Kinetic Energy
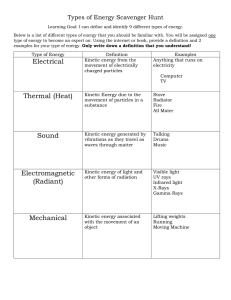
... Types of Energy Scavenger Hunt Learning Goal: I can define and identify 9 different types of energy. Below is a list of different types of energy that you should be familiar with. You will be assigned one type of energy to become an expert on. Using the internet or book, provide a definition and 2 e ...
... Types of Energy Scavenger Hunt Learning Goal: I can define and identify 9 different types of energy. Below is a list of different types of energy that you should be familiar with. You will be assigned one type of energy to become an expert on. Using the internet or book, provide a definition and 2 e ...
Energy Forms - Greenwood County School District 52
... • 1. This energy is in a form that can travel through a vacuum. • Example – light, x-rays, microwaves • ANYTHING that is found in the electromagnetic spectrum. ...
... • 1. This energy is in a form that can travel through a vacuum. • Example – light, x-rays, microwaves • ANYTHING that is found in the electromagnetic spectrum. ...
Energy Vocabulary
... potential energy: the energy that something has because of its position or condition kinetic energy: the energy of motion mechanical energy: the total potential and kinetic energy of an object light energy: a form of energy that can travel through space and which our sight can detect reflect: to bou ...
... potential energy: the energy that something has because of its position or condition kinetic energy: the energy of motion mechanical energy: the total potential and kinetic energy of an object light energy: a form of energy that can travel through space and which our sight can detect reflect: to bou ...
Intro to Energy - DuVall School News
... Energy can only be converted from one form to another (energy isn’t “lost”, it merely changes form) Energy conversions occur without loss or gain in energy (however, not all forms of energy are “useful”) ...
... Energy can only be converted from one form to another (energy isn’t “lost”, it merely changes form) Energy conversions occur without loss or gain in energy (however, not all forms of energy are “useful”) ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy Notes (9/28-29/2016)
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
PEKE - Science
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
Chemical Energy
... 3. Electromagnetic Energy – Energy that is reflected or emitted from objects in the form of electrical and magnetic waves that can travel through space. 4. Gravitational Energy – Energy an object possesses because of its position in a gravitational a. field. 5. Kinetic Energy – Energy in the form of ...
... 3. Electromagnetic Energy – Energy that is reflected or emitted from objects in the form of electrical and magnetic waves that can travel through space. 4. Gravitational Energy – Energy an object possesses because of its position in a gravitational a. field. 5. Kinetic Energy – Energy in the form of ...
Physics Chapter 5 Vocabulary Section 1 Energy: the ability to do
... Fossil fuels: nonrenewable energy resources that form in the Earth’s crust over millions of years from the buried remains of once-‐living organisms. ...
... Fossil fuels: nonrenewable energy resources that form in the Earth’s crust over millions of years from the buried remains of once-‐living organisms. ...
Chapter 9 Vocabulary Energy – the ability to do work Kinetic energy
... Potential energy - the energy an object has because of its position or shape Gravitational potential energy – energy due to an object’s position above the Earth’s surface. Mechanical energy - total energy of motion and position of an object Energy Conversion - a change from one form of energy into a ...
... Potential energy - the energy an object has because of its position or shape Gravitational potential energy – energy due to an object’s position above the Earth’s surface. Mechanical energy - total energy of motion and position of an object Energy Conversion - a change from one form of energy into a ...
Study Guide: Energy
... Concepts to understand: 1) What is kinetic and potential energy? Give examples of each. 2) What different forms does energy come in? What are other words to remember these? Give examples of each? 3) How does energy change or transform from one type into another? Why? Give examples. Where does energy ...
... Concepts to understand: 1) What is kinetic and potential energy? Give examples of each. 2) What different forms does energy come in? What are other words to remember these? Give examples of each? 3) How does energy change or transform from one type into another? Why? Give examples. Where does energy ...
Forms of Energy Quiz - RRMS 8th Grade Science
... J. The energy an object has because of its position or shape. 10. _____Kinetic ...
... J. The energy an object has because of its position or shape. 10. _____Kinetic ...
Energy - ChemConnections
... Sources: History: EIA; Projections: Short-Term Energy Outlook, March 2002. ...
... Sources: History: EIA; Projections: Short-Term Energy Outlook, March 2002. ...
Solutions - retremblay.net
... 1. The simplest definition of _energy_________ is that it is the capacity to do work. Work, in this context, may be defined as what is done to move an object against some sort of ___resistance___. 2. The capacity to do work resulting from the ___motion__ of an object is called kinetic energy, KE ...
... 1. The simplest definition of _energy_________ is that it is the capacity to do work. Work, in this context, may be defined as what is done to move an object against some sort of ___resistance___. 2. The capacity to do work resulting from the ___motion__ of an object is called kinetic energy, KE ...
Types of Energy
... These are the two main types of energy: Kinetic: energy in motion Potential: stored energy The following forms of energy can be grouped into those two types. Heat (Thermal Energy): internal motion of molecules. Ex. water boiling, turning to steam. Mechanical: energy from motion and moving parts. Ex. ...
... These are the two main types of energy: Kinetic: energy in motion Potential: stored energy The following forms of energy can be grouped into those two types. Heat (Thermal Energy): internal motion of molecules. Ex. water boiling, turning to steam. Mechanical: energy from motion and moving parts. Ex. ...
William Flynn Martin

William Flynn Martin (born October 4, 1950) is an American energy economist, educator and international diplomat. Martin served as Special Assistant to President Reagan for National Security Affairs, Executive Secretary of the National Security Council in the West Wing of the White House and Deputy Secretary of the Department of Energy during the Ronald Reagan administration. He was President of the Council of the University for Peace, appointed to the Council by Secretary General of the United Nations Kofi Annan and served as the Executive Director of the Republican Platform Committee during the re-election bid of George H.W. Bush. He has held senior appointments and advisory positions under several Presidents including: Ronald Reagan, George H.W. Bush and George W. Bush.Martin was born in Tulsa, Oklahoma. He achieved his Bachelor of Science from the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania in 1972 and his Master of Science from MIT in 1974. His master's thesis was the basis of an article he co-authored with George Cabot Lodge in the March, 1975 Harvard Business Review entitled Our Society in 1985: Business May Not Like It [1].


















