1-Electromagnetic Forces - MrD-Home
... Points in direction a compass would point Runs from North to South Allows for FM: Magnetic Forces (the reason a compass needle moves!) ...
... Points in direction a compass would point Runs from North to South Allows for FM: Magnetic Forces (the reason a compass needle moves!) ...
Word
... entering the Earth’s magnetic field where they Paths of follow helical paths along the field lines either charged north or south. The light observed as auroras is due particles to ionization of atoms in the atmosphere when they collide with high speed charged particles. The free B electrons resultin ...
... entering the Earth’s magnetic field where they Paths of follow helical paths along the field lines either charged north or south. The light observed as auroras is due particles to ionization of atoms in the atmosphere when they collide with high speed charged particles. The free B electrons resultin ...
Physical Science Review
... Gravitational field is affected by distance and mass. More distance less force. More mass more force. Electric field is affected by distance. The farther away the charge, the less force. In electric field, the opposite charges attract. Like charges repel Magnetic field is affected by distance ...
... Gravitational field is affected by distance and mass. More distance less force. More mass more force. Electric field is affected by distance. The farther away the charge, the less force. In electric field, the opposite charges attract. Like charges repel Magnetic field is affected by distance ...
Magnetic Field Lines
... N.B. sin(90o)= 1, sin(0o)= 0, .: F┴ = nBIl, F║= 0, .: B = [T = Nm-1A-1] i.e., Magnetic field (strength) is the force exerted by a magnet on a current-carrying wire per meter of current-carrying wire. Right-Hand Slap Rule: With your flat, open right hand, when your fingers point in the direction of t ...
... N.B. sin(90o)= 1, sin(0o)= 0, .: F┴ = nBIl, F║= 0, .: B = [T = Nm-1A-1] i.e., Magnetic field (strength) is the force exerted by a magnet on a current-carrying wire per meter of current-carrying wire. Right-Hand Slap Rule: With your flat, open right hand, when your fingers point in the direction of t ...
Assignment 9.
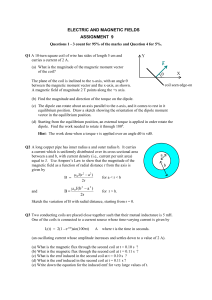
... (b) Find the magnitude and direction of the torque on the dipole. (c) The dipole can rotate about an axis parallel to the z-axis, and it comes to rest in it equilibrium position. Draw a sketch showing the orientation of the dipole moment vector in the equilibrium position. (d) Starting from the equi ...
... (b) Find the magnitude and direction of the torque on the dipole. (c) The dipole can rotate about an axis parallel to the z-axis, and it comes to rest in it equilibrium position. Draw a sketch showing the orientation of the dipole moment vector in the equilibrium position. (d) Starting from the equi ...
Semester exam chapter 7. PHYS4315
... b. Show that the magnetic flux through a perfectly conducting loop is constant. A superconductor is a perfect conductor with the additional property that the (constant) B inside is in fact zero. (This “flux exclusion” is known as the Meissner effect. c. Show that the current in a superconductor is c ...
... b. Show that the magnetic flux through a perfectly conducting loop is constant. A superconductor is a perfect conductor with the additional property that the (constant) B inside is in fact zero. (This “flux exclusion” is known as the Meissner effect. c. Show that the current in a superconductor is c ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.