Chapter 1 * Energy and Matter
... energy may also be changed to chemical energy For example, the burning of fuel is a chemical change that transforms chemical energy and releases it as thermal energy and electromagnetic energy When you push a bike up a hill, chemical energy from foods you ate is transformed into the kinetic ener ...
... energy may also be changed to chemical energy For example, the burning of fuel is a chemical change that transforms chemical energy and releases it as thermal energy and electromagnetic energy When you push a bike up a hill, chemical energy from foods you ate is transformed into the kinetic ener ...
Chapter 15
... • ex. Coal, Petroleum (oil), natural gas, nuclear, etc. • usually produce pollution ...
... • ex. Coal, Petroleum (oil), natural gas, nuclear, etc. • usually produce pollution ...
Energy:
... Calories are a unit of measurement of food energy. They measure the amount of potential heat energy contained in the chemical bonds of a food. People need a certain amount of calories per day. For the average teenage girl, the recommended daily allowance is 2200 calories. The average teenage boy nee ...
... Calories are a unit of measurement of food energy. They measure the amount of potential heat energy contained in the chemical bonds of a food. People need a certain amount of calories per day. For the average teenage girl, the recommended daily allowance is 2200 calories. The average teenage boy nee ...
How the Body Obtains and Uses Energy PPT
... Calories are a unit of measurement of food energy. They measure the amount of potential heat energy contained in the chemical bonds of a food. People need a certain amount of calories per day. For the average teenage girl, the recommended daily allowance is 2200 calories. The average teenage boy nee ...
... Calories are a unit of measurement of food energy. They measure the amount of potential heat energy contained in the chemical bonds of a food. People need a certain amount of calories per day. For the average teenage girl, the recommended daily allowance is 2200 calories. The average teenage boy nee ...
Work and Energy
... 5.3 Energy Transformations Energy transformations occur between different types of energy. — radiant energy — electrical energy — chemical energy — nuclear energy ...
... 5.3 Energy Transformations Energy transformations occur between different types of energy. — radiant energy — electrical energy — chemical energy — nuclear energy ...
Name:
... Systems In a closed, isolated system, objects do not the system. Under these conditions, the law of ...
... Systems In a closed, isolated system, objects do not the system. Under these conditions, the law of ...
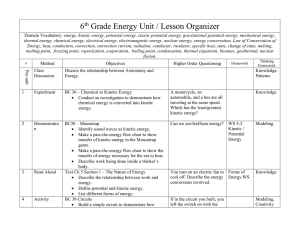
6th Grade Energy Unit / Lesson Organizer Domain Vocabulary
... Draw a diagram of a solar cooker. Begin a chart on energy sources. BC 67 Heat Absorbency Conduct an investigation to see if heat is absorbed by dark colors more than light colors. Graph the results of the investigation. Describe how a solar collector works. Trace the transfer of energy i ...
... Draw a diagram of a solar cooker. Begin a chart on energy sources. BC 67 Heat Absorbency Conduct an investigation to see if heat is absorbed by dark colors more than light colors. Graph the results of the investigation. Describe how a solar collector works. Trace the transfer of energy i ...
What is Energy? - Year 8 Science @SMCC
... you jump on a trampoline – what pushes you into the air. When you land on the mat, it moves down stretching the springs and storing energy called elastic potential energy. As the stretched springs return to their original size and shape, they release their stored energy. What other objects mig ...
... you jump on a trampoline – what pushes you into the air. When you land on the mat, it moves down stretching the springs and storing energy called elastic potential energy. As the stretched springs return to their original size and shape, they release their stored energy. What other objects mig ...
Energy: - Weebly
... The energy of motion is called kinetic energy. The faster an object moves, the more kinetic energy it has. The greater the mass of a moving object, the more kinetic energy it has. Kinetic energy depends on both mass and velocity. ...
... The energy of motion is called kinetic energy. The faster an object moves, the more kinetic energy it has. The greater the mass of a moving object, the more kinetic energy it has. Kinetic energy depends on both mass and velocity. ...
Physics Demonstration
... The light bulb not turned on Water stored behind a dam at a hydroelectric plant has potential energy. ...
... The light bulb not turned on Water stored behind a dam at a hydroelectric plant has potential energy. ...
notes on "Kinetic vs. Potential Energy."
... EX: fuel burned in a car, furnace, or power plant Different types of fuels have different kinds of molecules so some fuels produce more energy than others based upon their molecular composition. The chemical fuel for the human body is food. Some foods give your body more energy than others. When peo ...
... EX: fuel burned in a car, furnace, or power plant Different types of fuels have different kinds of molecules so some fuels produce more energy than others based upon their molecular composition. The chemical fuel for the human body is food. Some foods give your body more energy than others. When peo ...
Chapter 1.2 Basics of Energy and its various forms Part
... The conduction of heat takes places, when two bodies are in contact with one another. If one body is at a higher temperature than the other, the motion of the molecules in the hotter body will agitate the molecules at the point of contact in the cooler body and consequently result in increase in tem ...
