Why does the cloud spin? The Coriolis effect
... of cloud, while cloud orbits center of galaxy. Particles on outside rotate more slowly about galactic center Stars on inside rotate more rapidly Collisions occur Faster particles will win! Disk begins to swirl! ...
... of cloud, while cloud orbits center of galaxy. Particles on outside rotate more slowly about galactic center Stars on inside rotate more rapidly Collisions occur Faster particles will win! Disk begins to swirl! ...
The Solar System
... The AU and the size of Solar System • Defined as the average distance between the Earth and the Sun • It is approximately 150 million km (93 ...
... The AU and the size of Solar System • Defined as the average distance between the Earth and the Sun • It is approximately 150 million km (93 ...
Terrestrial Planets
... the Earth’s diameter) • Comets are icy bodies about 10 km or less across that can grow very long tails of gas and dust as they near the Sun and are vaporized by its heat ...
... the Earth’s diameter) • Comets are icy bodies about 10 km or less across that can grow very long tails of gas and dust as they near the Sun and are vaporized by its heat ...
Slides
... astrophysical Observatory in 1974, continue for decades. Doppler measurements in 2011-2014 have confirmed the mysterious to astronomy phenomenon of the pulsation of the photosphere with a period 9597.929(15) s that preserved initial phase for 41 years. The nature of the pulsation is not established. ...
... astrophysical Observatory in 1974, continue for decades. Doppler measurements in 2011-2014 have confirmed the mysterious to astronomy phenomenon of the pulsation of the photosphere with a period 9597.929(15) s that preserved initial phase for 41 years. The nature of the pulsation is not established. ...
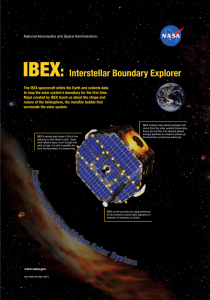
Exploring the Edge of the Solar System
... In the late 1970s and 1980s, the Voyager spacecraft expanded our knowledge of the outer Solar System. Voyagers 1 and 2 both explored the planets Jupiter and Saturn, and Voyager 2 explored Uranus and Neptune. After their planetary observations, both spacecraft continued outward in different direction ...
... In the late 1970s and 1980s, the Voyager spacecraft expanded our knowledge of the outer Solar System. Voyagers 1 and 2 both explored the planets Jupiter and Saturn, and Voyager 2 explored Uranus and Neptune. After their planetary observations, both spacecraft continued outward in different direction ...
Does the Sun rotate?
... and release huge amounts of X-rays. Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) – twisted magnetic field lines relax and release huge amounts of plasma (up to 4 million mph). ...
... and release huge amounts of X-rays. Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) – twisted magnetic field lines relax and release huge amounts of plasma (up to 4 million mph). ...
What can we learn by comparing the planets to one another?
... from the distance between the two locations on Earth ...
... from the distance between the two locations on Earth ...
Chapter 17 - Cloudfront.net
... contraction. At this point the Sun became a fully fledged star. From the remaining cloud of gas and dust (the "solar nebula"), the various planets formed. They are believed to have formed by accretion: the planets began as dust grains in orbit around the central protostar; then gathered by direct co ...
... contraction. At this point the Sun became a fully fledged star. From the remaining cloud of gas and dust (the "solar nebula"), the various planets formed. They are believed to have formed by accretion: the planets began as dust grains in orbit around the central protostar; then gathered by direct co ...
Rotation and Revolution - Environmental Science Institute
... Sun. This activity gives a visualization of how the Earth revolves around the Sun. One of Earth’s revolutions around the Sun takes about three hundred and sixty five days. One full rotation of the Earth is equal to approximately twenty-four hours. We base our time scale on Earth’s rotation. The mode ...
... Sun. This activity gives a visualization of how the Earth revolves around the Sun. One of Earth’s revolutions around the Sun takes about three hundred and sixty five days. One full rotation of the Earth is equal to approximately twenty-four hours. We base our time scale on Earth’s rotation. The mode ...
Formation of the Solar System
... rotation increased, the center of the disk flattened out and matter became more concentrated in the center of the disk, where the Sun eventually formed. The growth of the planets began as solid bits of matter began to collide and clump together through a process called accretion. The colliding matte ...
... rotation increased, the center of the disk flattened out and matter became more concentrated in the center of the disk, where the Sun eventually formed. The growth of the planets began as solid bits of matter began to collide and clump together through a process called accretion. The colliding matte ...
8 The Planet`s Motions
... • Sun moves eastward through ≈ 1 zodiac constellation per month (1° per day) • The moon moves eastward about 12° per day ...
... • Sun moves eastward through ≈ 1 zodiac constellation per month (1° per day) • The moon moves eastward about 12° per day ...
Forces and MotionTest
... 10) Which of the following is a result of gravity? a. Formation of a galaxy b. Formation of a solar system c. Formation of a planet d. All of the above are correct 11) Increasing the amount of solar energy that reaches Earth’s surface could cause which of the following? a. More earthquakes b. Warme ...
... 10) Which of the following is a result of gravity? a. Formation of a galaxy b. Formation of a solar system c. Formation of a planet d. All of the above are correct 11) Increasing the amount of solar energy that reaches Earth’s surface could cause which of the following? a. More earthquakes b. Warme ...
