AP Physics- Magnetism
... to a variety of materials. He even found that the earth was a permanent magnet with a magnetic force field. He concluded that poles always appear in pairs and that magnet poles cannot be isolated. ...
... to a variety of materials. He even found that the earth was a permanent magnet with a magnetic force field. He concluded that poles always appear in pairs and that magnet poles cannot be isolated. ...
Magnetostatics (magnetic fields and forces)
... saw that a compass needle deflected from magnetic north when the electric current from the battery was switched on or off. This deflection interestred Ørsted convincing him that magnetic fields might radiate from all sides of a live wire just as light and heat do. However, the initial reaction was s ...
... saw that a compass needle deflected from magnetic north when the electric current from the battery was switched on or off. This deflection interestred Ørsted convincing him that magnetic fields might radiate from all sides of a live wire just as light and heat do. However, the initial reaction was s ...
Fundamental Physics II with Lab - myANC
... Email: Arkansas Northeastern College has partnered with Google to host email addresses for ANC students. myANCmail accounts are created for each student enrolled in the current semester and is the email address your instructor will use to communicate with you. Access your email account by going to h ...
... Email: Arkansas Northeastern College has partnered with Google to host email addresses for ANC students. myANCmail accounts are created for each student enrolled in the current semester and is the email address your instructor will use to communicate with you. Access your email account by going to h ...
Problem Set 09
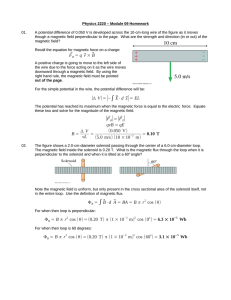
... the wire due to the force acting on it as the wire moves downward through a magnetic field. By using the right hand rule, the magnetic field must be pointed out of the page. For the simple potential in the wire, the potential difference will be: ...
... the wire due to the force acting on it as the wire moves downward through a magnetic field. By using the right hand rule, the magnetic field must be pointed out of the page. For the simple potential in the wire, the potential difference will be: ...
P3.3.1 - School
... b) This magnetism will interact with any other magnetism nearby. This could cause attraction or repulsion but can also cause MOVEMENT. c) The ELECTROMAGNET is a device in which magnetism can be SWITCHED ON or OFF and its STRENGTH can be CONTROLLED. d) It is designed to have AN IRON CORE, with a COIL ...
... b) This magnetism will interact with any other magnetism nearby. This could cause attraction or repulsion but can also cause MOVEMENT. c) The ELECTROMAGNET is a device in which magnetism can be SWITCHED ON or OFF and its STRENGTH can be CONTROLLED. d) It is designed to have AN IRON CORE, with a COIL ...
electric potential
... Often easier to apply than to solve directly Newton’s law equations. Only works for conservative forces. One has to be careful with SIGNS. ...
... Often easier to apply than to solve directly Newton’s law equations. Only works for conservative forces. One has to be careful with SIGNS. ...
Reference Frames and Relative Motion Uniform Circular Motion
... 1) Put your thumb in the direction of the F (right) and your fingers in the direction of v (up) The way that your fingers curl is the direction of B. 2) Put your palm in the direction of F (right), and your thumb in the direction of v (up), your fingers (keep them straight) point in the direction of ...
... 1) Put your thumb in the direction of the F (right) and your fingers in the direction of v (up) The way that your fingers curl is the direction of B. 2) Put your palm in the direction of F (right), and your thumb in the direction of v (up), your fingers (keep them straight) point in the direction of ...
• current and current density • conductivity and resistivity • chapter 29
... charge delivered in terms of electrons current direction defined to be in which positive charges seem to move (opposite to direction of electrons - charge carriers in metals, makes no difference at macroscopic level): current in a wire from positive to negative terminal of battery ...
... charge delivered in terms of electrons current direction defined to be in which positive charges seem to move (opposite to direction of electrons - charge carriers in metals, makes no difference at macroscopic level): current in a wire from positive to negative terminal of battery ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Slide 1 - plutonium
... Units of Chapter 27 • 27.1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields • 27.2 Electric Currents Produce Magnetic Fields • 27.3 Force on an Electric Current in a Magnetic Field; Definition of B: 1 & 2 • 27.4 Force on Electric Charge Moving in a Magnetic Field: 3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 ...
... Units of Chapter 27 • 27.1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields • 27.2 Electric Currents Produce Magnetic Fields • 27.3 Force on an Electric Current in a Magnetic Field; Definition of B: 1 & 2 • 27.4 Force on Electric Charge Moving in a Magnetic Field: 3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 ...
Voltage and Electric Potential
... conservative vector field. Therefore, we can write any electric field as the gradient of a specific scalar field V ( r ) : ...
... conservative vector field. Therefore, we can write any electric field as the gradient of a specific scalar field V ( r ) : ...
ELECTRIC FIELD LINES (19.6) There is an electric field vector for
... E vector at a point in space is tangent to the EFL through that point “Density” of EFLs (i.e. number of lines through unit area perpendicular to lines) is proportional to E (magnitude) in that region o Larger E → lines closer together EFLs start on positive charges and end on negative charges ...
... E vector at a point in space is tangent to the EFL through that point “Density” of EFLs (i.e. number of lines through unit area perpendicular to lines) is proportional to E (magnitude) in that region o Larger E → lines closer together EFLs start on positive charges and end on negative charges ...
Document
... • Compton showed Dp = hkinitial - hkfinal, so an photon (wave) is particle-like • DeBroglie hypothesized a particle could be wave-like, l = h/p • Davisson and Germer demonstrated wave-like interference phenomena for electrons to complete the duality model L1 January 18 ...
... • Compton showed Dp = hkinitial - hkfinal, so an photon (wave) is particle-like • DeBroglie hypothesized a particle could be wave-like, l = h/p • Davisson and Germer demonstrated wave-like interference phenomena for electrons to complete the duality model L1 January 18 ...
Faraday`s Law
... Complete the following sentence: When electrons from a heated filament accelerate through vacuum toward a positive plate, (a) only an electric field will be produced. (b) only a magnetic field will be produced. X (c) electromagnetic waves will be produced. (d) longitudinal waves will be produced. ...
... Complete the following sentence: When electrons from a heated filament accelerate through vacuum toward a positive plate, (a) only an electric field will be produced. (b) only a magnetic field will be produced. X (c) electromagnetic waves will be produced. (d) longitudinal waves will be produced. ...