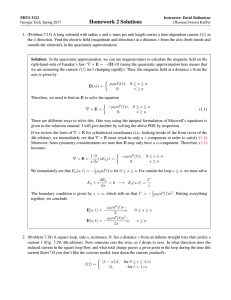
Chapter 4: Sound - Introduction Objectives Longitudinal Waves
... intensity. Wire wrapped around a ferrous material will intensify the magnetic field and induce a magnetic field in the iron. More wraps makes a stronger field. If the iron is a soft type it can become temporarily magnetized only while the current is flowing in the wire. If it is a harder core it wil ...
... intensity. Wire wrapped around a ferrous material will intensify the magnetic field and induce a magnetic field in the iron. More wraps makes a stronger field. If the iron is a soft type it can become temporarily magnetized only while the current is flowing in the wire. If it is a harder core it wil ...
"High density operation (SDC/IDB configuration) in LHD and its
... injected hydrogen pellets. In this recovery phase, the pressure profile becomes peaked; highcentral-beta plasma is formed by this. • Increase of the b0 is disturbed by so-called core density collapse(CDC) events. CDC is an abrupt event where the core density is collapsed within 1 ms. (much faster th ...
... injected hydrogen pellets. In this recovery phase, the pressure profile becomes peaked; highcentral-beta plasma is formed by this. • Increase of the b0 is disturbed by so-called core density collapse(CDC) events. CDC is an abrupt event where the core density is collapsed within 1 ms. (much faster th ...
PHET Magnetism
... Opposite charges attract while like charges repel. • Predict whether two charged objects will attract or repel each other, and explain why. 9-11 PS1H Electricity and magnetism are two aspects of a single electromagnetic force. Moving electric charges produce magnetic forces, and moving magnets produ ...
... Opposite charges attract while like charges repel. • Predict whether two charged objects will attract or repel each other, and explain why. 9-11 PS1H Electricity and magnetism are two aspects of a single electromagnetic force. Moving electric charges produce magnetic forces, and moving magnets produ ...
Chapter 30
... is constant on any circle of radius a The right-hand rule for determining the direction of the field is shown ...
... is constant on any circle of radius a The right-hand rule for determining the direction of the field is shown ...
by TG Skeggs © July 13, 2003
... because when both machines were switched 'on', they consisted of 2 completely isolated and identical space-times. This can trick the object into being in two places at the same time or even jump from 'Alice' to 'Bob' due to the interiors of both machines being isolated from the surrounding Universe. ...
... because when both machines were switched 'on', they consisted of 2 completely isolated and identical space-times. This can trick the object into being in two places at the same time or even jump from 'Alice' to 'Bob' due to the interiors of both machines being isolated from the surrounding Universe. ...
Displacement current : Physics Assignment
... In the middle of that century Maxwell struggled with the paradox of the capacitor, where charge entered one plate and then flowed out of the other plate apparently without traversing the space between the plates. It seemed that electric charge was being destroyed on one plate and being re-created wh ...
... In the middle of that century Maxwell struggled with the paradox of the capacitor, where charge entered one plate and then flowed out of the other plate apparently without traversing the space between the plates. It seemed that electric charge was being destroyed on one plate and being re-created wh ...
Magnets
... The torque acting on the loop will tend to rotate the loop to smaller values of θ until the torque becomes 0 at θ = 0° If the loop turns past this point and the current remains in the same direction, the torque reverses and turns the loop in the opposite direction General ...
... The torque acting on the loop will tend to rotate the loop to smaller values of θ until the torque becomes 0 at θ = 0° If the loop turns past this point and the current remains in the same direction, the torque reverses and turns the loop in the opposite direction General ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.