Jack - WhatsOutThere
... The Sun is the centre of the solar system, all the planets orbit around the Sun, its powerful gravitational pull holds all the planets in its orbit without this all the planets would float away into space. ...
... The Sun is the centre of the solar system, all the planets orbit around the Sun, its powerful gravitational pull holds all the planets in its orbit without this all the planets would float away into space. ...
Planet Beads - RAFT Colorado
... The Content Behind the Activity The Solar System contains 1 star (the Sun), 8 planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune), 10’s of satellites that orbit the planets, dwarf planets (Pluto, Ceres, and Eris), 1000’s of asteroids that orbit the Sun, and billions of comets. As ...
... The Content Behind the Activity The Solar System contains 1 star (the Sun), 8 planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune), 10’s of satellites that orbit the planets, dwarf planets (Pluto, Ceres, and Eris), 1000’s of asteroids that orbit the Sun, and billions of comets. As ...
Solar System Webquest
... This site will also link back to the StarChild site which you can also use. Heavenly Body Composition (what is it made of) Size ...
... This site will also link back to the StarChild site which you can also use. Heavenly Body Composition (what is it made of) Size ...
File - YEAR 11 EBSS PHYSICS DETAILED STUDIES
... Our best-known star It wasn’t until after Galileo and Newton that stars were Sun-like objects, a long way away. A good way to learn more about distant stars, was to learn more about the star closest to us, the sun. Galileo observed sunspots on the surface of the sun, this lead to the discovery th ...
... Our best-known star It wasn’t until after Galileo and Newton that stars were Sun-like objects, a long way away. A good way to learn more about distant stars, was to learn more about the star closest to us, the sun. Galileo observed sunspots on the surface of the sun, this lead to the discovery th ...
Lesson 2 | The Sun and Other Stars
... Key Concept How are stars layered? Directions: Use the diagram to respond to each statement on the lines provided. ...
... Key Concept How are stars layered? Directions: Use the diagram to respond to each statement on the lines provided. ...
Chart_set_4
... Solar system formed out of a "whirlpool" in a "universal fluid". Planets formed out of eddies in the fluid. Sun formed at center. Planets in cooler regions. Cloud called "Solar Nebula". This is pre-Newton and modern science. But basic idea correct, and the theory evolved as science advanced, as we'l ...
... Solar system formed out of a "whirlpool" in a "universal fluid". Planets formed out of eddies in the fluid. Sun formed at center. Planets in cooler regions. Cloud called "Solar Nebula". This is pre-Newton and modern science. But basic idea correct, and the theory evolved as science advanced, as we'l ...
Solarnet III / HELAS VII / SpaceInn 2015 funded - science
... • Fostering scientific exchange and synergies between these two areas of astrophysics • Reviewing both areas: ...
... • Fostering scientific exchange and synergies between these two areas of astrophysics • Reviewing both areas: ...
2016-2017 Sixth Grade Resource Guide: Quarter 2
... The Sun: http://video.nationalgeographic.com/video/101SWBAT: Identify that the sun is the central and largest videos/sun-101-sci Student Reading Delta Science body in the solar system & describe how the sun generates Content Reader-Earth, Moon and Sun energy. Compare and contrast the characteristics ...
... The Sun: http://video.nationalgeographic.com/video/101SWBAT: Identify that the sun is the central and largest videos/sun-101-sci Student Reading Delta Science body in the solar system & describe how the sun generates Content Reader-Earth, Moon and Sun energy. Compare and contrast the characteristics ...
File
... b. much closer to Earth than the planets c. just outside our solar system, whereas planets are inside d. moving in and out of the solar system over time ...
... b. much closer to Earth than the planets c. just outside our solar system, whereas planets are inside d. moving in and out of the solar system over time ...
Acquaintance with solar system. By Edgaras Montvila 6D
... of shining stars, right? brighter than the others ...
... of shining stars, right? brighter than the others ...
Heliosphere

The heliosphere is the bubble-like region of space dominated by the Sun, which extends far beyond the orbit of Pluto. Plasma ""blown"" out from the Sun, known as the solar wind, creates and maintains this bubble against the outside pressure of the interstellar medium, the hydrogen and helium gas that permeates the Milky Way Galaxy. The solar wind flows outward from the Sun until encountering the termination shock, where motion slows abruptly. The Voyager spacecraft have actively explored the outer reaches of the heliosphere, passing through the shock and entering the heliosheath, a transitional region which is in turn bounded by the outermost edge of the heliosphere, called the heliopause. The overall shape of the heliosphere is controlled by the interstellar medium, through which it is traveling, as well as the Sun, and does not appear to be perfectly spherical. The limited data available and unexplored nature of these structures have resulted in many theories.On September 12, 2013, NASA announced that Voyager 1 had exited the heliosphere on August 25, 2012, when it measured a sudden increase in plasma density of about forty times. Because the heliopause marks one boundary between the Sun's solar wind and the rest of the galaxy, a spacecraft such as Voyager 1 which has departed the heliosphere can be said to have reached interstellar space.