STUDY GUIDE test Oct 7th
... future of our universe look like? 2. Galaxies-four main shapes, what is our galaxy named and what shape is it? Be able to put space objects in order from biggest to smallest (use the galactic address info) 3. Stars-What is a star? How do they make light and heat? How are stars classified? What are c ...
... future of our universe look like? 2. Galaxies-four main shapes, what is our galaxy named and what shape is it? Be able to put space objects in order from biggest to smallest (use the galactic address info) 3. Stars-What is a star? How do they make light and heat? How are stars classified? What are c ...
Benchmark Number:
... A celestial body that appears as a fuzzy head usually surrounding a bright nucleus, that has a usually highly eccentric orbit, that consists primarily of ice and dust, and that often develops one or more long tails when near the sun. ...
... A celestial body that appears as a fuzzy head usually surrounding a bright nucleus, that has a usually highly eccentric orbit, that consists primarily of ice and dust, and that often develops one or more long tails when near the sun. ...
Study GuideCh6 with page refs
... 15. Most of the energy that the Sun produces is generated in its core. WB 132/ p. 300 16. Two main gases that make up the Sun are hydrogen and helium. WB 131/ p. 302 17. Solar energy is produced by fusion. p. 302 in text ONLY 18. The Sun is NOT mostly rock at its core. By deduction WB 132/ p. 300 19 ...
... 15. Most of the energy that the Sun produces is generated in its core. WB 132/ p. 300 16. Two main gases that make up the Sun are hydrogen and helium. WB 131/ p. 302 17. Solar energy is produced by fusion. p. 302 in text ONLY 18. The Sun is NOT mostly rock at its core. By deduction WB 132/ p. 300 19 ...
Nebular Theory
... Contraction: The cloud starts collapsing under its own gravity; over 100,000 years, it shrinks down to 100 AU, heats up (thermal energy), and compresses in the center. Accretion disk: The matter around the center spins up and flattens into a disk, while heat vaporizes the dust. Protostar: Forms in t ...
... Contraction: The cloud starts collapsing under its own gravity; over 100,000 years, it shrinks down to 100 AU, heats up (thermal energy), and compresses in the center. Accretion disk: The matter around the center spins up and flattens into a disk, while heat vaporizes the dust. Protostar: Forms in t ...
The Sun….center of the solar system
... The solar spectrum is a good match (although not perfect) to a blackbody spectrum ...
... The solar spectrum is a good match (although not perfect) to a blackbody spectrum ...
View PDF
... The sun’s warming of the Earth and tilt of the Earth on its axis have an importan t connection to the seasons. Earth’s motion is the basis for measuring time. Objects in the sky move in regular and predictable patterns around the Sun. The sun, stars and constellations appear to move in predictable p ...
... The sun’s warming of the Earth and tilt of the Earth on its axis have an importan t connection to the seasons. Earth’s motion is the basis for measuring time. Objects in the sky move in regular and predictable patterns around the Sun. The sun, stars and constellations appear to move in predictable p ...
1st.Prep.Unit _3_ lesson_1_
... They are big sized bodies emit enormous amounts of heat & light. They are a huge number & the distance between them very large so we measure them by light year. ...
... They are big sized bodies emit enormous amounts of heat & light. They are a huge number & the distance between them very large so we measure them by light year. ...
The Solar System
... • Formation from collapse of cloud of gas and dust 4.6 billion years ago. • Collisions and cratering dominated for first 150 million years, leaving current planetary system. • Inventory: 1 star, 8+1 planets, moons, asteroids, comets, solar wind. • Terrestrial (rock)+ Jovian (gas) planets GENS4001 X1 ...
... • Formation from collapse of cloud of gas and dust 4.6 billion years ago. • Collisions and cratering dominated for first 150 million years, leaving current planetary system. • Inventory: 1 star, 8+1 planets, moons, asteroids, comets, solar wind. • Terrestrial (rock)+ Jovian (gas) planets GENS4001 X1 ...
