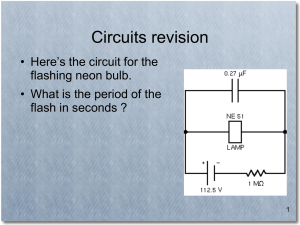
Exam 1 (Chapters 1-4) - UNC Physics and Astronomy
... 5. Three point charges are arranged on the corners of a square as shown (clockwise starting from upper right: zero, +Q, -2Q, +Q). What charge must be placed at the empty corner of the square so that both the electric field and electric potential are zero at the center? +Q d 1. -Q 2. +2Q d 3. -2Q 4. ...
... 5. Three point charges are arranged on the corners of a square as shown (clockwise starting from upper right: zero, +Q, -2Q, +Q). What charge must be placed at the empty corner of the square so that both the electric field and electric potential are zero at the center? +Q d 1. -Q 2. +2Q d 3. -2Q 4. ...
PPT - LSU Physics & Astronomy
... and grows in magnitude as the charge on the capacitor increases. The magnetic field induced by this changing electric field is shown at four points on a circle with a radius r less than the plate radius R. ...
... and grows in magnitude as the charge on the capacitor increases. The magnetic field induced by this changing electric field is shown at four points on a circle with a radius r less than the plate radius R. ...
PURDUE UNIVERSITY PHYS221 FINAL EXAM
... 3. The distance from earth to the center of our galaxy is about 23 000 ly (1 ly = 1 light year= 9.47 x 1015 m), as measured by an earth-based observer. A spaceship is to make this journey at a speed of 0.9992c. According to a clock on board the spaceship, how long will it take to make the trip? Expr ...
... 3. The distance from earth to the center of our galaxy is about 23 000 ly (1 ly = 1 light year= 9.47 x 1015 m), as measured by an earth-based observer. A spaceship is to make this journey at a speed of 0.9992c. According to a clock on board the spaceship, how long will it take to make the trip? Expr ...
Magnetic Force on a Current-Carrying Wire – Warm Up
... • DC Power supply (5 A) • DC Ammeter THEORY The force on a wire of length L carrying current I in a magnetic field ! is given by ...
... • DC Power supply (5 A) • DC Ammeter THEORY The force on a wire of length L carrying current I in a magnetic field ! is given by ...
Physics 241 – Exam #2
... directed perpendicular to the plane of the loop, and into the plane of the drawing. This field varies with time as B = 0.65 − 1.5t where the field is measured in tesla and time in seconds. What is the magnitude of the force on one of the straight sections of the loop at t = 0? L ...
... directed perpendicular to the plane of the loop, and into the plane of the drawing. This field varies with time as B = 0.65 − 1.5t where the field is measured in tesla and time in seconds. What is the magnitude of the force on one of the straight sections of the loop at t = 0? L ...
Magnetism - Iroquois Central School District / Home Page
... Pole do not coincide. The magnetic pole is about 1500 km (930 mi) south of the geographic North Pole and it wanders. A compass actually indicates the direction of magnetic north, not true north. Therefore a navigator must need to know the magnetic declination for a specific area. This is the angular ...
... Pole do not coincide. The magnetic pole is about 1500 km (930 mi) south of the geographic North Pole and it wanders. A compass actually indicates the direction of magnetic north, not true north. Therefore a navigator must need to know the magnetic declination for a specific area. This is the angular ...
Slide 1
... RS comes up from the plane of the diagram. Induced emf and hence current is set up in the coil. By Fleming’s Right Hand Rule, the direction of the current is PQRSR2B2B1R1P. After half the rotation of the coil, the arm PQ comes up and RS goes down into the plane of the diagram. By Fleming’s Right Han ...
... RS comes up from the plane of the diagram. Induced emf and hence current is set up in the coil. By Fleming’s Right Hand Rule, the direction of the current is PQRSR2B2B1R1P. After half the rotation of the coil, the arm PQ comes up and RS goes down into the plane of the diagram. By Fleming’s Right Han ...
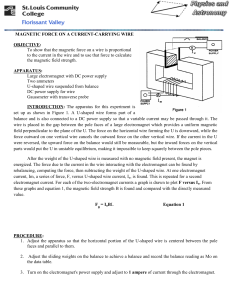
MAGNETIC FORCE ON A CURRENT
... U-shaped wire suspended from balance DC power supply for wire Gaussmeter with transverse probe INTRODUCTION: The apparatus for this experiment is set up as shown in Figure 1. A U-shaped wire forms part of a balance and is also connected to a DC power supply so that a variable current may be passed t ...
... U-shaped wire suspended from balance DC power supply for wire Gaussmeter with transverse probe INTRODUCTION: The apparatus for this experiment is set up as shown in Figure 1. A U-shaped wire forms part of a balance and is also connected to a DC power supply so that a variable current may be passed t ...
dA Chapter 3: Electricity and Magnetism Duration: 10 days Day 1
... An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. You have just made a mag ...
... An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. You have just made a mag ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.