Gravitoelectromagnetism (GEM): A Group
... since the spin of the graviton gives rise to the field equations of GEM. In this formulation gravity is described by two tensor fields (gravitoelectromagnetic fields) which are symmetric and traceless tensors of rank two that satisfy a set of Maxwell-like field equations. The fact that these tensor ...
... since the spin of the graviton gives rise to the field equations of GEM. In this formulation gravity is described by two tensor fields (gravitoelectromagnetic fields) which are symmetric and traceless tensors of rank two that satisfy a set of Maxwell-like field equations. The fact that these tensor ...
Exam IV_v0001_final - University of Colorado Boulder
... Your exam should have pages numbered 1-17 (questions begin on page 3) This exam consists of 42 multiple-choice questions. Each is worth the same. Fill in the bubble sheet with a #2 pencil. PLEASE follow all directions carefully. Print and bubble in your name on the bubble sheet. Print and bubble in ...
... Your exam should have pages numbered 1-17 (questions begin on page 3) This exam consists of 42 multiple-choice questions. Each is worth the same. Fill in the bubble sheet with a #2 pencil. PLEASE follow all directions carefully. Print and bubble in your name on the bubble sheet. Print and bubble in ...
EM_Course_Module_4 - University of Illinois at Urbana
... volume V by the current source J0 is accounted for by the sum of the time rates of increase of the energies stored in the electric and magnetic fields in the volume, plus another term, which we must interpret as the power carried by the electromagnetic field out of the volume V, for conservation of ...
... volume V by the current source J0 is accounted for by the sum of the time rates of increase of the energies stored in the electric and magnetic fields in the volume, plus another term, which we must interpret as the power carried by the electromagnetic field out of the volume V, for conservation of ...
Document
... Let’s look at each of the symbols: “n”=# of discrete charges in the system qi is the ith charge in the system. “k” is coulomb’s constant rp is the vector from the origin pointed towards the point p in space. This would also be the location of the positive test charge so the notation that we have dev ...
... Let’s look at each of the symbols: “n”=# of discrete charges in the system qi is the ith charge in the system. “k” is coulomb’s constant rp is the vector from the origin pointed towards the point p in space. This would also be the location of the positive test charge so the notation that we have dev ...
Electrostatics PP
... • Suppose that you are measuring an electric field using a positive test charge of 3.0x10^-6C. This test charge experiences a force of 0.12N. What is the magnitude of the electric field strength at the location of the test charge? ...
... • Suppose that you are measuring an electric field using a positive test charge of 3.0x10^-6C. This test charge experiences a force of 0.12N. What is the magnitude of the electric field strength at the location of the test charge? ...
college physics
... A pendulum is comprised of a 2.1 m long massless string with a 1.0 g mass at its free end. This mass carries a net charge of +2.3 nC. The pendulum hangs in a uniform electric field of strength 1500 N/C oriented horizontally. (A) what is the net force on the charged pendulum mass? (B) When in equilib ...
... A pendulum is comprised of a 2.1 m long massless string with a 1.0 g mass at its free end. This mass carries a net charge of +2.3 nC. The pendulum hangs in a uniform electric field of strength 1500 N/C oriented horizontally. (A) what is the net force on the charged pendulum mass? (B) When in equilib ...
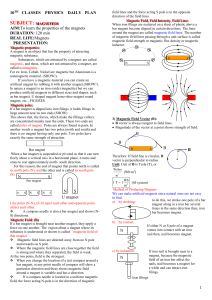
7TH CLASSES PHYSICS DAILY PLAN
... When you change the location of a test compass around a bar magnet, at any point needle of compass will show a particular direction and these shows magnetic field around a magnet is variable and has a direction. ...
... When you change the location of a test compass around a bar magnet, at any point needle of compass will show a particular direction and these shows magnetic field around a magnet is variable and has a direction. ...