18ElectricForcesandElectricFields
... You are to determine the magnitude and direction of the electric field at a point between two large parallel conducting plates. The two plates have equal but opposite charges, but it is not known which is positive and which is negative. The plates are mounted vertically on insulating stands. • (a) A ...
... You are to determine the magnitude and direction of the electric field at a point between two large parallel conducting plates. The two plates have equal but opposite charges, but it is not known which is positive and which is negative. The plates are mounted vertically on insulating stands. • (a) A ...
Chap18-Cutnell
... Example 1 A Lot of Electrons In nature, atoms are normally found with equal numbers of protons and electrons, so they are electrically neutral. ...
... Example 1 A Lot of Electrons In nature, atoms are normally found with equal numbers of protons and electrons, so they are electrically neutral. ...
Document
... • Used when all the particles need to move with the same velocity • A uniform electric field is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field • When the force due to the electric field is equal but opposite to the force due to the magnetic field, the particle moves in a straight line • This occurs for ...
... • Used when all the particles need to move with the same velocity • A uniform electric field is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field • When the force due to the electric field is equal but opposite to the force due to the magnetic field, the particle moves in a straight line • This occurs for ...
EE3321 ELECTROMAGENTIC FIELD THEORY
... The magnitude of the electrostatic force between two point electric charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of each charge and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges. ...
... The magnitude of the electrostatic force between two point electric charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of each charge and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges. ...
From Gravitons to Galaxies (A New View of the Universe)
... If Newton’s law of gravity is assumed, then mainstream science has to conclude that our galaxy is surrounded by dark, undetectable matter that is one hundred times more massive than that of the galaxy. There is no observational evidence that this unbelievably huge mass of dark matter exists. Gravita ...
... If Newton’s law of gravity is assumed, then mainstream science has to conclude that our galaxy is surrounded by dark, undetectable matter that is one hundred times more massive than that of the galaxy. There is no observational evidence that this unbelievably huge mass of dark matter exists. Gravita ...
Chapter 21
... • Select a cylindrical Gaussian surface (of radius r and length ℓ) • Electric field is constant in magnitude and perpendicular to the surface at every point on the curved part of the surface • The end view confirms the field is perpendicular to the curved surface • The field through the ends of the ...
... • Select a cylindrical Gaussian surface (of radius r and length ℓ) • Electric field is constant in magnitude and perpendicular to the surface at every point on the curved part of the surface • The end view confirms the field is perpendicular to the curved surface • The field through the ends of the ...
Partial solutions from Ch1 to Ch6
... Chapter 6: Uniform Circular Motion and Gravitation ................................................................... 49 6.1 Rotation Angle and Angular Velocity .................................................................................. 49 6.2 Centripetal Acceleration ....................... ...
... Chapter 6: Uniform Circular Motion and Gravitation ................................................................... 49 6.1 Rotation Angle and Angular Velocity .................................................................................. 49 6.2 Centripetal Acceleration ....................... ...
9646 Physics H2 syllabus for 2016
... Each of these skill areas will be approximately equally weighted to a total of 36 marks. This paper may include data handling/interpretation questions that do not require apparatus, in order to test the skill areas of PDO and ACE. ...
... Each of these skill areas will be approximately equally weighted to a total of 36 marks. This paper may include data handling/interpretation questions that do not require apparatus, in order to test the skill areas of PDO and ACE. ...
JECT TO LORENTZ FORCE IAA-AAS-DyCoSS2-04-11
... equilibrium positions and the shaded regions are the regions where the equilibrium positions will be stable. Figure (8, left) and figure (8, right) are given for . The locations of the stable re‐ gions are nearly unaffected by the changing values of the charge to mass ratios but the loca‐ tions and ...
... equilibrium positions and the shaded regions are the regions where the equilibrium positions will be stable. Figure (8, left) and figure (8, right) are given for . The locations of the stable re‐ gions are nearly unaffected by the changing values of the charge to mass ratios but the loca‐ tions and ...
Chapters 16 and 17
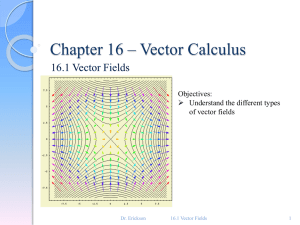
... 1. Field lines indicate the direction of the field; the field is tangent to the line. 2. The magnitude of the field is proportional to the density of the lines. 3. Field lines start on positive charges and end on negative charges; the number is proportional to the magnitude of the charge. ...
... 1. Field lines indicate the direction of the field; the field is tangent to the line. 2. The magnitude of the field is proportional to the density of the lines. 3. Field lines start on positive charges and end on negative charges; the number is proportional to the magnitude of the charge. ...