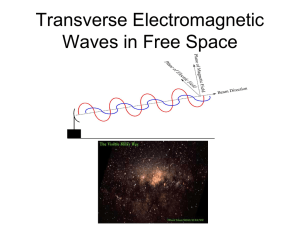
Transverse Electromagnetic Waves in Free Space
... where C is the rectangle in the XY plane of length l width x, and S is the open surface spanning the contour C ...
... where C is the rectangle in the XY plane of length l width x, and S is the open surface spanning the contour C ...
Page 1 Problem An electron is released from rest in a uniform
... This is an indication of how much more powerful the electric force is than the gravitational force. Problem 27 Problem An electron is released from rest in a uniform electric field and accelerates to the ...
... This is an indication of how much more powerful the electric force is than the gravitational force. Problem 27 Problem An electron is released from rest in a uniform electric field and accelerates to the ...
一 - 國立嘉義大學
... 4. A hollow material cubic of inner and outer length 8 and 9cm correspondingly, floats just half-submerged in a liquid of density 800kd/m3. What is the density of the material for which the cubic was made? (A) 0.4 (B) 1.0 (C) 1.3 (D) 1.7 5. A uniformly charged insulating sphere of radius R and total ...
... 4. A hollow material cubic of inner and outer length 8 and 9cm correspondingly, floats just half-submerged in a liquid of density 800kd/m3. What is the density of the material for which the cubic was made? (A) 0.4 (B) 1.0 (C) 1.3 (D) 1.7 5. A uniformly charged insulating sphere of radius R and total ...
Exercise 9 - Magnetism-The Lorentz Force
... (a) the speed of the electron, (b) the magnetic field, (c) the frequency of revolution, and (d) the period of motion. A cosmic ray proton (mp = 1.67 x 10-27 kg) strikes the Earth near the equator with a vertical velocity of 2.8 x 10 7 m/s. Assume that the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic ...
... (a) the speed of the electron, (b) the magnetic field, (c) the frequency of revolution, and (d) the period of motion. A cosmic ray proton (mp = 1.67 x 10-27 kg) strikes the Earth near the equator with a vertical velocity of 2.8 x 10 7 m/s. Assume that the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic ...
MCA PPT Review - Math On Monday
... Free fall is motion under the influence of gravity. When you toss an object in the air it is in free fall, whether it is going up or down. Its velocity will decrease as it goes up and increase as it goes down because the Earth pulls on it due to its gravity. Close to the surface, the acceleration du ...
... Free fall is motion under the influence of gravity. When you toss an object in the air it is in free fall, whether it is going up or down. Its velocity will decrease as it goes up and increase as it goes down because the Earth pulls on it due to its gravity. Close to the surface, the acceleration du ...
Force and Newton`s First Law
... 1st - A car will sit at a stoplight until you press the gas 2nd - It is harder to carry a box of rocks than a box of popcorn 3rd - When birds fly, they push their wings down in order to go up ...
... 1st - A car will sit at a stoplight until you press the gas 2nd - It is harder to carry a box of rocks than a box of popcorn 3rd - When birds fly, they push their wings down in order to go up ...
Ch 10 - Genovese
... Measuring Mass Using Orbital Motion • We’ve learned that a lot of things are connected. – The masses of bodies and their separation determines how much gravitational force they exert on each other. – The force on a body and its mass determines what acceleration it will experience. – Acceleration is ...
... Measuring Mass Using Orbital Motion • We’ve learned that a lot of things are connected. – The masses of bodies and their separation determines how much gravitational force they exert on each other. – The force on a body and its mass determines what acceleration it will experience. – Acceleration is ...
Correlation Of The Imbalance Of Electric Charges To Universal
... atom off, they still [can‘t find out] where mass and gravity come from. After watching it, I decided to light up a smoke, and opened a full pack of smokes (yes I know [it‘s] bad for my health)... the thing clear plastic wrapper I have, instantly stuck to my monitor thanks to static electricity. So h ...
... atom off, they still [can‘t find out] where mass and gravity come from. After watching it, I decided to light up a smoke, and opened a full pack of smokes (yes I know [it‘s] bad for my health)... the thing clear plastic wrapper I have, instantly stuck to my monitor thanks to static electricity. So h ...
Sects. 5.3 through 5.4
... Consider an object on which the net force is a resistive force proportional to the square of its speed. For example, assume that the resistive force acting on a speed skater is f = –kmv2, where k is a constant and m is the skater’s mass. The skater crosses the finish line of a straightline race with ...
... Consider an object on which the net force is a resistive force proportional to the square of its speed. For example, assume that the resistive force acting on a speed skater is f = –kmv2, where k is a constant and m is the skater’s mass. The skater crosses the finish line of a straightline race with ...