] e = -1.6 x 10-19 C 0 = 8.85 x 10-12 F/m ...
Magnetism - Howard Elementary School
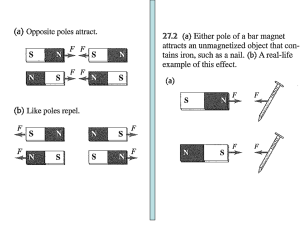
... There are 2 main ways that magnets are similar to electric charges: like charges repel and opposites attract, and the force between is inversely proportional to the distance between them. This means that closer is stronger, and further is weaker. Electric charges are positive or negative, magnetic p ...
... There are 2 main ways that magnets are similar to electric charges: like charges repel and opposites attract, and the force between is inversely proportional to the distance between them. This means that closer is stronger, and further is weaker. Electric charges are positive or negative, magnetic p ...