Magnets and electricity - Rm. E
... Magnet: any material that attracts iron or objects made of iron. Magnetic force: when you bring two magnets together, they exert a push or a pull on each other. Magnetic poles: two magnets can push each other apart because of their ends. Magnetic field: the area surrounding a magnet where magnet ...
... Magnet: any material that attracts iron or objects made of iron. Magnetic force: when you bring two magnets together, they exert a push or a pull on each other. Magnetic poles: two magnets can push each other apart because of their ends. Magnetic field: the area surrounding a magnet where magnet ...
Eileen and Brendan Sharkey
... 11. Which way is current flowing through the length of wire? Which way does the other compass point? ...
... 11. Which way is current flowing through the length of wire? Which way does the other compass point? ...
Properties of Matter Vocabulary Cards
... In a solution, one substance spreads out evenly (dissolves) in another substance. Even though one substance dissolves in another, most physical properties remain the same. o Example: sugar and water – Even though the sugar dissolves in the water, if you taste the water, it will taste sweet because t ...
... In a solution, one substance spreads out evenly (dissolves) in another substance. Even though one substance dissolves in another, most physical properties remain the same. o Example: sugar and water – Even though the sugar dissolves in the water, if you taste the water, it will taste sweet because t ...
المملكة العربية السعودية
... The electric force vector is along the direction of the electric field, whereas the magnetic force vector is perpendicular to the magnetic field. The electric force acts on a charged particle regardless of whether the particle is moving, whereas the magnetic force acts on a charged particle only ...
... The electric force vector is along the direction of the electric field, whereas the magnetic force vector is perpendicular to the magnetic field. The electric force acts on a charged particle regardless of whether the particle is moving, whereas the magnetic force acts on a charged particle only ...
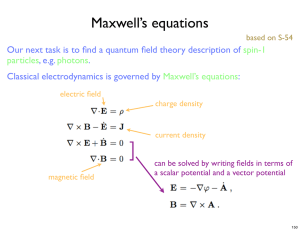
Maxwell`s Formulation – Differential Forms on Euclidean Space
... circuit is still complete. However, using Amperes law to find the magnetic field at a point in space, it was possible to select one closed loop passing through the capacitor, so that no current passed through the closed loop. This would indicate that there was no magnetic field at that point. Howeve ...
... circuit is still complete. However, using Amperes law to find the magnetic field at a point in space, it was possible to select one closed loop passing through the capacitor, so that no current passed through the closed loop. This would indicate that there was no magnetic field at that point. Howeve ...
Classifying Matter and the Periodic Table
... particles varies directly as the product of their charges and inversely as the square of the separation distances. • force (newtons) = k x 1st charge x 2nd charge / distance2 ...
... particles varies directly as the product of their charges and inversely as the square of the separation distances. • force (newtons) = k x 1st charge x 2nd charge / distance2 ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.