Chapter 2 Coulomb’s Law
... Before we discuss this animation, consider Figure 2.2.2(b), which shows one frame of a movie of the interaction of two charges with opposite signs. Here the charge on the small sphere is opposite to that on the van de Graaff sphere. By Coulomb’s law, the two objects now attract one another, and the ...
... Before we discuss this animation, consider Figure 2.2.2(b), which shows one frame of a movie of the interaction of two charges with opposite signs. Here the charge on the small sphere is opposite to that on the van de Graaff sphere. By Coulomb’s law, the two objects now attract one another, and the ...
+q - Indico
... The fact that the total induced charge on an electrode, once ALL charges have arrived at the electrodes, is equal to the actual charge that has ARRIVED at the electrode, leads to very different ‘vocabulary for detectors in different detectors. In wire chambers the ions take hundreds of microseconds ...
... The fact that the total induced charge on an electrode, once ALL charges have arrived at the electrodes, is equal to the actual charge that has ARRIVED at the electrode, leads to very different ‘vocabulary for detectors in different detectors. In wire chambers the ions take hundreds of microseconds ...
Electromagnetic induction, flux and flux linkage
... illustrates another important feature of eddy currents. Leaving the ring floating for some time (or pushing it down) will quickly make the ring get hot [care needed; the ring can get very hot]. This is an example of eddy current heating. It is put to good practical use, e.g. in the production of pur ...
... illustrates another important feature of eddy currents. Leaving the ring floating for some time (or pushing it down) will quickly make the ring get hot [care needed; the ring can get very hot]. This is an example of eddy current heating. It is put to good practical use, e.g. in the production of pur ...
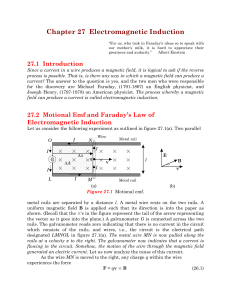
Chapter 27 Electromagnetic Induction
... Lenz’s law is also a statement of the law of conservation of energy. If the induced magnetic field is in the same direction as the changing magnetic field, the total magnetic field will increase even more, which would in turn induce a larger magnetic field, which would again increase the total magne ...
... Lenz’s law is also a statement of the law of conservation of energy. If the induced magnetic field is in the same direction as the changing magnetic field, the total magnetic field will increase even more, which would in turn induce a larger magnetic field, which would again increase the total magne ...
Low-field microwave absorption in pulsed lased deposited FeSi thin films
... H ( ≈ 2000 Oe). Thin films of FeSi are promising candidates for spintronics applications where magnetic semiconducting films serve as injectors and collectors of spin polarized currents in Si transistors. Thin films portray a high Curie temperature TC ( ≈ 30 K) in contrast to the bulk with TC ( ≈ 0 ...
... H ( ≈ 2000 Oe). Thin films of FeSi are promising candidates for spintronics applications where magnetic semiconducting films serve as injectors and collectors of spin polarized currents in Si transistors. Thin films portray a high Curie temperature TC ( ≈ 30 K) in contrast to the bulk with TC ( ≈ 0 ...
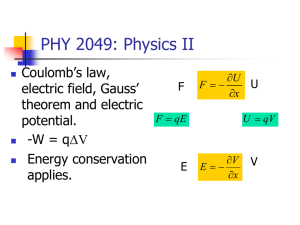
PHY 2049: Physics II
... PHY 2049: Physics II Calculate the Electric Field at P Calculate the el. potential at P ...
... PHY 2049: Physics II Calculate the Electric Field at P Calculate the el. potential at P ...
Quantized magnetoresistance in atomic-size
... of the conduction electrons, the absence of scattering results in ballistic electron transport1 and the conductance becomes quantized2, 3, 4. In ferromagnetic metals, the spin angular momentum of the electrons results in spin-dependent conductance quantization5, 6, 7 and various unusual magnetoresis ...
... of the conduction electrons, the absence of scattering results in ballistic electron transport1 and the conductance becomes quantized2, 3, 4. In ferromagnetic metals, the spin angular momentum of the electrons results in spin-dependent conductance quantization5, 6, 7 and various unusual magnetoresis ...
Novel quantum phenomena and excitation modes
... to the low-temperature dynamics of normal-superconductor interfaces in a type-I superconductor. Chapter 1 illustrates the study of the magnetic irreversibility in disk-shaped lead samples by means of hysteresis loops and relaxation measurements along the descending branch within the intermediate sta ...
... to the low-temperature dynamics of normal-superconductor interfaces in a type-I superconductor. Chapter 1 illustrates the study of the magnetic irreversibility in disk-shaped lead samples by means of hysteresis loops and relaxation measurements along the descending branch within the intermediate sta ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.