Chapters 6 and 8: Some Additional Forces
... the mass of the earth. It is also much larger, with a radius of 5.85 x 107 m. What is the value of g on the surface of Saturn? ...
... the mass of the earth. It is also much larger, with a radius of 5.85 x 107 m. What is the value of g on the surface of Saturn? ...
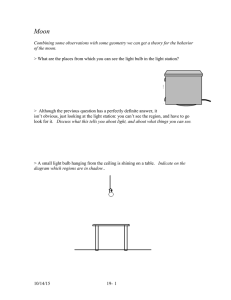
Moon
... many lunar months are there in a year? We found that there are 29.5 days between full moons. Unlike the length of a day, this does not change appreciably from month to month. Note that it is just a bit shorter than most months (which are 30 or 31 days long), so the date of full moon creeps a day or ...
... many lunar months are there in a year? We found that there are 29.5 days between full moons. Unlike the length of a day, this does not change appreciably from month to month. Note that it is just a bit shorter than most months (which are 30 or 31 days long), so the date of full moon creeps a day or ...
Solar System
... • Nucleus = solid portion of a comet (inner layer). • Coma = halo of dust and gas that forms around the nucleus of a comet. Comets have “tails” that may extend millions of km into space! They face away from the sun. • Like other objects in space, comets orbit the sun. Comets have an elliptical shape ...
... • Nucleus = solid portion of a comet (inner layer). • Coma = halo of dust and gas that forms around the nucleus of a comet. Comets have “tails” that may extend millions of km into space! They face away from the sun. • Like other objects in space, comets orbit the sun. Comets have an elliptical shape ...
Review: Quiz 1 Concepts Celestial sphere
... our frames of reference. Horizon: The horizontal circle. Divides the celestial sphere into up (visible), and down (hidden). Meridian: The vertical circle that touches the poles. Divides east & west. Various kinds of days begin and end with the sun on the meridian. Celestial equator: Divides north & ...
... our frames of reference. Horizon: The horizontal circle. Divides the celestial sphere into up (visible), and down (hidden). Meridian: The vertical circle that touches the poles. Divides east & west. Various kinds of days begin and end with the sun on the meridian. Celestial equator: Divides north & ...
Comets, Meteors, and Asteroids
... Lunar Rocks Lunar rocks are igneous, and most rocks near the surface are composed mainly of oxygen and ...
... Lunar Rocks Lunar rocks are igneous, and most rocks near the surface are composed mainly of oxygen and ...
History of Astronomy
... average distance from the Sun, which is the semimajor axis distance, will take longer to circle the Sun Third law hints at the nature of the force holding the planets in orbit Third law can be used to determine the semimajor axis, a, if the period, P, is known, a measurement that is not difficul ...
... average distance from the Sun, which is the semimajor axis distance, will take longer to circle the Sun Third law hints at the nature of the force holding the planets in orbit Third law can be used to determine the semimajor axis, a, if the period, P, is known, a measurement that is not difficul ...
9/29/16 pacing planet distance
... beginning of this line. Now pace off the distances to each planet as shown in the last column of the distance table on the next page. ...
... beginning of this line. Now pace off the distances to each planet as shown in the last column of the distance table on the next page. ...
Unit A: Trees and Forests
... given names to, like Orion or the Big Dipper. The stars are not really grouped together in space, but look like they are from Earth. People in different places on the Earth have different parts of the night sky blocked out by the Earth itself, so Canadians cannot see all the same constellations that ...
... given names to, like Orion or the Big Dipper. The stars are not really grouped together in space, but look like they are from Earth. People in different places on the Earth have different parts of the night sky blocked out by the Earth itself, so Canadians cannot see all the same constellations that ...
`Magnificent Desolation` transcript
... American astronaut Neil Armstrong spoke these famous words when he made history on July 20 1969, as the first human being to set foot on the Moon. The moon is our nearest neighbour in space; it is our only natural satellite and has been known since prehistoric times. At three and a half thousand ...
