Atomic Force Microscope (AFM)
... The name of the technique arises from the quantum mechanical tunnelling-type mechanism by which the electrons can move between the tip and substrate. Quantum mechanical tunnelling permits particles to tunnel through a potential barrier which they could not surmount according to the classical laws o ...
... The name of the technique arises from the quantum mechanical tunnelling-type mechanism by which the electrons can move between the tip and substrate. Quantum mechanical tunnelling permits particles to tunnel through a potential barrier which they could not surmount according to the classical laws o ...
Chapter 29 MEMS
... Films are used widely in microelectronicdevice fabrication, especially insulating and conducting films. Epitaxy - is the growth of a vapor deposit, epitaxy or electrodeposit happens when the crystal orientation of the deposit is related directly to the crystal orientation in the crystalline substrat ...
... Films are used widely in microelectronicdevice fabrication, especially insulating and conducting films. Epitaxy - is the growth of a vapor deposit, epitaxy or electrodeposit happens when the crystal orientation of the deposit is related directly to the crystal orientation in the crystalline substrat ...
Course Descriptions
... renewable energy sources. Fossil fuel supplies and climate change are seemingly intimately related. On the other hand the global community is actively developing renewable energy sources for replacing fossil fuels and minimizing the impact on climate change. Materials science can be a key enabler fo ...
... renewable energy sources. Fossil fuel supplies and climate change are seemingly intimately related. On the other hand the global community is actively developing renewable energy sources for replacing fossil fuels and minimizing the impact on climate change. Materials science can be a key enabler fo ...
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) ISSN(e) : www.iosrjournals.org
... approaches the nanoscale and as the percentage of atoms at the surface of a material becomes significant. In order to explore novel physical properties & phenomenon, real size potential applications of nanostructure & nanomaterial’s, the ability to fabricate & process nanomaterials is the first corn ...
... approaches the nanoscale and as the percentage of atoms at the surface of a material becomes significant. In order to explore novel physical properties & phenomenon, real size potential applications of nanostructure & nanomaterial’s, the ability to fabricate & process nanomaterials is the first corn ...
Units and Properties - Instructor Guide - Final
... 1.1 Define the following properties: specific volume, density, mass, weight, intensive, and extensive. 1.2 Define the thermodynamic properties of temperature and convert between the Fahrenheit, Celsius, Kelvin, and Rankine scales. ...
... 1.1 Define the following properties: specific volume, density, mass, weight, intensive, and extensive. 1.2 Define the thermodynamic properties of temperature and convert between the Fahrenheit, Celsius, Kelvin, and Rankine scales. ...
Diamond-like Carbon Thin Film with Controlled Zeta
... If the absorption is purely nonlinear, the laser intensity required to induce a permanent change will depend nonlinearly on the bandgap of the substrate material. Because the bandgap energy varies from material to material, the nonlinear absorption would vary a lot. However, the threshold intensity ...
... If the absorption is purely nonlinear, the laser intensity required to induce a permanent change will depend nonlinearly on the bandgap of the substrate material. Because the bandgap energy varies from material to material, the nonlinear absorption would vary a lot. However, the threshold intensity ...
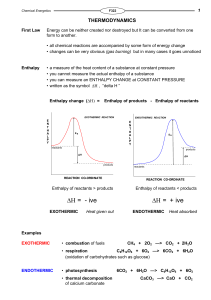
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
... 5) Record temp of water with metal in it (that temp is the final temp for both the metal & water) 6) Calculate the sh of the metal ...
... 5) Record temp of water with metal in it (that temp is the final temp for both the metal & water) 6) Calculate the sh of the metal ...
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
... A bowler lifts a 5.4-kg (12-lb) bowling ball from ground level to a height of 1.6 m (5.2 ft) and then drops it. (a) What happens to the potential energy of the ball as it is raised? (b) What quantity of work, in J, is used to raise the ball? (c) After the ball is dropped, it gains kinetic energy. If ...
... A bowler lifts a 5.4-kg (12-lb) bowling ball from ground level to a height of 1.6 m (5.2 ft) and then drops it. (a) What happens to the potential energy of the ball as it is raised? (b) What quantity of work, in J, is used to raise the ball? (c) After the ball is dropped, it gains kinetic energy. If ...
Lecture 4 (Dec.9)
... 14.1: Molecular Mass, the Mole and Avogadro’s Number. 14.2: The Ideal Gas Law. 14.3: Kinetic Theory of Gases. ...
... 14.1: Molecular Mass, the Mole and Avogadro’s Number. 14.2: The Ideal Gas Law. 14.3: Kinetic Theory of Gases. ...