LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 12.Explain how the specific resistance of the material of a wire can be determined using Carey-Foster bridge. 13.Obtain an expression for the force acting on a charge q moving with a velocity v in a magnetic field of uniform intensity B. 14.Explain the theory of transformer. 15.Obtain an expression ...
... 12.Explain how the specific resistance of the material of a wire can be determined using Carey-Foster bridge. 13.Obtain an expression for the force acting on a charge q moving with a velocity v in a magnetic field of uniform intensity B. 14.Explain the theory of transformer. 15.Obtain an expression ...
Name Date_____________________ Per. ______ HW Physics
... 5. A beam of protons (mp = 1.672 × 10-27 kg) is accelerated to a speed of 5.0x106 m/s in a particle accelerator and emerges horizontally from the accelerator into a uniform magnetic field. What B field would cancel out the force of gravity and keep the beam of protons moving in a straight line? (Hi ...
... 5. A beam of protons (mp = 1.672 × 10-27 kg) is accelerated to a speed of 5.0x106 m/s in a particle accelerator and emerges horizontally from the accelerator into a uniform magnetic field. What B field would cancel out the force of gravity and keep the beam of protons moving in a straight line? (Hi ...
Electricity & Optics Physics 24100 Lecture 21 – Chapter 30 sec. 1-4
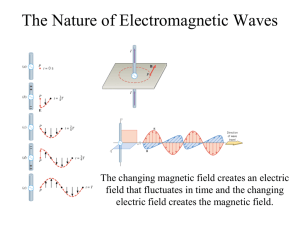
... but the electric flux is not zero. The electric flux changes as charge flows onto the capacitor. ...
... but the electric flux is not zero. The electric flux changes as charge flows onto the capacitor. ...
Home Work Problem Set 9
... 9-2 A charge q is distributed uniformly around a thin ring of radius r. The ring is rotating about an axis through its center and perpendicular to its plane, at an angular speed ω. (a) Show that the magnetic moment due to the rotating charge has magnitude (b) What is the direction of this magnetic m ...
... 9-2 A charge q is distributed uniformly around a thin ring of radius r. The ring is rotating about an axis through its center and perpendicular to its plane, at an angular speed ω. (a) Show that the magnetic moment due to the rotating charge has magnitude (b) What is the direction of this magnetic m ...
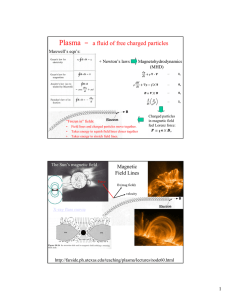
Lecture 14.1 : Electromagnetic Fields
... ‣Please fill out the evaluation form...it is completely confidential. ...
... ‣Please fill out the evaluation form...it is completely confidential. ...
ece221h1s: electric and magnetic fields
... Textbook (Ulaby): Note, in the problems below you can ignore the effects of any self-inductance of the loop. This means that you only have to consider the applied magnetic field, so you can ignore the induced magnetic field if there is one (i.e., if the loop is closed such that an induced current ca ...
... Textbook (Ulaby): Note, in the problems below you can ignore the effects of any self-inductance of the loop. This means that you only have to consider the applied magnetic field, so you can ignore the induced magnetic field if there is one (i.e., if the loop is closed such that an induced current ca ...
Two-level quantum dot in the Aharonov–Bohm ring. Towards understanding “phase lapse” P.
... energy scale (Δ < 0). When the gate voltage decreases, ε1 crosses the Fermi energy as the first, is followed by ε2 crossing. It results in a temporal decrease of particle number of ε1; a part of charge from ε1 can be absorbed into ε2 which becomes unoccupied when approaching the Fermi level. It resu ...
... energy scale (Δ < 0). When the gate voltage decreases, ε1 crosses the Fermi energy as the first, is followed by ε2 crossing. It results in a temporal decrease of particle number of ε1; a part of charge from ε1 can be absorbed into ε2 which becomes unoccupied when approaching the Fermi level. It resu ...
Exercise 9 - Magnetism-The Lorentz Force
... A cosmic ray proton (mp = 1.67 x 10-27 kg) strikes the Earth near the equator with a vertical velocity of 2.8 x 10 7 m/s. Assume that the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field at the equator is 30 mT. Calculate the ratio of the magnetic force on the proton to the gravitational force on ...
... A cosmic ray proton (mp = 1.67 x 10-27 kg) strikes the Earth near the equator with a vertical velocity of 2.8 x 10 7 m/s. Assume that the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field at the equator is 30 mT. Calculate the ratio of the magnetic force on the proton to the gravitational force on ...
Atomic Diffraction Dr. Janine Shertzer College of the Holy Cross
... The wave-particle duality is fundamental to quantum mechanics. Light can behave like a particle (photon); matter can behave like a wave. The wavelength associated with a particle is inversely proportional to its momentum p: λ = h / p, where h is Planck’s constant. For cold atoms, the wavelength is l ...
... The wave-particle duality is fundamental to quantum mechanics. Light can behave like a particle (photon); matter can behave like a wave. The wavelength associated with a particle is inversely proportional to its momentum p: λ = h / p, where h is Planck’s constant. For cold atoms, the wavelength is l ...