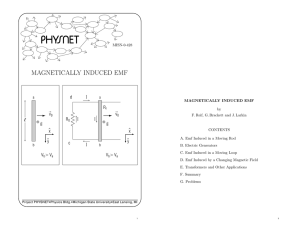
ABSTRACT Phase Transitions of High-Temperature Superconductors Su Li
... ns is the number density of superconducting electrons and m 4πλ2 Λ= 2 = c ns e2 ...
... ns is the number density of superconducting electrons and m 4πλ2 Λ= 2 = c ns e2 ...
Higher Secondary Exam -2011 CRACKER (PHYSICS) BRILLIANT SUCCESS
... third edition of Brilliant Success’s Study Package Series(2011). We are happy to receive the great feedbacks from our reader’s who had secured more that 90% in Physics (HSE-2010). It is our pride to get such great achievements from our esteemed readers who had come out with flying colours in HSE-201 ...
... third edition of Brilliant Success’s Study Package Series(2011). We are happy to receive the great feedbacks from our reader’s who had secured more that 90% in Physics (HSE-2010). It is our pride to get such great achievements from our esteemed readers who had come out with flying colours in HSE-201 ...
Normal incidence – propagating waves
... Examination of a standing wave suggests that it should be possible to insert another conductor (a conductive wall) at any of the nodes where the tangential electric field is zero without changing a structure of electric field! The applicable boundary condition, therefore, is that the tangential elec ...
... Examination of a standing wave suggests that it should be possible to insert another conductor (a conductive wall) at any of the nodes where the tangential electric field is zero without changing a structure of electric field! The applicable boundary condition, therefore, is that the tangential elec ...
Broad Feshbach Resonance in the 6Li-40K Mixture
... intersect with the energy of the threshold. Threshold effects cause the approximately linear magnetic field dependence of the bound-state energies to change to quadratic behavior close to the field of resonance [3,5]. This provides information about the width of a Feshbach resonance. The ABM, as dis ...
... intersect with the energy of the threshold. Threshold effects cause the approximately linear magnetic field dependence of the bound-state energies to change to quadratic behavior close to the field of resonance [3,5]. This provides information about the width of a Feshbach resonance. The ABM, as dis ...
Basic Atomic Physics
... all BEC atoms, is by evaporation, and the evaporation rate is limited by the elastic collision rate. Because of hydrogen’s small cross section, evaporation proceeds relatively slowly. The techniques for trapping and cooling hydrogen are described in detail elsewhere.5 The source of cold atoms is a c ...
... all BEC atoms, is by evaporation, and the evaporation rate is limited by the elastic collision rate. Because of hydrogen’s small cross section, evaporation proceeds relatively slowly. The techniques for trapping and cooling hydrogen are described in detail elsewhere.5 The source of cold atoms is a c ...
The Dipole Potential of Lipid Membranes
... that were necessary to quantify the dipole potential. Under such acidic conditions the former zwitterionic lipids could get protonated and even the phase of the lipids could change. In the highly artificial membranes used in their experiments one went without the addition of membrane proteins. In a ...
... that were necessary to quantify the dipole potential. Under such acidic conditions the former zwitterionic lipids could get protonated and even the phase of the lipids could change. In the highly artificial membranes used in their experiments one went without the addition of membrane proteins. In a ...
Introduction to Modern Solid State Physics
... where mi are integers. Such a lattice of building blocks is called the Bravais lattice. The crystal structure could be understood by the combination of the propertied of the building block (basis) and of the Bravais lattice. Note that • There is no unique way to choose ai . We choose a1 as shortest ...
... where mi are integers. Such a lattice of building blocks is called the Bravais lattice. The crystal structure could be understood by the combination of the propertied of the building block (basis) and of the Bravais lattice. Note that • There is no unique way to choose ai . We choose a1 as shortest ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... (where P is “a raffle is held” and S is “there are no entrants”) because when raffles are held, people generally enter them. That is, the best we can do is to say “If a raffle were held, there might be no entrants,” with S being a highly unlikely occurrence. Thus the introduction of the antecedent P ...
... (where P is “a raffle is held” and S is “there are no entrants”) because when raffles are held, people generally enter them. That is, the best we can do is to say “If a raffle were held, there might be no entrants,” with S being a highly unlikely occurrence. Thus the introduction of the antecedent P ...
Inconsistencies of the Adiabatic Theorem and the Berry Phase
... Hall-effect [7] to understanding of damping of collective excitations in finite fermi systems [8]. Furthermore, adiabatic theorem and Berry phase have played important roles in design of quantum algorithms [9] and implementation of geometric quantum computations [10]. Recently, Marzlin and Sanders ( ...
... Hall-effect [7] to understanding of damping of collective excitations in finite fermi systems [8]. Furthermore, adiabatic theorem and Berry phase have played important roles in design of quantum algorithms [9] and implementation of geometric quantum computations [10]. Recently, Marzlin and Sanders ( ...
Simultaneous Recovery of Two Ultrashort Laser
... by modification of only one of the fields, P std or Gstd, on a given iteration.18 On the even iterations we generate a new guess for P std by minimizing Z with respect to P std, and on the odd iterations we generate a new guess for Gstd by minimizing Z with respect to Gstd. The algorithm continues u ...
... by modification of only one of the fields, P std or Gstd, on a given iteration.18 On the even iterations we generate a new guess for P std by minimizing Z with respect to P std, and on the odd iterations we generate a new guess for Gstd by minimizing Z with respect to Gstd. The algorithm continues u ...
Light shining through walls
... For macroscopic objects like us these dimensions appear unresolved in every-day life. Since we cannot determine the position of strings in the extra-dimensions we can build an effective theory where all the extra dimensions are shrunk into our three dimensional world. This process is called compacti ...
... For macroscopic objects like us these dimensions appear unresolved in every-day life. Since we cannot determine the position of strings in the extra-dimensions we can build an effective theory where all the extra dimensions are shrunk into our three dimensional world. This process is called compacti ...