Boardworks Space Physics W8
... This photograph shows Pluto and its moon, Charon. Pluto’s orbit is surrounded by smaller objects that have not been cleared by its gravitational field. Pluto and the other ‘smaller’ planet-like objects such as Eris and Ceres have now been reclassified as Dwarf Planets. 4 of 9 ...
... This photograph shows Pluto and its moon, Charon. Pluto’s orbit is surrounded by smaller objects that have not been cleared by its gravitational field. Pluto and the other ‘smaller’ planet-like objects such as Eris and Ceres have now been reclassified as Dwarf Planets. 4 of 9 ...
Rendezvous with Rosetta
... Solar System, Kuiper belt & Oort cloud • Distance from Sun: 30 Trillion km! • Size: Completely surrounding Solar System! • Material & Shape: The Oort Cloud is not disk-shaped like the Kuiper Belt; it’s round like a ball,It completely envelops the sun and the rest of our solar system. Billions of ic ...
... Solar System, Kuiper belt & Oort cloud • Distance from Sun: 30 Trillion km! • Size: Completely surrounding Solar System! • Material & Shape: The Oort Cloud is not disk-shaped like the Kuiper Belt; it’s round like a ball,It completely envelops the sun and the rest of our solar system. Billions of ic ...
exercise 1
... periodically slowed down until they began moving in the opposite, western direction— retrograde motion. After a short distance, they slowed down again and resumed their eastward motion. So the ancient peoples called the planets wanderers. ...
... periodically slowed down until they began moving in the opposite, western direction— retrograde motion. After a short distance, they slowed down again and resumed their eastward motion. So the ancient peoples called the planets wanderers. ...
clicking here. - Bakersfield College
... Moon A rocky sphere that orbits the Earth. Neptune The eighth planet from the Sun. Observatory A place or building that uses large telescopes for observing outer space. Olympus Mons The largest mountain in the solar system. This mountain is a volcano and found on Mars. Orbit The path one object take ...
... Moon A rocky sphere that orbits the Earth. Neptune The eighth planet from the Sun. Observatory A place or building that uses large telescopes for observing outer space. Olympus Mons The largest mountain in the solar system. This mountain is a volcano and found on Mars. Orbit The path one object take ...
幻灯片1
... go around the Sun. None of them has an environment with air, so people and things cannot grow. The Sun and its planets are called the solar system. The solar system is a small part of our galaxy. ...
... go around the Sun. None of them has an environment with air, so people and things cannot grow. The Sun and its planets are called the solar system. The solar system is a small part of our galaxy. ...
Power Point
... elliptical in shape. • The nine known planets, in order of distance from the sun, are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, and Pluto. ...
... elliptical in shape. • The nine known planets, in order of distance from the sun, are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, and Pluto. ...
Steve Tomczyk & Scott McIntosh - National Center for Atmospheric
... Instrumentation Program, where an engineering group consisting of seven engineers and three interns collaborates with HAO scientists to develop state-ofthe-art instruments for the observation of the Sun and the Earth’s upper atmosphere. Scott received his bachelors degree in Astronomy from Villanova ...
... Instrumentation Program, where an engineering group consisting of seven engineers and three interns collaborates with HAO scientists to develop state-ofthe-art instruments for the observation of the Sun and the Earth’s upper atmosphere. Scott received his bachelors degree in Astronomy from Villanova ...
2. Universe, Solar System and Earth`s formation
... HOW DID THE SOLAR SYSTEM FORM? • Star formation occurs in our Galaxy. ...
... HOW DID THE SOLAR SYSTEM FORM? • Star formation occurs in our Galaxy. ...
Pacing Our Solar System
... Pacing Our Solar System The chart below gives the scaled sizes and distances of the planets if the Sun were the size of a softball. Using these numbers, mark the distances in the model of planetary orbits, as instructed. One very large stride is roughly equal to a meter. As you can see, most of spac ...
