Unit 9 Test Review – Work and Energy
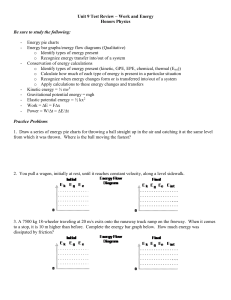
... 2. You pull a wagon, initially at rest, until it reaches constant velocity, along a level sidewalk. ...
... 2. You pull a wagon, initially at rest, until it reaches constant velocity, along a level sidewalk. ...
Energy Notes
... Potential Energy - Energy an object has because of its postion or shape. Kinetic Energy - Energy an object has because it is moving. Heat Energy - The energy related to the temperature of a substance. Chemical Energy - Energy stored in chemical bonds. Electromagnetic Energy - Energy which can travel ...
... Potential Energy - Energy an object has because of its postion or shape. Kinetic Energy - Energy an object has because it is moving. Heat Energy - The energy related to the temperature of a substance. Chemical Energy - Energy stored in chemical bonds. Electromagnetic Energy - Energy which can travel ...
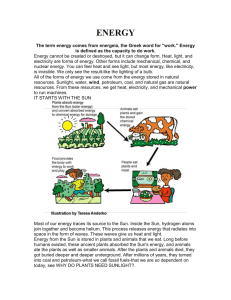
ENERGY
... Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change form. Heat, light, and electricity are forms of energy. Other forms include mechanical, chemical, and nuclear energy. You can feel heat and see light, but most energy, like electricity, is invisible. We only see the result-like the lighting of ...
... Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change form. Heat, light, and electricity are forms of energy. Other forms include mechanical, chemical, and nuclear energy. You can feel heat and see light, but most energy, like electricity, is invisible. We only see the result-like the lighting of ...
Vocabulary for Energy Unit
... Chemical energy – energy stored in between smaller particles holding them together to make larger ones, i.e. “food” energy Conduction - a way to transfer energy directly from one object to another because the particles bump into each other, particles do not change location they vibrate in place tran ...
... Chemical energy – energy stored in between smaller particles holding them together to make larger ones, i.e. “food” energy Conduction - a way to transfer energy directly from one object to another because the particles bump into each other, particles do not change location they vibrate in place tran ...
2nd 6 Weeks - Forms of Energy, Circuits and Force
... Electricity - a form of energy that is produced when electrons move from one place to another ...
... Electricity - a form of energy that is produced when electrons move from one place to another ...
Technology Chapter 27: Energy: The Foundation of Technology
... Chemical energy: energy stored within a chemical substance. Electrical energy: energy associated with electrons moving along a conductor. Energy: the ability to do work. Exhaustible energy resources: materials that cannot be replaced. Fission: the process of splitting atoms to release vast quantitie ...
... Chemical energy: energy stored within a chemical substance. Electrical energy: energy associated with electrons moving along a conductor. Energy: the ability to do work. Exhaustible energy resources: materials that cannot be replaced. Fission: the process of splitting atoms to release vast quantitie ...
Energy - Wsfcs
... energy is moving electric charges that produce electricity or electrical energy. This is found in batteries, or power lines used to run such devices as computers , radios or lights. ...
... energy is moving electric charges that produce electricity or electrical energy. This is found in batteries, or power lines used to run such devices as computers , radios or lights. ...
Work, Power, and Machines
... • objects can have energy (can do work) because of their position or make up – a stretched rubber band – a can of gasoline – gravitational; an object that is held up and can fall ...
... • objects can have energy (can do work) because of their position or make up – a stretched rubber band – a can of gasoline – gravitational; an object that is held up and can fall ...
File
... ability to do something is produced in an object. For example, an object which can affect other objects because of its movement is said to have kinetic energy. (Kinetic is a word from Greek which means movement) An object which can affect other objects because it gives off light is said to have ligh ...
... ability to do something is produced in an object. For example, an object which can affect other objects because of its movement is said to have kinetic energy. (Kinetic is a word from Greek which means movement) An object which can affect other objects because it gives off light is said to have ligh ...
Law of the Conservation of Energy
... batteries and gasoline. All of these types of energy interact with one another. The chemical energy from food can be turned into kinetic energy when you start running around or into potential energy when you climb up to the top of the slide and wait before sliding down. Energy cannot be created or d ...
... batteries and gasoline. All of these types of energy interact with one another. The chemical energy from food can be turned into kinetic energy when you start running around or into potential energy when you climb up to the top of the slide and wait before sliding down. Energy cannot be created or d ...
Energy - Griffin School District
... Nervous System (human or other animal) Plumbing System (house) Transportation System (state or country) Operating System (computer) Electrical System (car) Solar System (astronomy) ...
... Nervous System (human or other animal) Plumbing System (house) Transportation System (state or country) Operating System (computer) Electrical System (car) Solar System (astronomy) ...
What is Energy?
... 4. What are some forms of energy? Potential Chemical – batteries, fossil fuels, food. Mechanical – compressed springs, stretched rubber bands Nuclear – splitting/combining of atoms, energy released from an atom Gravitational – energy of position ...
