Lecture Notes: Y F Chapter 28
... End of Chapter 28 You are responsible for the material covered in T&F Sections 28.1 -28.7 You are expected to: ...
... End of Chapter 28 You are responsible for the material covered in T&F Sections 28.1 -28.7 You are expected to: ...
Aharonov–Bohm Effect and Magnetic Monopoles
... would make the magnet itself detectable along its whole length. Moreover, in quantum field theory the AB effect would disturb the free-wave modes of the charged fields — instead of plane waves we would get eigenswaves of some x-dependent differential operator. This would give rise to a Casimir effec ...
... would make the magnet itself detectable along its whole length. Moreover, in quantum field theory the AB effect would disturb the free-wave modes of the charged fields — instead of plane waves we would get eigenswaves of some x-dependent differential operator. This would give rise to a Casimir effec ...
Gauge invariance and the Aharonov-Bohm effect
... Gauge invariance. In quantum mechanics, it is possible to get transformations between gauges for state kets by means of a unitary operator, that is, we can define for each gauge transformation a unitary operator that acts on state kets. We shall try to obtain a form for this unitary operator, and by ...
... Gauge invariance. In quantum mechanics, it is possible to get transformations between gauges for state kets by means of a unitary operator, that is, we can define for each gauge transformation a unitary operator that acts on state kets. We shall try to obtain a form for this unitary operator, and by ...
Seminar 4: CHARGED PARTICLE IN ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD
... term generalized potential is also used). It can be thought that the possibility of using such a strange potential is purely academic but this is not the case! On the contrary, it appears that all the fundamental forces in physics can be expressed in the form (2), for a suitably chosen potential fun ...
... term generalized potential is also used). It can be thought that the possibility of using such a strange potential is purely academic but this is not the case! On the contrary, it appears that all the fundamental forces in physics can be expressed in the form (2), for a suitably chosen potential fun ...
Phys 208 - Recitation E-Fields
... A constant magnetic field, , is directed horizontally, parallel to the ground. A straight segment of copper wire, with mass density and diameter , is also parallel to the ground and perpendicular to the magnetic field. Determine the amount of current, in terms of the physical parameters of the syste ...
... A constant magnetic field, , is directed horizontally, parallel to the ground. A straight segment of copper wire, with mass density and diameter , is also parallel to the ground and perpendicular to the magnetic field. Determine the amount of current, in terms of the physical parameters of the syste ...
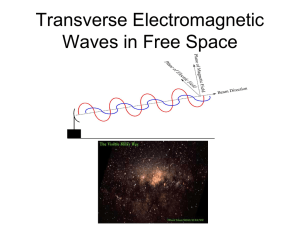
Chapter 9 The Nature of Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic Radiation
... • EMR requires no medium to travel- can travel thru a vacuum • Speed • 300,000 kilometers /sec • 186,000 miles /sec ...
... • EMR requires no medium to travel- can travel thru a vacuum • Speed • 300,000 kilometers /sec • 186,000 miles /sec ...
Key Homework 5.4. 1. a. A direct current I flows in a straight wire of
... b. Use the magnetic vector potential determined in (a) to determine the magnetic field B. c. Compare your answer with equation 5.35 and show that the answer is consistent with equation 5.35. ...
... b. Use the magnetic vector potential determined in (a) to determine the magnetic field B. c. Compare your answer with equation 5.35 and show that the answer is consistent with equation 5.35. ...
Worksheet 14 - Iowa State University
... 1. An electron is traveling to the right with a speed of 8.5 x 106 m/s when a magnetic field is turned on. The strength of the magnetic field is 500 Gauss, and it is directed into the paper. (a) Describe the path of the electron after the field has been turned on (assuming only magnetic effects). (b ...
... 1. An electron is traveling to the right with a speed of 8.5 x 106 m/s when a magnetic field is turned on. The strength of the magnetic field is 500 Gauss, and it is directed into the paper. (a) Describe the path of the electron after the field has been turned on (assuming only magnetic effects). (b ...
3. (a) The force on the electron is Thus, the magnitude of FB is 6.2
... to repeating the above computation with a change in the sign in the charge. Thus, FB has the same magnitude but points in the negative z direction, namely, ...
... to repeating the above computation with a change in the sign in the charge. Thus, FB has the same magnitude but points in the negative z direction, namely, ...
2015 chapter 16-17 study guide
... There is a repulsive force between two charged objects when? There is an attractive force between two charged objects when? When there is an equal amount of positive and negative charges on an object, the object is? Electric force varies depending on the? Electric field lines? Electric field lines i ...
... There is a repulsive force between two charged objects when? There is an attractive force between two charged objects when? When there is an equal amount of positive and negative charges on an object, the object is? Electric force varies depending on the? Electric field lines? Electric field lines i ...
Series 5 - Problems
... As a simple (but instructive) example of time evolution, let’s consider the first physical scenario we learned for time-independent quantum mechanics - the particle in a box. Take V (x) = 0 for 0 < x < L and V (x) = ∞ everwhere else. a) What are the energy eigenstates, the energy eigenvalues (in ter ...
... As a simple (but instructive) example of time evolution, let’s consider the first physical scenario we learned for time-independent quantum mechanics - the particle in a box. Take V (x) = 0 for 0 < x < L and V (x) = ∞ everwhere else. a) What are the energy eigenstates, the energy eigenvalues (in ter ...