Electromagnetic radiation and steady states of hydrogen atom
... For an isolated hydrogen atom, the ground state which the electron and the nucleus rotate along their circular orbits with the cutoff frequency υc is the unique steady structure, the electron moving on higher energy orbit will automatically come back to ground state orbit by spontaneous radiation ba ...
... For an isolated hydrogen atom, the ground state which the electron and the nucleus rotate along their circular orbits with the cutoff frequency υc is the unique steady structure, the electron moving on higher energy orbit will automatically come back to ground state orbit by spontaneous radiation ba ...
Against Dogma: On Superluminal Propagation in Classical
... have already been produced. In this way, the title of the paper may be misleading, as I do not mean to argue that the dogma noted above is false. But I do hope to show that we do not understand the relationship between relativity theory and superluminal propagation as well as we might think, even i ...
... have already been produced. In this way, the title of the paper may be misleading, as I do not mean to argue that the dogma noted above is false. But I do hope to show that we do not understand the relationship between relativity theory and superluminal propagation as well as we might think, even i ...
OpenStax_Physics_CH18_ImageSlideshow
... leaves hung from a (conducting) metal stem and is insulated from the room air in a glass-walled container. (a) A positively charged glass rod is brought near the tip of the electroscope, attracting electrons to the top and leaving a net positive charge on the leaves. Like charges in the light flexib ...
... leaves hung from a (conducting) metal stem and is insulated from the room air in a glass-walled container. (a) A positively charged glass rod is brought near the tip of the electroscope, attracting electrons to the top and leaving a net positive charge on the leaves. Like charges in the light flexib ...
PHYS 308
... 2. The electrostatic potential on a sphere of radius R is given by V(R,) = Asin2. a) Express V(R,) as a sum of Legendre polynomials. b) Find an expression for the electrostatic potential V(r,) for ra), is given by C=ab ...
... 2. The electrostatic potential on a sphere of radius R is given by V(R,) = Asin2. a) Express V(R,) as a sum of Legendre polynomials. b) Find an expression for the electrostatic potential V(r,) for r
x - The General Science Journal, Science Journals
... What we have demonstrated is the very important character of the set of four-dimensional systems with three real coordinates and one imaginary coordinate. It is seen that these systems are oriented from each other, in a manner which can be represented by a combination of circular and hyperbolic angl ...
... What we have demonstrated is the very important character of the set of four-dimensional systems with three real coordinates and one imaginary coordinate. It is seen that these systems are oriented from each other, in a manner which can be represented by a combination of circular and hyperbolic angl ...
Chapter 31
... The induced electric field is a nonconservative field that is generated by a changing magnetic field The field cannot be an electrostatic field because if the field were electrostatic, and hence conservative, the line integral of E ds would be zero and it isn’t ...
... The induced electric field is a nonconservative field that is generated by a changing magnetic field The field cannot be an electrostatic field because if the field were electrostatic, and hence conservative, the line integral of E ds would be zero and it isn’t ...
Chapter 23 Objective Questions The magnitude of the electric force
... the two fixed charges a distance x from the midpoint between those charges (Fig. P23.14). (a) Show that if x is small compared with d, the motion of –Q is simple harmonic along the perpendicular bisector. (b) Determine the period of that motion. (c) How fast will the charge –Q be moving when it is a ...
... the two fixed charges a distance x from the midpoint between those charges (Fig. P23.14). (a) Show that if x is small compared with d, the motion of –Q is simple harmonic along the perpendicular bisector. (b) Determine the period of that motion. (c) How fast will the charge –Q be moving when it is a ...
HKDSE Physics Notes Waves Mechanics Mechanics Electricity
... 1.2 Kinetic theory (a) All matter is made up of very tiny particles. (b) These particles are constantly in motion. (c) Forces between particles: (i) When particles are close together, they attract/repel each other strongly. (ii) When particles are far apart, they hardly attract/repel each other. Sol ...
... 1.2 Kinetic theory (a) All matter is made up of very tiny particles. (b) These particles are constantly in motion. (c) Forces between particles: (i) When particles are close together, they attract/repel each other strongly. (ii) When particles are far apart, they hardly attract/repel each other. Sol ...
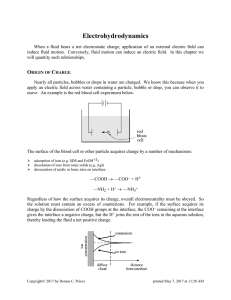
20. Electric Charge, Force, & Field
... Principle of superposition argument holds for all charge distributions Gauss’ & Colomb’s laws are both expression of the inverse square law. ...
... Principle of superposition argument holds for all charge distributions Gauss’ & Colomb’s laws are both expression of the inverse square law. ...