... American astronaut Neil Armstrong spoke these famous words when he made history on July 20 1969, as the first human being to set foot on the Moon. The moon is our nearest neighbour in space; it is our only natural satellite and has been known since prehistoric times. At three and a half thousand ...
In the Spring of 2007 two of us began planning a new course in
... b. The Moon is somewhat flattened and disk-like. It appears more or less round depending on the precise angle from which we see it. c. Earth’s clouds cover potions of the Moon resulting in the changing phases that we see. d. The sunlight reflected from Earth lights up the Moon. It is less effective ...
... b. The Moon is somewhat flattened and disk-like. It appears more or less round depending on the precise angle from which we see it. c. Earth’s clouds cover potions of the Moon resulting in the changing phases that we see. d. The sunlight reflected from Earth lights up the Moon. It is less effective ...
Common Misconceptions in Astronomy and History
... Copernicus was the First Person to Postulate a Sun-Centered Universe Actually, it was the Greek, Heracleides (388 BC - 315 BC) and later, Aristarchus of Samos (310 BC - 230 BC) who first entertained the heliocentric notion that a rotating Earth could be in revolution around the sun. The concept lost ...
... Copernicus was the First Person to Postulate a Sun-Centered Universe Actually, it was the Greek, Heracleides (388 BC - 315 BC) and later, Aristarchus of Samos (310 BC - 230 BC) who first entertained the heliocentric notion that a rotating Earth could be in revolution around the sun. The concept lost ...
Skylights - May 2017 - Astronomical Society of Northern New England
... times larger than our sun and probably has at least one Jupiter-sized planet orbiting around it. Pioneer 10, our first deep-space probe launched in 1972, will pass fairly close to this star in about 2 million years if no one intercepts it before then. So when you look at these two orange objects in ...
... times larger than our sun and probably has at least one Jupiter-sized planet orbiting around it. Pioneer 10, our first deep-space probe launched in 1972, will pass fairly close to this star in about 2 million years if no one intercepts it before then. So when you look at these two orange objects in ...
The Orrery - Eli Whitney Museum
... should find that the stars move toward the West indicating that the Earth’s orbit in also counter-clockwise. This experiment requires more precise measurement and often many days between readings. Remember the Earth only moves one degree each day in its trip around the Sun. Do you see a pattern? Mos ...
... should find that the stars move toward the West indicating that the Earth’s orbit in also counter-clockwise. This experiment requires more precise measurement and often many days between readings. Remember the Earth only moves one degree each day in its trip around the Sun. Do you see a pattern? Mos ...
ON THE ORIGIN OF THE MOON
... additional mathematical computations (5) have shown that large gas planets can form not in times order 10 million years, as it was before estimated, but just in about one century! And quite strong arguments by Ackerman (6,7) even indicate that the so called gas planets may have a solid inner part, c ...
... additional mathematical computations (5) have shown that large gas planets can form not in times order 10 million years, as it was before estimated, but just in about one century! And quite strong arguments by Ackerman (6,7) even indicate that the so called gas planets may have a solid inner part, c ...
Astrophysics - Student Reference Packet
... stays in the same place and the other stars appear to move in circular paths around this “celestial pole”. They complete one rotation every 24 hrs (called diurnal motion) although we can only observe part of their path (we can’t see them during the day because the scattered blue light of our Sun is ...
... stays in the same place and the other stars appear to move in circular paths around this “celestial pole”. They complete one rotation every 24 hrs (called diurnal motion) although we can only observe part of their path (we can’t see them during the day because the scattered blue light of our Sun is ...
The Nature of Force
... pulls another object, you say that the first object is exerting a force on the second object. • Forces are described not only by how strong they are, but also by the direction in which they act. ...
... pulls another object, you say that the first object is exerting a force on the second object. • Forces are described not only by how strong they are, but also by the direction in which they act. ...
The Facts on the Moon
... results in the moon always keeping one side turned toward the earth and the other side turned away from the earth. This type of motion is called synchronous rotation. The side turned away from the earth is called the moon’s dark side, even though it is lit half of the time. The moo ...
