Energy - Charles W. Davidson College of Engineering
... Example: A car’s engine – Spark plugs initiate the combustion of fuel vapor in the engine cylinder, which releases energy from the gasoline. – Cylinders and pistons transform the expansion force of the combusted fuel/air to mechanical force, which in turn accelerates the car and increases the car’s ...
... Example: A car’s engine – Spark plugs initiate the combustion of fuel vapor in the engine cylinder, which releases energy from the gasoline. – Cylinders and pistons transform the expansion force of the combusted fuel/air to mechanical force, which in turn accelerates the car and increases the car’s ...
Chapter 9 Energy and Energy Resources
... Can objects have potential and kinetic energy at the same time? • An object can have both potential and kinetic energy at the same time. ...
... Can objects have potential and kinetic energy at the same time? • An object can have both potential and kinetic energy at the same time. ...
Pifer.weebly.com – Physical Science page Types of Energy Chapter
... When radiant energy comes into contact with ___________________, it changes the properties of that matter. For example, when micro-waves set off in a microwave oven, the water molecules in the food are charged and caused to ___________________ billions of times per second, generating heat, that cau ...
... When radiant energy comes into contact with ___________________, it changes the properties of that matter. For example, when micro-waves set off in a microwave oven, the water molecules in the food are charged and caused to ___________________ billions of times per second, generating heat, that cau ...
energy
... • The concept of energy transformation can be illustrated in a number of common activities. – An engine, such as the engine in a car, converts the chemical energy of gas and oxygen into the mechanical energy of engine movement. – A light bulb changes the chemical energy of the bulb into electromagne ...
... • The concept of energy transformation can be illustrated in a number of common activities. – An engine, such as the engine in a car, converts the chemical energy of gas and oxygen into the mechanical energy of engine movement. – A light bulb changes the chemical energy of the bulb into electromagne ...
Overview - RI
... straight black line. The graph shows that when potential energy is increasing, the kinetic energy is decreasing and vice versa. 3. Use the “Step back” or “Step forward” button to describe the change in kinetic energy as the spring moves from the most compressed position to the most stretched ...
... straight black line. The graph shows that when potential energy is increasing, the kinetic energy is decreasing and vice versa. 3. Use the “Step back” or “Step forward” button to describe the change in kinetic energy as the spring moves from the most compressed position to the most stretched ...
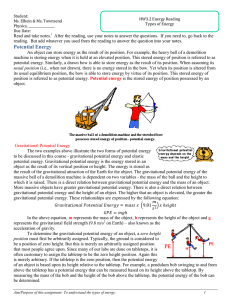
Potential Energy
... materials as the result of their stretching or compressing. Elastic potential energy can be stored in rubber bands, bungee cords, trampolines, springs, an arrow drawn into a bow, etc. The amount of elastic potential energy stored in such a device is related to the amount of stretch of the device - t ...
... materials as the result of their stretching or compressing. Elastic potential energy can be stored in rubber bands, bungee cords, trampolines, springs, an arrow drawn into a bow, etc. The amount of elastic potential energy stored in such a device is related to the amount of stretch of the device - t ...
Energy Use - Effingham County Schools
... All power plants convert heat into electricity using steam. At nuclear power plants, the heat to make the steam is created when atoms split- fission. Fission takes place when the nucleus of a heavy atom like plutonium or uranium is split into two when struck by a neutron. This releases more neutron ...
... All power plants convert heat into electricity using steam. At nuclear power plants, the heat to make the steam is created when atoms split- fission. Fission takes place when the nucleus of a heavy atom like plutonium or uranium is split into two when struck by a neutron. This releases more neutron ...
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry
... neither be created or destroyed but converted from one form to another. A system’s Internal Energy (E) = kinetic energy (KE) + potential energy (PE) of all the particles in the system. • While the values of KE and PE at a given instant are difficult to determine, changes in KE and/or PE can be deter ...
... neither be created or destroyed but converted from one form to another. A system’s Internal Energy (E) = kinetic energy (KE) + potential energy (PE) of all the particles in the system. • While the values of KE and PE at a given instant are difficult to determine, changes in KE and/or PE can be deter ...
JOURNAL OF KONES 2006 NO 4
... rocket propulsion, methods of transformation of electric energy into mechanical energy can be generally divided into thermal, electrostatic and electromagnetic processes. Said processes have given names to electric motors of rockets: electro-thermal, ionic, plasma [1]. Energy of Earth elements is th ...
... rocket propulsion, methods of transformation of electric energy into mechanical energy can be generally divided into thermal, electrostatic and electromagnetic processes. Said processes have given names to electric motors of rockets: electro-thermal, ionic, plasma [1]. Energy of Earth elements is th ...
Unit 9: Energy, Work, and Power
... PS-6.1: Explain how the law of conservation of energy applies to the transformation of various forms of energy (including mechanical energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, light energy, sound energy, and thermal energy). PS-6.2: Explain the factors that determine potential and kinetic energy an ...
... PS-6.1: Explain how the law of conservation of energy applies to the transformation of various forms of energy (including mechanical energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, light energy, sound energy, and thermal energy). PS-6.2: Explain the factors that determine potential and kinetic energy an ...
