Electromagnetism - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... -if a generator produces a small current, opposing force on armature is small and easy to turn -if it produces larger current, force will be larger and more difficult to turn -to produce greater electrical energy, more mechanical energy must be supplied to armature rotation consistent with law of ...
... -if a generator produces a small current, opposing force on armature is small and easy to turn -if it produces larger current, force will be larger and more difficult to turn -to produce greater electrical energy, more mechanical energy must be supplied to armature rotation consistent with law of ...
Magnetism Activity Write-up
... Describe the science: Magnetic poles that are alike repel each other and magnetic poles that are unlike attract each other. Magnetic field lines spread out from one pole, curve around a magnet and return to the other pole. In a magnetized material, all or most of the domains are arranged in the same ...
... Describe the science: Magnetic poles that are alike repel each other and magnetic poles that are unlike attract each other. Magnetic field lines spread out from one pole, curve around a magnet and return to the other pole. In a magnetized material, all or most of the domains are arranged in the same ...
1. A magnetic compass needle is placed in the plane... as shown in Figure. In which plane should a straight... X- Guess Questions solved SA-1: Magnetic effects of currents
... magnet get deflected when a bar magnet or a current carrying loop is brought near it. Describe some salient features of magnetic lines of field concept. Answer: Current carrying loops behave like bar magnets and both have their associated lines of field. This modifies the already existing earth’s ma ...
... magnet get deflected when a bar magnet or a current carrying loop is brought near it. Describe some salient features of magnetic lines of field concept. Answer: Current carrying loops behave like bar magnets and both have their associated lines of field. This modifies the already existing earth’s ma ...
Mathematics and waves
... around the source producing it. Eq- spherical, cylindrical, or planer symmetry. ...
... around the source producing it. Eq- spherical, cylindrical, or planer symmetry. ...
Force on a coil
... A circular coil consists of 5 loops, each of diameter 1.0 m. The coil is placed in an external magnetic field of 0.5T (telsa). When the coil carries a current of 4.0 A, a torque of magnitude 3.93 Nm , acts on it . Find the angle between the normal to the plane of the coil and the direction of the ma ...
... A circular coil consists of 5 loops, each of diameter 1.0 m. The coil is placed in an external magnetic field of 0.5T (telsa). When the coil carries a current of 4.0 A, a torque of magnitude 3.93 Nm , acts on it . Find the angle between the normal to the plane of the coil and the direction of the ma ...
Problem Set 10
... longitudinal magnetic field in the core changes from 1.60 T in one direction to 1.60 T in the opposite direction, how much charge flows through a point in the circuit during the ...
... longitudinal magnetic field in the core changes from 1.60 T in one direction to 1.60 T in the opposite direction, how much charge flows through a point in the circuit during the ...
Practice Electric Power Test
... No, its speed does not change. The force acting just goes to change its direction – the force is always at right angles to the velocity and hence has no component in the direction of the proton. (2 marks) ...
... No, its speed does not change. The force acting just goes to change its direction – the force is always at right angles to the velocity and hence has no component in the direction of the proton. (2 marks) ...
Magnetism Problem Set #2
... 3. The figure above shows a long, straight wire that has a steady current I in the +y-direction. A small object with charge +q hangs from a thread near the wire. A student wants to investigate the magnetic force on the object due to the current but is not able to observe or measure changes in the t ...
... 3. The figure above shows a long, straight wire that has a steady current I in the +y-direction. A small object with charge +q hangs from a thread near the wire. A student wants to investigate the magnetic force on the object due to the current but is not able to observe or measure changes in the t ...
week 10, 1B
... 110V voltage), what would be the power wasted by the wire that transports the electricity. (These numbers are for illustration purpose only. They may not be realistic.) 5. A signal V1=V0cos(100t) with V0=3V is fed to the following circuit. Determine the effective voltage across the capacitor. What i ...
... 110V voltage), what would be the power wasted by the wire that transports the electricity. (These numbers are for illustration purpose only. They may not be realistic.) 5. A signal V1=V0cos(100t) with V0=3V is fed to the following circuit. Determine the effective voltage across the capacitor. What i ...
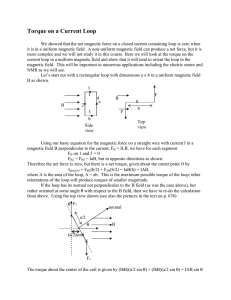
Torque on a Current Loop
... where θ is the angle between the normal (direction of the vector representing the area) and magnetic field. This can be re-written as G G τ = IA × B where the direction of A is along the normal to its area using a right hand rule (right hand fingers curl around the circuit loop along I and your thu ...
... where θ is the angle between the normal (direction of the vector representing the area) and magnetic field. This can be re-written as G G τ = IA × B where the direction of A is along the normal to its area using a right hand rule (right hand fingers curl around the circuit loop along I and your thu ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.