... Pacing Our Solar System The chart below gives the scaled sizes and distances of the planets if the Sun were the size of a softball. Using these numbers, mark the distances in the model of planetary orbits, as instructed. One very large stride is roughly equal to a meter. As you can see, most of spac ...
Chapter 27 Study Notes
... core of Earth is an iron- and magnesium-rich rock layer called the ______. mantle ...
... core of Earth is an iron- and magnesium-rich rock layer called the ______. mantle ...
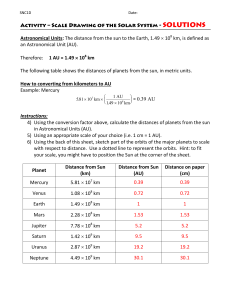
Activity – Scale Drawing of the Solar System
... 4) Using the conversion factor above, calculate the distances of planets from the sun in Astronomical Units (AU). 5) Using an appropriate scale of your choice (i.e. 1 cm = 1 AU). 6) Using the back of this sheet, sketch part of the orbits of the major planets to scale with respect to distance. Use a ...
... 4) Using the conversion factor above, calculate the distances of planets from the sun in Astronomical Units (AU). 5) Using an appropriate scale of your choice (i.e. 1 cm = 1 AU). 6) Using the back of this sheet, sketch part of the orbits of the major planets to scale with respect to distance. Use a ...
Summary of camp and co
... night, seasons, and tides Worksheets for sundial and shadow-sticks, finding north in the day-time, and south at night Solar system model: relative sizes, orbits and distances of planets and sun Night-time observing (if applicable): major constellations, moon and planets, use of basic star charts. Na ...
... night, seasons, and tides Worksheets for sundial and shadow-sticks, finding north in the day-time, and south at night Solar system model: relative sizes, orbits and distances of planets and sun Night-time observing (if applicable): major constellations, moon and planets, use of basic star charts. Na ...
File
... • A young solar nebula collapses under the force of gravity • The nebula flattens and becomes warmer near its center causing nuclear fusion to begin. • Remnants from the formation of the sun begin to coalesce and form planetesimals • Matter with higher density remains in close proximity to the sun f ...
... • A young solar nebula collapses under the force of gravity • The nebula flattens and becomes warmer near its center causing nuclear fusion to begin. • Remnants from the formation of the sun begin to coalesce and form planetesimals • Matter with higher density remains in close proximity to the sun f ...
Our Star, the Sun
... of water. Occasionally, a neutrino entering the tank interacts with one or another of the particles.! Neutrinos emitted in thermonuclear reactions in the Sun s core have been detected, but in smaller numbers than ...
... of water. Occasionally, a neutrino entering the tank interacts with one or another of the particles.! Neutrinos emitted in thermonuclear reactions in the Sun s core have been detected, but in smaller numbers than ...
Heliosphere

The heliosphere is the bubble-like region of space dominated by the Sun, which extends far beyond the orbit of Pluto. Plasma ""blown"" out from the Sun, known as the solar wind, creates and maintains this bubble against the outside pressure of the interstellar medium, the hydrogen and helium gas that permeates the Milky Way Galaxy. The solar wind flows outward from the Sun until encountering the termination shock, where motion slows abruptly. The Voyager spacecraft have actively explored the outer reaches of the heliosphere, passing through the shock and entering the heliosheath, a transitional region which is in turn bounded by the outermost edge of the heliosphere, called the heliopause. The overall shape of the heliosphere is controlled by the interstellar medium, through which it is traveling, as well as the Sun, and does not appear to be perfectly spherical. The limited data available and unexplored nature of these structures have resulted in many theories.On September 12, 2013, NASA announced that Voyager 1 had exited the heliosphere on August 25, 2012, when it measured a sudden increase in plasma density of about forty times. Because the heliopause marks one boundary between the Sun's solar wind and the rest of the galaxy, a spacecraft such as Voyager 1 which has departed the heliosphere can be said to have reached interstellar space.