... results in the moon always keeping one side turned toward the earth and the other side turned away from the earth. This type of motion is called synchronous rotation. The side turned away from the earth is called the moon’s dark side, even though it is lit half of the time. The moo ...
Final Exam Review – December 2015
... 30. Describe the characteristics of the sun below. Type of star: _________________________________________ Size of the sun: _______________________________________ Color of the sun: ______________________________________ Location of the sun: ___________________________________ How much closer is the ...
... 30. Describe the characteristics of the sun below. Type of star: _________________________________________ Size of the sun: _______________________________________ Color of the sun: ______________________________________ Location of the sun: ___________________________________ How much closer is the ...
Astronomy 101 Course Review and Summary
... Aristotle (4th cent BC) showed that the Earth is round. Greek astronomers developed a geocentric model for the universe. Ptolemy (2nd cent) used epicycles to explain retrograde motion of planers. Copernicus (16th cent) proposed a heliocentric model for the universe. In the model of Copernicus, retro ...
... Aristotle (4th cent BC) showed that the Earth is round. Greek astronomers developed a geocentric model for the universe. Ptolemy (2nd cent) used epicycles to explain retrograde motion of planers. Copernicus (16th cent) proposed a heliocentric model for the universe. In the model of Copernicus, retro ...
Fulltext PDF
... There is no doubt that Newton's Principia was a monumental intellectual achievement of a magnitude so far unsurpassed. Newton tied all known laws of terrestrial mechanics and celestial mechanics into a firm, single physical basis. The basis of his conclusions were primarily the observations of bodie ...
... There is no doubt that Newton's Principia was a monumental intellectual achievement of a magnitude so far unsurpassed. Newton tied all known laws of terrestrial mechanics and celestial mechanics into a firm, single physical basis. The basis of his conclusions were primarily the observations of bodie ...
43 Astronomy 43.1 Recall that Earth is one of the many planets in
... Objects on Earth cast shadows that help show Earth’s rotation. The angle of the Sun changes the length of an object’s shadow. ● In the morning, the Sun appears low in the sky; objects cast long shadows ● As Earth rotates, the Sun appears higher in the sky, and the shadows get shorter ● At noo ...
... Objects on Earth cast shadows that help show Earth’s rotation. The angle of the Sun changes the length of an object’s shadow. ● In the morning, the Sun appears low in the sky; objects cast long shadows ● As Earth rotates, the Sun appears higher in the sky, and the shadows get shorter ● At noo ...
astronomy ch 2 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Galileo discovered that Venus, like the Moon, undergoes a series of phases as seen from Earth. In the Ptolemaic (geocentric) model, Venus would be seen in only new or crescent phases. However, as Galileo observed, Venus is seen in all phases, which agrees with the Copernican model as shown. ...
... Galileo discovered that Venus, like the Moon, undergoes a series of phases as seen from Earth. In the Ptolemaic (geocentric) model, Venus would be seen in only new or crescent phases. However, as Galileo observed, Venus is seen in all phases, which agrees with the Copernican model as shown. ...
Unit XII Study Guide
... ____ 29. Much of the mass of the universe may be composed of a. electromagnetic waves. c. background radiation. b. cosmic microwaves. d. dark matter. Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 30. Because Earth’s orbit around the sun is an ellipse, and Earth is not always the same distance from ...
... ____ 29. Much of the mass of the universe may be composed of a. electromagnetic waves. c. background radiation. b. cosmic microwaves. d. dark matter. Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 30. Because Earth’s orbit around the sun is an ellipse, and Earth is not always the same distance from ...
EarthScience_Topic 3
... The right half of the Moon appears lighted and the left side of the Moon appears dark. During the time between the New Moon and the First Quarter Moon, the part of the Moon that appears lighted gets larger and larger every day, and will continue to grow until the Full Moon. ...
... The right half of the Moon appears lighted and the left side of the Moon appears dark. During the time between the New Moon and the First Quarter Moon, the part of the Moon that appears lighted gets larger and larger every day, and will continue to grow until the Full Moon. ...