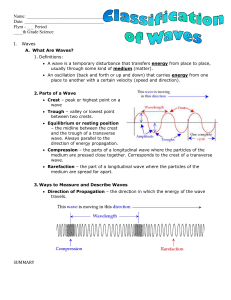
Lecture Notes 01: Introduction/Overview, Coulomb's Law, Electric Field, Principle of Superposition
... Note that if dielectric properties of free space (vacuum) were different than they are, then Coulomb’s Law, i.e. the force between electrically charged particles would be different. Consider a universe in which we could change the EM properties of the vacuum at will: im ( ε o → 0 ) : FC → ∞ !! “stro ...
... Note that if dielectric properties of free space (vacuum) were different than they are, then Coulomb’s Law, i.e. the force between electrically charged particles would be different. Consider a universe in which we could change the EM properties of the vacuum at will: im ( ε o → 0 ) : FC → ∞ !! “stro ...
Unit 14 - HKU Physics
... spherical distribution of charge between it and the center of the sphere. Since charges are free to move, the charge at A would respond to this force by moving toward the surface. Clearly, then, a uniform distribution of charge within the sphere’s volume is not in equilibrium. In fact, the argument ...
... spherical distribution of charge between it and the center of the sphere. Since charges are free to move, the charge at A would respond to this force by moving toward the surface. Clearly, then, a uniform distribution of charge within the sphere’s volume is not in equilibrium. In fact, the argument ...
Chapter 4: Electric Potential
... F = mg = constant and F = qE = constant . Because the forces are analogous, we can conclude that the electrical force is also a conservative force and gives rise to a potential energy. This is called the electrical potential energy associated with a charge in an electric field. As we mentioned in th ...
... F = mg = constant and F = qE = constant . Because the forces are analogous, we can conclude that the electrical force is also a conservative force and gives rise to a potential energy. This is called the electrical potential energy associated with a charge in an electric field. As we mentioned in th ...
Quanta and Waves Q` and solutions
... An electron microscope accelerates electrons until they have a wavelength of 40 pm (40 × 10 –12 m). Calculate the p.d. in the microscope required to do this assuming the electrons start from rest. ...
... An electron microscope accelerates electrons until they have a wavelength of 40 pm (40 × 10 –12 m). Calculate the p.d. in the microscope required to do this assuming the electrons start from rest. ...
Chapter 12
... exerted on a positive test charge. We can talk about the field at a point in space even if there is no charge at that point. The electric field can exist even in a vacuum. The field concept can also be used to define a gravitational field or a magnetic field, as well as others. ...
... exerted on a positive test charge. We can talk about the field at a point in space even if there is no charge at that point. The electric field can exist even in a vacuum. The field concept can also be used to define a gravitational field or a magnetic field, as well as others. ...
Chapter 12 Electrostatic Phenomena
... However, within each atom or molecule, charges can move. Each atom becomes an electric dipole: the center of the negative charge is slightly displaced from the center of the positive charge. The material is polarized. ...
... However, within each atom or molecule, charges can move. Each atom becomes an electric dipole: the center of the negative charge is slightly displaced from the center of the positive charge. The material is polarized. ...
What is Not Taken into Account and they Did Not Notice Ampere
... itself. Such dynamic properties of charge allow instead of two symmetrical laws of magneto electric and electromagnetic induction to introduce one law of electro-electrical induction, which is the fundamental law of induction. This method gives the possibility to directly solve all problems of induc ...
... itself. Such dynamic properties of charge allow instead of two symmetrical laws of magneto electric and electromagnetic induction to introduce one law of electro-electrical induction, which is the fundamental law of induction. This method gives the possibility to directly solve all problems of induc ...
Lecture #5 01/25/05
... For those of you who are interested, “Div, Grad, Curl and all that” in Ch 2 has a more quantitative analysis of Gauss’ law. ...
... For those of you who are interested, “Div, Grad, Curl and all that” in Ch 2 has a more quantitative analysis of Gauss’ law. ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... As a result of his own researchers, Gilbert himself proposed the real cause of the lining-up of a suspended magnetic needle or lodestone: The Earth itself is a lodestone and thus can act on other magnetic materials. Gilbert performed a clever experiment to show that his hypothesis was a likely one. ...
... As a result of his own researchers, Gilbert himself proposed the real cause of the lining-up of a suspended magnetic needle or lodestone: The Earth itself is a lodestone and thus can act on other magnetic materials. Gilbert performed a clever experiment to show that his hypothesis was a likely one. ...
Slide 1
... We calculate rate effects in RPCs by using the exact time dependend solutions for the electric field of a point charge on the resistive plate of an RPC. ...
... We calculate rate effects in RPCs by using the exact time dependend solutions for the electric field of a point charge on the resistive plate of an RPC. ...
Electromagnetism Laws and Equations
... we generally cannot take the electric field E outside the integral, like we did with Gauss’s Law, as the electric field won’t be constant between the two points, i.e. the magnitude of E is a function of l. E can only be taken out of the integral in equation 8 in uniform electric fields, i.e. between ...
... we generally cannot take the electric field E outside the integral, like we did with Gauss’s Law, as the electric field won’t be constant between the two points, i.e. the magnitude of E is a function of l. E can only be taken out of the integral in equation 8 in uniform electric fields, i.e. between ...
Note 3 - Introduction to Line integrals, Curl and Stoke`s Theorem
... Like for divergence the concept of curl is also important in electromagnetic theory. We showed in an example that ∇ × F = 0 for a rr̂2 field and since every electrostatic field is a superposition of fields on this form this result carries over to electric field E. ...
... Like for divergence the concept of curl is also important in electromagnetic theory. We showed in an example that ∇ × F = 0 for a rr̂2 field and since every electrostatic field is a superposition of fields on this form this result carries over to electric field E. ...
Aalborg Universitet Adaptive Review of Three Fundamental Questions in Physics
... of its improvement has been rising very extensively. The neutron and positron were discovered in 1932 which before that only electron, proton and photon were known. Today, the Standard Model of elementary particles is the leading dominant theory. The fundamental particle is a particle whose substruc ...
... of its improvement has been rising very extensively. The neutron and positron were discovered in 1932 which before that only electron, proton and photon were known. Today, the Standard Model of elementary particles is the leading dominant theory. The fundamental particle is a particle whose substruc ...
Document
... negative 2. Principle of conservation of charge:The algebraic sum of all the electric charges in any closed system is constant. 3. Quantization of charge: basic charge e = 1.6 10 19 C ...
... negative 2. Principle of conservation of charge:The algebraic sum of all the electric charges in any closed system is constant. 3. Quantization of charge: basic charge e = 1.6 10 19 C ...