... 4. What are some forms of energy? Potential Chemical – batteries, fossil fuels, food. Mechanical – compressed springs, stretched rubber bands Nuclear – splitting/combining of atoms, energy released from an atom Gravitational – energy of position ...
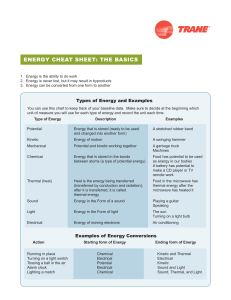
energy CheAt Sheet: the bASiCS
... Types of Energy and Examples You can use this chart to keep track of your baseline data. Make sure to decide at the beginning which unit of measure you will use for each type of energy and record the unit each time. ...
... Types of Energy and Examples You can use this chart to keep track of your baseline data. Make sure to decide at the beginning which unit of measure you will use for each type of energy and record the unit each time. ...
ENERGY and Energy Transformations
... accomplish a task Energy Transformation - the change of energy from one form to another ...
... accomplish a task Energy Transformation - the change of energy from one form to another ...
Weekly Overview - School District 27J
... Briefly describe the Law of Conservation of Mass (you are more than welcome to use your notes and textbook to help you). Based on your description, explain what you believe the Law of Conservation of Energy is. Support your answer with a real world example. ...
... Briefly describe the Law of Conservation of Mass (you are more than welcome to use your notes and textbook to help you). Based on your description, explain what you believe the Law of Conservation of Energy is. Support your answer with a real world example. ...
Energy - Gyanpedia
... to the positively charged one.. In any continuous system of conductors, electrons will flow from the point of lowest potential to the point of highest potential. A system of this kind is called an electric circuit. ...
... to the positively charged one.. In any continuous system of conductors, electrons will flow from the point of lowest potential to the point of highest potential. A system of this kind is called an electric circuit. ...
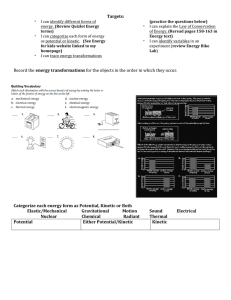
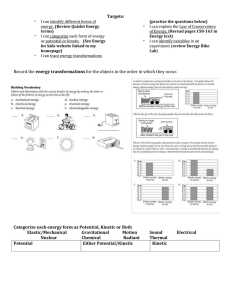
Targets: * I can identify different forms of energy. (Review Quizlet
... Categorize each energy form as Potential, Kinetic or Both ...
... Categorize each energy form as Potential, Kinetic or Both ...
Name: Period:______ Date:______ Infinite Potential Forms of
... 9. How fast do electromagnetic waves travel? Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light. 10. What types of properties do electromagnetic waves have? Do they need a medium through which to travel? Electromagnetic waves have electric and magnetic properties. They do not need a medium. 11. What ...
... 9. How fast do electromagnetic waves travel? Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light. 10. What types of properties do electromagnetic waves have? Do they need a medium through which to travel? Electromagnetic waves have electric and magnetic properties. They do not need a medium. 11. What ...
Energy
... Types of Energy 1) kinetic- energy of an object in motion 2) potential- the energy of an object’s position or shape. ...
... Types of Energy 1) kinetic- energy of an object in motion 2) potential- the energy of an object’s position or shape. ...
forms of energy worksheet
... 5. The scientific rule that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed is called the Law of _________________. 7. The energy of position – such as a rock on a hill is ____________________ energy. 8. The movement of objects and substances from place to place is _________________ energy. 10. En ...
... 5. The scientific rule that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed is called the Law of _________________. 7. The energy of position – such as a rock on a hill is ____________________ energy. 8. The movement of objects and substances from place to place is _________________ energy. 10. En ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant
... Not all the energy going into a system is being used to do the intended job A tungsten filament light bulb is a worrying example. For a typical 100w bulb about 10w of useful light energy the rest is lost as unwanted heat. Other examples include: •Car engine (60%) ...
... Not all the energy going into a system is being used to do the intended job A tungsten filament light bulb is a worrying example. For a typical 100w bulb about 10w of useful light energy the rest is lost as unwanted heat. Other examples include: •Car engine (60%) ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant
... Not all the energy going into a system is being used to do the intended job A tungsten filament light bulb is a worrying example. For a typical 100w bulb about 10w of useful light energy the rest is lost as unwanted heat. Other examples include: •Car engine (60%) ...
... Not all the energy going into a system is being used to do the intended job A tungsten filament light bulb is a worrying example. For a typical 100w bulb about 10w of useful light energy the rest is lost as unwanted heat. Other examples include: •Car engine (60%) ...
L29_AS2_2008_09_KE_GPE_Efficiency
... Not all the energy going into a system is being used to do the intended job A tungsten filament light bulb is a worrying example. For a typical 100w bulb about 10w of useful light energy the rest is lost as unwanted heat. Other examples include: •Car engine (60%) ...
... Not all the energy going into a system is being used to do the intended job A tungsten filament light bulb is a worrying example. For a typical 100w bulb about 10w of useful light energy the rest is lost as unwanted heat. Other examples include: •Car engine (60%) ...