Lecture 5
... charges is the algebraic sum of the electric potentials due to the individual charges ...
... charges is the algebraic sum of the electric potentials due to the individual charges ...
SS Review for Final
... An electric bell connected to a battery is sealed inside a large jar. What happens as the air is removed from the jar? (A) The bell’s loudness increases because of decreased air resistance. (B) The bell’s loudness decreases because sound waves can not travel through a vacuum. (C) The electric circu ...
... An electric bell connected to a battery is sealed inside a large jar. What happens as the air is removed from the jar? (A) The bell’s loudness increases because of decreased air resistance. (B) The bell’s loudness decreases because sound waves can not travel through a vacuum. (C) The electric circu ...
Solutions - Georgia Tech
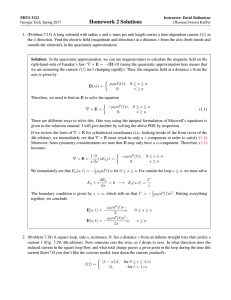
... Solution: The magnetic field inside the solenoid is B = µ0 nI and so the magnetic flux through a single turn is Φsingle turn = πR2 µ0 nI. There are nl turns through a length l, so the magnetic flux through nl turns is Φ = πR2 µ0 n2 Il. Since the self-inductance L is defined as the proportionality co ...
... Solution: The magnetic field inside the solenoid is B = µ0 nI and so the magnetic flux through a single turn is Φsingle turn = πR2 µ0 nI. There are nl turns through a length l, so the magnetic flux through nl turns is Φ = πR2 µ0 n2 Il. Since the self-inductance L is defined as the proportionality co ...
Transitions between atomic energy levels and selection rules
... final states and their normalization are chosen consistently. ...
... final states and their normalization are chosen consistently. ...
Getting the most action out of least action: A proposal
... and the sum’s magnitude depends on how far a path must deviate from the least-action world line to yield a contributed arrow that makes an angle of with the least-action arrow. Therefore it should be possible in principle to forego the sum entirely and calculate the arrow representing the sum over ...
... and the sum’s magnitude depends on how far a path must deviate from the least-action world line to yield a contributed arrow that makes an angle of with the least-action arrow. Therefore it should be possible in principle to forego the sum entirely and calculate the arrow representing the sum over ...
Ch01
... characterised by the fact that the voltages induced by time–varying magnetic fields (fluxes) are negligible with respect to any static or steady–state voltage developed in the same region. Equivalently, this state can be characterised by the fact that the magnetic energy density is negligible with r ...
... characterised by the fact that the voltages induced by time–varying magnetic fields (fluxes) are negligible with respect to any static or steady–state voltage developed in the same region. Equivalently, this state can be characterised by the fact that the magnetic energy density is negligible with r ...
Chapter 28 - The Magnetic Field
... The North Magnetic Pole moves over time due to magnetic changes in the Earth's core. In 2001, it was determined by the Geological Survey of Canada to lie near Ellesmere Island in northern Canada at 81.3°N 110.8°W. It was situated at 83.1°N 117.8°W in 2005. In 2009, while still situated within the Ca ...
... The North Magnetic Pole moves over time due to magnetic changes in the Earth's core. In 2001, it was determined by the Geological Survey of Canada to lie near Ellesmere Island in northern Canada at 81.3°N 110.8°W. It was situated at 83.1°N 117.8°W in 2005. In 2009, while still situated within the Ca ...
Magnetism - Norwell Public Schools
... the “Right Hand Rule.” Assuming the charge is positive, you point the fingers of your right hand in the direction of the charge’s velocity (v). While doing this, you face your palm in the direction of the magnetic field (B) [this can be envisioned as the direction in which your fingers will bend]. W ...
... the “Right Hand Rule.” Assuming the charge is positive, you point the fingers of your right hand in the direction of the charge’s velocity (v). While doing this, you face your palm in the direction of the magnetic field (B) [this can be envisioned as the direction in which your fingers will bend]. W ...
Gauss`s Law 3.1 Quiz
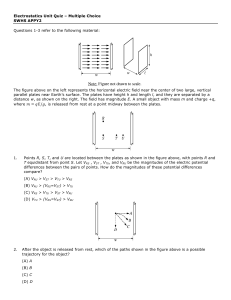
... the face of the cube shown below. Find flux of electric field through this face ...
... the face of the cube shown below. Find flux of electric field through this face ...
final exam review pdf
... 2) A standing wave is produced on a 5m long string. What is the wavelength of the wave produced from the 4th harmonic. a) 5m b) 10m c) 20m d) 2.5m e) 2m 3) The amount of potential energy an object has depends on the path taken to get to a certain height. a. True b. False 4) If a positively charged o ...
... 2) A standing wave is produced on a 5m long string. What is the wavelength of the wave produced from the 4th harmonic. a) 5m b) 10m c) 20m d) 2.5m e) 2m 3) The amount of potential energy an object has depends on the path taken to get to a certain height. a. True b. False 4) If a positively charged o ...
Diffusion of Arc Plasmas across a Magnetic Field
... where kTe is in electron volts and В in kilogauss. Note that this coefficient varies as B~l and is pressure independent, whereas the classical coefficient varies as B~2 and is directly proportional to the pressure. In order to test these theories, Neidigh3 has carried out a series of experiments at ...
... where kTe is in electron volts and В in kilogauss. Note that this coefficient varies as B~l and is pressure independent, whereas the classical coefficient varies as B~2 and is directly proportional to the pressure. In order to test these theories, Neidigh3 has carried out a series of experiments at ...
Electrostatics
... 5.1.5 Describe and explain the process of electrostatic induction If a positively charged object is brought near to a conducting material the charges in the conductor will move, part of the conductor near the positively charged object is negatively charged and the part far from the positively charge ...
... 5.1.5 Describe and explain the process of electrostatic induction If a positively charged object is brought near to a conducting material the charges in the conductor will move, part of the conductor near the positively charged object is negatively charged and the part far from the positively charge ...
MAGNETIC DEFLECTION
... magnet to set up a magnetic field that will exert a force on one electric current, the electron beam. Then we will use a second current in a solenoid to set up a magnetic field to exert a force on the electron beam. We think of the magnet or the second current in the solenoid as establishing a magne ...
... magnet to set up a magnetic field that will exert a force on one electric current, the electron beam. Then we will use a second current in a solenoid to set up a magnetic field to exert a force on the electron beam. We think of the magnet or the second current in the solenoid as establishing a magne ...