Document
... ! If charged particle is not moving - no effect ! If particle is moving: force perpendicular to both field and velocity ! the charge sign must be accounted for ...
... ! If charged particle is not moving - no effect ! If particle is moving: force perpendicular to both field and velocity ! the charge sign must be accounted for ...
AC Circuits - San Jose State University
... any closed path equals mo times the current, Iencircled, encircled by the closed loop. ...
... any closed path equals mo times the current, Iencircled, encircled by the closed loop. ...
Magnetic fields
... Magnets have two ends – poles – called north and south. Like poles repel; unlike poles attract. ...
... Magnets have two ends – poles – called north and south. Like poles repel; unlike poles attract. ...
Notes–Maxwell`s Equations
... magnetic system. Mathematically denies the existence of a magnetic monopole. Relates induced electric field (voltage, induced current, etc.) to changing magnetic flux. The negative sign indicating direction of Emf opposes the change in Bflux. Notice also the definition of electric potential (V) on t ...
... magnetic system. Mathematically denies the existence of a magnetic monopole. Relates induced electric field (voltage, induced current, etc.) to changing magnetic flux. The negative sign indicating direction of Emf opposes the change in Bflux. Notice also the definition of electric potential (V) on t ...
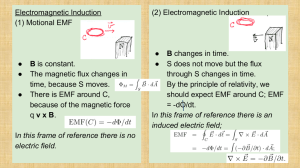
Electromagnetic Induction (2) Electromagnetic Induction (1) Motional EMF ●
... By Ampere’s law, the eddy currents create a magnetic field directed upward (right hand rule again!). This opposes the change of flux. ...
... By Ampere’s law, the eddy currents create a magnetic field directed upward (right hand rule again!). This opposes the change of flux. ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.