PLC Activity #2 Electric Fields & Potentials
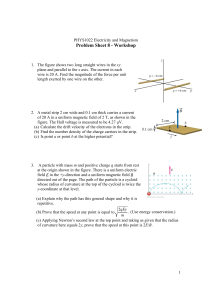
... direction of the field? (b) Four other particles similarly travel through small holes in either plate A or plate B and then into the region between the plates. Three have charges +q1, +q2, and -q3. The fourth (labeled n) is a neutron, which is electrically neutral. Does the speed of each of those fo ...
... direction of the field? (b) Four other particles similarly travel through small holes in either plate A or plate B and then into the region between the plates. Three have charges +q1, +q2, and -q3. The fourth (labeled n) is a neutron, which is electrically neutral. Does the speed of each of those fo ...
Circular Motion
... Gravitational force is the mutual force of attraction between particles of matter. Orbiting objects are in free fall- Newton observed that if an object were projected at just the right speed, the object would fall down toward Earth in just the same way that Earth curved out from under it. So, it wou ...
... Gravitational force is the mutual force of attraction between particles of matter. Orbiting objects are in free fall- Newton observed that if an object were projected at just the right speed, the object would fall down toward Earth in just the same way that Earth curved out from under it. So, it wou ...
I What is relativity? How did the concept of space-time arise?
... equations imply a speed for electromagnetic waves given by 1/ єoµo , where єo and µo are respectively the permittivity and permeability of free space. This when evaluated is in fact the speed of light (about 300,000 km/s). In spite of its stunning successes, it had one huge problem. Not all inertial ...
... equations imply a speed for electromagnetic waves given by 1/ єoµo , where єo and µo are respectively the permittivity and permeability of free space. This when evaluated is in fact the speed of light (about 300,000 km/s). In spite of its stunning successes, it had one huge problem. Not all inertial ...
Slide 1
... a) The electric field component in a particular direction. b) The magnetic field component in a particular direction. c) Either a or b above. d) The displacement of a charged particle in a direction transverse to the wave velocity direction. ...
... a) The electric field component in a particular direction. b) The magnetic field component in a particular direction. c) Either a or b above. d) The displacement of a charged particle in a direction transverse to the wave velocity direction. ...
Gravitation
... Galileo was the first who recognize the fact that all bodies, irrespective of their masses, fall towards the earth with a constant acceleration. The value of acceleration due to gravity obtained by Galileo is close to the more accurate value obtained later. Kepler who formulated three laws known ...
... Galileo was the first who recognize the fact that all bodies, irrespective of their masses, fall towards the earth with a constant acceleration. The value of acceleration due to gravity obtained by Galileo is close to the more accurate value obtained later. Kepler who formulated three laws known ...
Slide 1
... The total mechanical energy of a system is the sum of the kinetic energies (KE) of motion and potential energies (PE) associated with the position of the system in space. We express kinetic energy in two useful ways: ...
... The total mechanical energy of a system is the sum of the kinetic energies (KE) of motion and potential energies (PE) associated with the position of the system in space. We express kinetic energy in two useful ways: ...
Electric fields ppt File
... in their beaks to detect the electric fields produced by muscles in their prey ...
... in their beaks to detect the electric fields produced by muscles in their prey ...
Q ~ ~ ~ ~ # $ ~ ( 3 0 %... 1. (5%)
... 3. A sample of a monoatomic ideal gas occupies 5.00 L at atmospheric pressure and 300 K (point A in the figure). It is heated at constant volume to 3.00 atill (point B). Then, it is allowed to expand isothermally to 1.OO atm (yoint C) and at last is compressed isobarically (constant pressure) to it ...
... 3. A sample of a monoatomic ideal gas occupies 5.00 L at atmospheric pressure and 300 K (point A in the figure). It is heated at constant volume to 3.00 atill (point B). Then, it is allowed to expand isothermally to 1.OO atm (yoint C) and at last is compressed isobarically (constant pressure) to it ...
