$doc.title
... and magnetic fields are oscillating a) perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation of the wave b) perpendicular to each other and parallel to the direction of propagation of the ...
... and magnetic fields are oscillating a) perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation of the wave b) perpendicular to each other and parallel to the direction of propagation of the ...
Electromagnetic Waves
... When light enters a medium with a higher index of refraction it will bend toward the normal (the angle gets smaller). When light enters a medium with lower index (e.g. from water to air) then it will bend away from the normal (the angle gets larger). This creates an interesting possibility – what if ...
... When light enters a medium with a higher index of refraction it will bend toward the normal (the angle gets smaller). When light enters a medium with lower index (e.g. from water to air) then it will bend away from the normal (the angle gets larger). This creates an interesting possibility – what if ...
File - miss marsh science
... Proteins are made up of chains of small molecules called amino acids. There are over 20 different kinds of amino acid. Proteins are used by the body for growth and repair. ...
... Proteins are made up of chains of small molecules called amino acids. There are over 20 different kinds of amino acid. Proteins are used by the body for growth and repair. ...
Spectroscopy PPT
... Continuous – unbroken band of colors from a source sending out all visible wavelengths. ...
... Continuous – unbroken band of colors from a source sending out all visible wavelengths. ...
Proteomics2_2012
... Often focus on proteins identified by at least 2 different PSMs (or proteins with single PSMs of very high posterior probability) ...
... Often focus on proteins identified by at least 2 different PSMs (or proteins with single PSMs of very high posterior probability) ...
Determination of Amino Acid Sequence
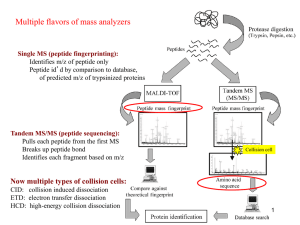
... Sequencing of peptides Ordering peptide fragments Compare sequences generated from different cleavage methods Locating disulfide bonds Comparison of cleavage fragment with or without breaking disulfide bonds ...
... Sequencing of peptides Ordering peptide fragments Compare sequences generated from different cleavage methods Locating disulfide bonds Comparison of cleavage fragment with or without breaking disulfide bonds ...
NEW GCSE REVISION Beginning of the Universe - crypt
... The red-shift of a distant galaxy ______________ with distance from us. a) i) The further away a distant galaxy is, the ______________ the speed at which it is moving away from us. ii) All the distant galaxies are moving ______________ from each other. b) i) The Universe must be ______________ becau ...
... The red-shift of a distant galaxy ______________ with distance from us. a) i) The further away a distant galaxy is, the ______________ the speed at which it is moving away from us. ii) All the distant galaxies are moving ______________ from each other. b) i) The Universe must be ______________ becau ...
Chapter 33 The Nature And Propagation Of Light
... So far the electric field vector oscillates in a fixed direction perpendicular to the light direction. That is called linear or planar polarization. But two electromagnetic waves can occupy the same location without interferring each other. (This is called the principle of superposition.) So one can ...
... So far the electric field vector oscillates in a fixed direction perpendicular to the light direction. That is called linear or planar polarization. But two electromagnetic waves can occupy the same location without interferring each other. (This is called the principle of superposition.) So one can ...
The Synthesis of Proteins
... consisting of three bases that selects specific amino acids and “escorts” them to the growing protein chain so that they join at just the proper position. ...
... consisting of three bases that selects specific amino acids and “escorts” them to the growing protein chain so that they join at just the proper position. ...
Page 1 Proteins - Made up of amino acid monomers (yep, you got it
... common, but weak formed when δ+ H from –OH or –NH of the R group attract the δ- O of a –CO group, or another R group Ionic bonds: form between amino and carboyl groups on some R groups stronger than hydrogen bonds, but are weaker than disulphide bonds Disulphide bonds: covalent bond that is formed b ...
... common, but weak formed when δ+ H from –OH or –NH of the R group attract the δ- O of a –CO group, or another R group Ionic bonds: form between amino and carboyl groups on some R groups stronger than hydrogen bonds, but are weaker than disulphide bonds Disulphide bonds: covalent bond that is formed b ...
Flow Cytometry
... antibody isotype • E.g. we have a mouse IgG2a anti-CD14-FITC antibody so an isotype would be mouse IgG2a-FITC, usually used at same concentration under same conditions • Allow a measure of non-specific binding ...
... antibody isotype • E.g. we have a mouse IgG2a anti-CD14-FITC antibody so an isotype would be mouse IgG2a-FITC, usually used at same concentration under same conditions • Allow a measure of non-specific binding ...
Basis of Thermophily
... • Phylum Euarchaeota contains highly basic histone-like proteins that wind and compact DNA into nucleosome-like structures ...
... • Phylum Euarchaeota contains highly basic histone-like proteins that wind and compact DNA into nucleosome-like structures ...
A PRESENTATION ON AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS
... Peptides are formed by condensation of the -COOH group of one amino acid and the NH group of another amino acid. The acid forming the peptide bond is named first. Example: if a dipeptide is formed from alanine and glycine so that the COOH group of glycine reacts with the NH group of alanine, then th ...
... Peptides are formed by condensation of the -COOH group of one amino acid and the NH group of another amino acid. The acid forming the peptide bond is named first. Example: if a dipeptide is formed from alanine and glycine so that the COOH group of glycine reacts with the NH group of alanine, then th ...
more details
... rest of the protein undergoes co-evolution that increases the propensity of this new amino acid. As a result, subsequent substitutions at this location will be, in general, less favourable. This has similarities to the phenomenon known as the "Stokes shift" in spectroscopy, where vibrational relaxat ...
... rest of the protein undergoes co-evolution that increases the propensity of this new amino acid. As a result, subsequent substitutions at this location will be, in general, less favourable. This has similarities to the phenomenon known as the "Stokes shift" in spectroscopy, where vibrational relaxat ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... • Secondary structure = domains of repeating structures, such as β-pleated sheets and α-helices • Tertiary structure = 3-dimensional shape of a folded polypeptide, maintained by disulfide bonds, electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic effects ...
... • Secondary structure = domains of repeating structures, such as β-pleated sheets and α-helices • Tertiary structure = 3-dimensional shape of a folded polypeptide, maintained by disulfide bonds, electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic effects ...
Light
... b) People emit infrared light that is invisible to our eyes. c) People are too small to emit enough light for us to see. ...
... b) People emit infrared light that is invisible to our eyes. c) People are too small to emit enough light for us to see. ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.