Homework 5 - University of St. Thomas
... moving 21x103m/s and (b) the field strength required if the field were at 45° to the electron’s velocity. #21: How long does it take to complete a circular orbit perpendicular to a 1.0G magnetic field? #26: A wire carrying 15A makes a 25° angle with a uniform magnetic field. The magnetic force per u ...
... moving 21x103m/s and (b) the field strength required if the field were at 45° to the electron’s velocity. #21: How long does it take to complete a circular orbit perpendicular to a 1.0G magnetic field? #26: A wire carrying 15A makes a 25° angle with a uniform magnetic field. The magnetic force per u ...
PHYS1444-003,Fall 05, Term Exam #2, Nov. 7
... wire have to carry if the magnetic force on the wire equals the gravitational force? (5 points) Ans] The gravitational force must be balanced by the magnetic force exerted on the wire by the field which is perpendicular to the wire. Thus we can establish the ...
... wire have to carry if the magnetic force on the wire equals the gravitational force? (5 points) Ans] The gravitational force must be balanced by the magnetic force exerted on the wire by the field which is perpendicular to the wire. Thus we can establish the ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... depends on their magnetic _____, _____ or _____. Opposite poles _____, like poles _____. A magnetic field is produced by the _____ of electric charges. Clusters of magnetically aligned atoms are magnetic _____. A magnetic _____ surrounds a current carrying wire. When a current carrying wire is made ...
... depends on their magnetic _____, _____ or _____. Opposite poles _____, like poles _____. A magnetic field is produced by the _____ of electric charges. Clusters of magnetically aligned atoms are magnetic _____. A magnetic _____ surrounds a current carrying wire. When a current carrying wire is made ...
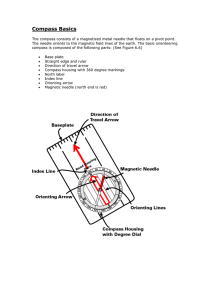
Compass Basics - NSW Public Schools
... directly at the top. Unfortunately for the wilderness traveler, true north is not at the same point on the earth as the magnetic north Pole which is where your compass points. Magnetic North: Think of the earth as a giant magnet (it is actually). The shape of the earth's magnetic field is roughly th ...
... directly at the top. Unfortunately for the wilderness traveler, true north is not at the same point on the earth as the magnetic north Pole which is where your compass points. Magnetic North: Think of the earth as a giant magnet (it is actually). The shape of the earth's magnetic field is roughly th ...
Document
... Physics-505 Homework Set (5) This set is due by Sunday 27th of Jumada-II, 1435 (27th of April 2014) at 10.00 p.m. ...
... Physics-505 Homework Set (5) This set is due by Sunday 27th of Jumada-II, 1435 (27th of April 2014) at 10.00 p.m. ...
Please review my solution to the problem and explain in
... Please review my solution to the problem and explain in detail what I may be doing wrong and what concepts I may not be applying correctly. I am not sure if I am apply the crossed fields concept correct in presuming that B is perpendicular. ...
... Please review my solution to the problem and explain in detail what I may be doing wrong and what concepts I may not be applying correctly. I am not sure if I am apply the crossed fields concept correct in presuming that B is perpendicular. ...
Magnetic Flux
... 2. A circular coil has 10 turns and diameter 2.0 cm. It is placed in a uniform magnetic field of strength 300 mT. The plane of the coil and the direction of the field make an angle of 30 0. Determine the magnetic flux linkage through the coil. Ans : 4.17 X 10-4 Wb 3. A circular coil is placed in a u ...
... 2. A circular coil has 10 turns and diameter 2.0 cm. It is placed in a uniform magnetic field of strength 300 mT. The plane of the coil and the direction of the field make an angle of 30 0. Determine the magnetic flux linkage through the coil. Ans : 4.17 X 10-4 Wb 3. A circular coil is placed in a u ...
Unit 2
... ◦ The region of magnetic force around each magnet ◦ Magnetic Lines Map out the magnetic fields around magnet. Spread out from one pole, curve around magnet, and return to other pole. ...
... ◦ The region of magnetic force around each magnet ◦ Magnetic Lines Map out the magnetic fields around magnet. Spread out from one pole, curve around magnet, and return to other pole. ...
ch29-Magnetic Fields due to Currents
... Fig. 29-4 A right-hand rule gives the direction of the magnetic field due to a current in a wire. (a) The magnetic field B at any point to the left of the wire is perpendicular to the dashed radial line and directed into the page, in the direction of the fingertips, as indicated by the x. (b) If the ...
... Fig. 29-4 A right-hand rule gives the direction of the magnetic field due to a current in a wire. (a) The magnetic field B at any point to the left of the wire is perpendicular to the dashed radial line and directed into the page, in the direction of the fingertips, as indicated by the x. (b) If the ...
ch29
... Fig. 29-4 A right-hand rule gives the direction of the magnetic field due to a current in a wire. (a) The magnetic field B at any point to the left of the wire is perpendicular to the dashed radial line and directed into the page, in the direction of the fingertips, as indicated by the x. (b) If the ...
... Fig. 29-4 A right-hand rule gives the direction of the magnetic field due to a current in a wire. (a) The magnetic field B at any point to the left of the wire is perpendicular to the dashed radial line and directed into the page, in the direction of the fingertips, as indicated by the x. (b) If the ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.