Problem Sheet 8
... (c) the –ve charge electrons move in the opposite direction to I. –e v x B points towards a where the electrons will accumulate. Thus Vb > Va 3. (a) Initially the electric field accelerates the particle upwards. It is then moving in a perpendicular B field that generates a force perpendicular to the ...
... (c) the –ve charge electrons move in the opposite direction to I. –e v x B points towards a where the electrons will accumulate. Thus Vb > Va 3. (a) Initially the electric field accelerates the particle upwards. It is then moving in a perpendicular B field that generates a force perpendicular to the ...
Chap 24 S2016
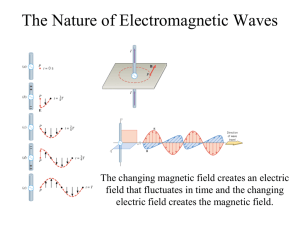
... All electromagnetic waves move through a vacuum at the same speed, and the symbol c is used to denote its value. This speed is called the speed of light in a vacuum and is c = 3.00 × 108 m/s. In air, electromagnetic waves travel at nearly the same speed as they do in a vacuum, but, in general, they ...
... All electromagnetic waves move through a vacuum at the same speed, and the symbol c is used to denote its value. This speed is called the speed of light in a vacuum and is c = 3.00 × 108 m/s. In air, electromagnetic waves travel at nearly the same speed as they do in a vacuum, but, in general, they ...
Math 1321 Week 14 Lab Worksheet Due Thursday 04/18
... Many forces in our known universe can be modeled with conservative force fields. In particular the gravitational field and the electric field due to a static point charge can be modeled in such a way. This is nice because it allows us to make computations such as how much interaction an object and t ...
... Many forces in our known universe can be modeled with conservative force fields. In particular the gravitational field and the electric field due to a static point charge can be modeled in such a way. This is nice because it allows us to make computations such as how much interaction an object and t ...
2005 C Mechanics 1. (a) ____ increases
... ____longer to rise ____longer to fall The acceleration is greater on the way up because the forces due to gravity and air resistance are in the same direction, thus, making a greater net force on the ball than on the way down where these two forces act in opposite directions. The distance it rises i ...
... ____longer to rise ____longer to fall The acceleration is greater on the way up because the forces due to gravity and air resistance are in the same direction, thus, making a greater net force on the ball than on the way down where these two forces act in opposite directions. The distance it rises i ...
true or false questions
... The rate at which velocity changes with time is called acceleration. When a car rounds a comer at a constant speed, its acceleration is zero. As a ball falls freely, the distance it falls each second is the same. If you slide a hockey puck across a frictionless ice rink, there must be a horizontal f ...
... The rate at which velocity changes with time is called acceleration. When a car rounds a comer at a constant speed, its acceleration is zero. As a ball falls freely, the distance it falls each second is the same. If you slide a hockey puck across a frictionless ice rink, there must be a horizontal f ...
Recitation Week 7
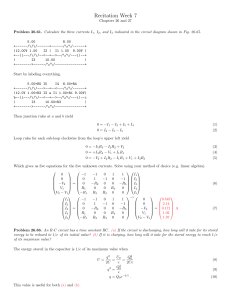
... Problem 26.86. An R-C circuit has a time constant RC. (a) If the circuit is discharging, how long will it take for its stored energy to be reduced to 1/e of its initial value? (b) If it is charging, how long will it take for the stored energy to reach 1/e of its maximum value? The energy stored in t ...
... Problem 26.86. An R-C circuit has a time constant RC. (a) If the circuit is discharging, how long will it take for its stored energy to be reduced to 1/e of its initial value? (b) If it is charging, how long will it take for the stored energy to reach 1/e of its maximum value? The energy stored in t ...
Lecture Notes: Y F Chapter 28
... The “strength” of the source of E is q r The “strength” of the source of B is qv ...
... The “strength” of the source of E is q r The “strength” of the source of B is qv ...