File
... You may not know it, but energy is all around us. In fact you are made of energy. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. In order to do any work you need energy. Electronics use energy, cars use energy and even your body uses energy. The Bulldozer uses energy to move the dirt. ...
... You may not know it, but energy is all around us. In fact you are made of energy. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. In order to do any work you need energy. Electronics use energy, cars use energy and even your body uses energy. The Bulldozer uses energy to move the dirt. ...
Name: Date: Subject: Energy Objectives Objective 1: ASWBAT to
... You may not know it, but energy is all around us. In fact you are made of energy. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. In order to do any work you need energy. Electronics use energy, cars use energy and even your body uses energy. The Bulldozer uses energy to move the dirt. ...
... You may not know it, but energy is all around us. In fact you are made of energy. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. In order to do any work you need energy. Electronics use energy, cars use energy and even your body uses energy. The Bulldozer uses energy to move the dirt. ...
Unit Plan: Energy
... 1. Energy exists in various forms and can be transformed from one form to another (Law of Conservation of Energy). 2. The mechanical energy of a system is the sum of its kinetic and potential. 3. Kinetic and potential energy are descriptions of the forms that energy can have. 4. Work is the result o ...
... 1. Energy exists in various forms and can be transformed from one form to another (Law of Conservation of Energy). 2. The mechanical energy of a system is the sum of its kinetic and potential. 3. Kinetic and potential energy are descriptions of the forms that energy can have. 4. Work is the result o ...
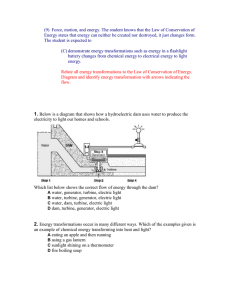
(9) Force, motion, and energy - 2010
... C The thermal energy stored in the stone floor released too much heat. D The heat from all the people visiting the greenhouse raised the temperature. ...
... C The thermal energy stored in the stone floor released too much heat. D The heat from all the people visiting the greenhouse raised the temperature. ...
is energy
... the US come from specific substances and technologies • The chart at the right represents a breakdown of energy sources in the United States as of 2010 • What percentage of the total resources are finite (will run out)? ...
... the US come from specific substances and technologies • The chart at the right represents a breakdown of energy sources in the United States as of 2010 • What percentage of the total resources are finite (will run out)? ...
LESSON 3: AN ENERGY MIX Renewable And Nonrenewable
... Utilizing the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s Energy Kids website students will be able to define and categorize sources of renewable and nonrenewable energy as well as present day uses for the various types of energy. Renewable-identified as sources of energy that are “naturally replenishe ...
... Utilizing the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s Energy Kids website students will be able to define and categorize sources of renewable and nonrenewable energy as well as present day uses for the various types of energy. Renewable-identified as sources of energy that are “naturally replenishe ...
Conservation of Energy
... Heat and work are the methods of transferring energy for a system in thermal equilibrium Q represents the net heat transfer—it is the sum of all heat transfers into and out of the system. Q is positive for net heat transfer into the system. W is the total work done on and by the system. W is positiv ...
... Heat and work are the methods of transferring energy for a system in thermal equilibrium Q represents the net heat transfer—it is the sum of all heat transfers into and out of the system. Q is positive for net heat transfer into the system. W is the total work done on and by the system. W is positiv ...
Print-ready released items - Iowa Testing Programs
... The roller coaster car’s potential energy at Position B will be closest to which of the following? A Half the roller coaster car’s potential energy at Position A CORRECT: At Position B, the roller coaster car will be almost at half the height it is at Position A. Therefore, the roller coaster car's ...
... The roller coaster car’s potential energy at Position B will be closest to which of the following? A Half the roller coaster car’s potential energy at Position A CORRECT: At Position B, the roller coaster car will be almost at half the height it is at Position A. Therefore, the roller coaster car's ...
Forms of Energy
... are constantly in motion, they have kinetic energy. The faster the particles move, the more kinetic energy they have. These particles are arranged in specific ways in different objects. Therefore, they also have potential energy. The total potential and kinetic energy of the particles in an object i ...
... are constantly in motion, they have kinetic energy. The faster the particles move, the more kinetic energy they have. These particles are arranged in specific ways in different objects. Therefore, they also have potential energy. The total potential and kinetic energy of the particles in an object i ...
Energy:
... If an object or organism does work (exerts a force over a distance to move an object) the object or organism uses energy. ...
... If an object or organism does work (exerts a force over a distance to move an object) the object or organism uses energy. ...
Lesson 3: An Energy Mix Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources
... Utilizing the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s Energy Kids website students will be able to define and categorize sources of renewable and nonrenewable energy as well as present day uses for the various types of energy. Renewable-identified as sources of energy that are “naturally replenishe ...
... Utilizing the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s Energy Kids website students will be able to define and categorize sources of renewable and nonrenewable energy as well as present day uses for the various types of energy. Renewable-identified as sources of energy that are “naturally replenishe ...
Regenerative brake

A regenerative brake is an energy recovery mechanism which slows a vehicle or object by converting its kinetic energy into a form which can be either used immediately or stored until needed. This contrasts with conventional braking systems, where the excess kinetic energy is converted to heat by friction in the brakes and therefore wasted. In addition to improving the overall efficiency of the vehicle, regeneration can also greatly extend the life of the braking system as its parts do not wear as quickly.