... The conduction of heat takes places, when two bodies are in contact with one another. If one body is at a higher temperature than the other, the motion of the molecules in the hotter body will agitate the molecules at the point of contact in the cooler body and consequently result in increase in tem ...
P1 Conservation and Dissipation of Energy Grade Descriptor
... I can use the principle of conservation of energy and forces to explain why objects become heated by frictional forces. I can apply the equation for work done in a wide range of contexts. I can evaluate in detail an experiment to measure work done, explaining why there is variation in the measuremen ...
... I can use the principle of conservation of energy and forces to explain why objects become heated by frictional forces. I can apply the equation for work done in a wide range of contexts. I can evaluate in detail an experiment to measure work done, explaining why there is variation in the measuremen ...
Energy - nnhschemistry
... Energy can be sorted into one of two categories – either – kinetic (the “doing the work” phase) or – potential (the getting ready to do work or the “stored” phase) ...
... Energy can be sorted into one of two categories – either – kinetic (the “doing the work” phase) or – potential (the getting ready to do work or the “stored” phase) ...
Name: Chapter 14: Changing Forms of Energy Words to Know
... Potential energy (or ‘stored’ energy) is energy that is not causing any changes NOW, but could cause changes in the FUTURE There are several different kinds of potential energy The object’s position determines its type of potential energy Potential energy often turns into kinetic energy- when the ob ...
... Potential energy (or ‘stored’ energy) is energy that is not causing any changes NOW, but could cause changes in the FUTURE There are several different kinds of potential energy The object’s position determines its type of potential energy Potential energy often turns into kinetic energy- when the ob ...
CHAPTER 3 Introduction to the Quantum Theory of Solids
... 5.7 x 10-9 eV, which is orders of magnitude larger than the change in energy of 10-19 eV between energy states in the allowed energy band. This example serves to demonstrate that a difference in adjacent energy states of 10-19 eV is indeed very small, so that the discrete energies within an allowed ...
... 5.7 x 10-9 eV, which is orders of magnitude larger than the change in energy of 10-19 eV between energy states in the allowed energy band. This example serves to demonstrate that a difference in adjacent energy states of 10-19 eV is indeed very small, so that the discrete energies within an allowed ...
Calculating potential and kinetic energy
... The specific heat capacity (or just specific heat) of a material is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram (g) of the material 1 degree Celsius (°C). It takes 4.18 joules to raise the temperature of 1 g of water 1°C (at a temperature of 25°C). One kilojoule (kJ) eq ...
... The specific heat capacity (or just specific heat) of a material is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram (g) of the material 1 degree Celsius (°C). It takes 4.18 joules to raise the temperature of 1 g of water 1°C (at a temperature of 25°C). One kilojoule (kJ) eq ...
Name: Period: _____ Date
... I. open system J. power K. radiant energy L. thermal energy M. Watts N. work O. energy ...
... I. open system J. power K. radiant energy L. thermal energy M. Watts N. work O. energy ...
Choose the best answer for each question: A circuit in which the
... 28. Objects that have potential energy do not use their energy until they move. That is why it is called “potential” energy. 29. Energy appears in different forms, such as motion and heat. 30. Energy cannot travel in different forms, such as light, sound or electricity. 31. Energy can be transferred ...
... 28. Objects that have potential energy do not use their energy until they move. That is why it is called “potential” energy. 29. Energy appears in different forms, such as motion and heat. 30. Energy cannot travel in different forms, such as light, sound or electricity. 31. Energy can be transferred ...
Focus Plan - Texarkana Independent School District
... 11.1 The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, conducts field and laboratory investigations using safe, environmentally appropriate, and ethical practices. The student is expected to: (A) demonstrate safe practices during field and laboratory investigations 11.2 The student uses scientifi ...
... 11.1 The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, conducts field and laboratory investigations using safe, environmentally appropriate, and ethical practices. The student is expected to: (A) demonstrate safe practices during field and laboratory investigations 11.2 The student uses scientifi ...
Let`s Convert Energy
... Energy is all around us, all of the time. It may, however, be known by different names depending on its source. Light, whether it comes from the sun or a light bulb, is radiant energy. Gravitational energy is the energy an object has due to its position above the ground. Food and fuel contain chemic ...
... Energy is all around us, all of the time. It may, however, be known by different names depending on its source. Light, whether it comes from the sun or a light bulb, is radiant energy. Gravitational energy is the energy an object has due to its position above the ground. Food and fuel contain chemic ...
Created with Sketch. Calculating potential and kinetic energy
... The specific heat capacity (or just specific heat) of a material is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram (g) of the material 1 degree Celsius (°C). It takes 4.18 joules to raise the temperature of 1 g of water 1°C (at a temperature of 25°C). One kilojoule (kJ) eq ...
... The specific heat capacity (or just specific heat) of a material is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram (g) of the material 1 degree Celsius (°C). It takes 4.18 joules to raise the temperature of 1 g of water 1°C (at a temperature of 25°C). One kilojoule (kJ) eq ...