Name: Cathode Ray Tubes – Points of Clarification
... In order to reduce the deflection experienced by the electrons, the path radius must be larger. According to our equation for radius above, a larger radius can be achieved by decreasing the strength of the magnetic field, since r is inversely proportional to B. The strength of the magnetic field is ...
... In order to reduce the deflection experienced by the electrons, the path radius must be larger. According to our equation for radius above, a larger radius can be achieved by decreasing the strength of the magnetic field, since r is inversely proportional to B. The strength of the magnetic field is ...
File
... rub it in one direction with one pole of a magnet. Electric current can also be applied to metal causing it to become magnetized. ...
... rub it in one direction with one pole of a magnet. Electric current can also be applied to metal causing it to become magnetized. ...
Chap 21. Electromagnetic Induction Sec. 1
... voltage in the ciruit. The phasor diagram for the same is given below Resistance, Impedance for a resistance is Xr = R ...
... voltage in the ciruit. The phasor diagram for the same is given below Resistance, Impedance for a resistance is Xr = R ...
TE Activity: Yogurt Cup Speakers
... Introduction/Motivation (Return to Contents) Can you imagine life without radios? Do you know that the object that makes the speaker in th electromagnet is created with a battery (or some other source of electricity) and a wire. A batte Although electrons collect at the negative end of the battery, ...
... Introduction/Motivation (Return to Contents) Can you imagine life without radios? Do you know that the object that makes the speaker in th electromagnet is created with a battery (or some other source of electricity) and a wire. A batte Although electrons collect at the negative end of the battery, ...
Electromagnetism: What You Need to Know
... If you wish to see for yourself this magnetic field in action, place a compass near a current carrying wire. To observe the full effect, the face of the compass must be placed at a right angle to the wire. The compass, which is just a magnet, will align itself with the magnetic field around the wire ...
... If you wish to see for yourself this magnetic field in action, place a compass near a current carrying wire. To observe the full effect, the face of the compass must be placed at a right angle to the wire. The compass, which is just a magnet, will align itself with the magnetic field around the wire ...
Magnets - Bari Science Lab
... • The electric current produced by the generator changes direction each time the coil makes a half turn. Because the electric current changes direction, it is an alternating current. • The energy that generators convert into electrical energy comes from different sources such as fossil fuels and nuc ...
... • The electric current produced by the generator changes direction each time the coil makes a half turn. Because the electric current changes direction, it is an alternating current. • The energy that generators convert into electrical energy comes from different sources such as fossil fuels and nuc ...
Magnets - mrzimmerman.org
... decreases as their separation increases. • An unmagnetized magnet material would be attracted to both poles. ...
... decreases as their separation increases. • An unmagnetized magnet material would be attracted to both poles. ...
dekalb reads - GEOCITIES.ws
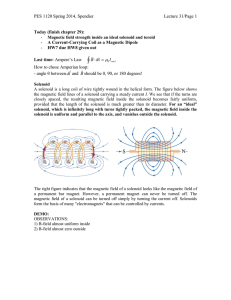
... 4. How can you increase the strength of a wire’s magnetic field? 5. Define solenoid. 6. How can you increase the strength of the magnetic field of a solenoid. (Hint: there are 3 ways to do so. Write all the 3 ways) 7. Define electromagnet. 8. Magnetism is caused by __________________________. 9. ___ ...
... 4. How can you increase the strength of a wire’s magnetic field? 5. Define solenoid. 6. How can you increase the strength of the magnetic field of a solenoid. (Hint: there are 3 ways to do so. Write all the 3 ways) 7. Define electromagnet. 8. Magnetism is caused by __________________________. 9. ___ ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.