109 solar system prt 1.p65.p65
... 2. Describe and explain what would happen to any object moving in a circular path if the centripetal force were removed. 3. The radius of the moon’s orbit around the earth is 384,000km. Calculate the distance it travels in one orbit. The orbital period of the moon is 27.3 days. How fast does the moo ...
... 2. Describe and explain what would happen to any object moving in a circular path if the centripetal force were removed. 3. The radius of the moon’s orbit around the earth is 384,000km. Calculate the distance it travels in one orbit. The orbital period of the moon is 27.3 days. How fast does the moo ...
Archaeoastronomy, Astronomy of Celts, A. Gaspani
... explaining the apparent motion of the Sun, the Moon, the visible planets, and the stars. Another set of questions about astronomical knowledge arises from the need to carry out some measurements of the position of the observed celestial bodies in order to collect the basic data required to compute t ...
... explaining the apparent motion of the Sun, the Moon, the visible planets, and the stars. Another set of questions about astronomical knowledge arises from the need to carry out some measurements of the position of the observed celestial bodies in order to collect the basic data required to compute t ...
the particle was on Earth`s surface
... 14-2 Newton's Law of Gravitation Nowton published the law of gravitation In 1687. It may be stated as follows: Every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directely proportional to the product of the masses of the particles and inversely proportinal to the squa ...
... 14-2 Newton's Law of Gravitation Nowton published the law of gravitation In 1687. It may be stated as follows: Every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directely proportional to the product of the masses of the particles and inversely proportinal to the squa ...
Earth Science Exams and Keys 2014 Season
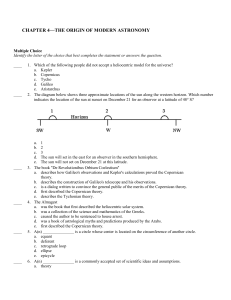
... 51. Eclipses do NOT occur every month because the Moon’s D) period of rotation and period of revolution are A) rate of rotation is 15o each hour B) orbit is inclined to Earth’s orbit the same C) period of revolution is 27.3 days The diagram below represents a model of a moon, or satellite, orbiting ...
... 51. Eclipses do NOT occur every month because the Moon’s D) period of rotation and period of revolution are A) rate of rotation is 15o each hour B) orbit is inclined to Earth’s orbit the same C) period of revolution is 27.3 days The diagram below represents a model of a moon, or satellite, orbiting ...
Presentation - ScienceScene
... Tension - Tension force is the force exerted by a string, spring, beam or other object which is being stretched compressed. The electric forces among the molecules give rise to the force. ...
... Tension - Tension force is the force exerted by a string, spring, beam or other object which is being stretched compressed. The electric forces among the molecules give rise to the force. ...
University of Arizona Department of Astronomy
... increases with decreasing distance •When children hear a car’s horn, they learn that sound intensity increases with decreasing distance •When children see a bright flashlight, they learn that brightness increases with decreasing distance CLOSE MEANS MORE ...
... increases with decreasing distance •When children hear a car’s horn, they learn that sound intensity increases with decreasing distance •When children see a bright flashlight, they learn that brightness increases with decreasing distance CLOSE MEANS MORE ...
Celestial Motions
... – The tilt of the Earth’s axis causes sunlight to hit different parts of the Earth more directly during the summer and less directly during the winter. – We can specify the position of an object in the local sky by its altitude above the horizon and its direction along the horizon. – The summer and ...
... – The tilt of the Earth’s axis causes sunlight to hit different parts of the Earth more directly during the summer and less directly during the winter. – We can specify the position of an object in the local sky by its altitude above the horizon and its direction along the horizon. – The summer and ...
Revision sheet - Nour Al Maaref International School
... A. Centripetal force is a force that makes a body follow a curved path. B. Centripetal force is a force that makes objects move in straight lines. C. Centripetal force is a force that is directed away from a center of rotation. D. Centripetal force is a force in which a smaller body acts on a larger ...
... A. Centripetal force is a force that makes a body follow a curved path. B. Centripetal force is a force that makes objects move in straight lines. C. Centripetal force is a force that is directed away from a center of rotation. D. Centripetal force is a force in which a smaller body acts on a larger ...
How the Earth Moves Transcript
... stars – in reality the stars are widely separated in their distance away from Earth, and only appear to be close as they lie in the same direction when viewed from our vantage point. However, that wasn’t clear to most ancient civilisation, who (quite reasonably) believed that all the stars were loc ...
... stars – in reality the stars are widely separated in their distance away from Earth, and only appear to be close as they lie in the same direction when viewed from our vantage point. However, that wasn’t clear to most ancient civilisation, who (quite reasonably) believed that all the stars were loc ...
CHP 4
... b. They contain horizon sight lines to astronomical phenomena. c. They were built without the influence of classical Greek astronomy. d. They indicate the rising and setting points of the moon. e. They are in the northern hemisphere. Ptolemy's model of the universe a. was heliocentric. b. included e ...
... b. They contain horizon sight lines to astronomical phenomena. c. They were built without the influence of classical Greek astronomy. d. They indicate the rising and setting points of the moon. e. They are in the northern hemisphere. Ptolemy's model of the universe a. was heliocentric. b. included e ...
rotation of the Earth
... ancient Greeks were already aware that the Moon would appear in slightly different locations relative to the stars when viewed from different locations on the Earth, and used this effect to accurately estimate its distance from Earth. However, the lack of any parallax between the stars demonstrated ...
... ancient Greeks were already aware that the Moon would appear in slightly different locations relative to the stars when viewed from different locations on the Earth, and used this effect to accurately estimate its distance from Earth. However, the lack of any parallax between the stars demonstrated ...
Introduction to Astronomy - Northumberland Astronomical Society
... Aristarchus of Samos attempted to calculate the sizes of the Sun and Moon their distances from the Earth. For example: ...
... Aristarchus of Samos attempted to calculate the sizes of the Sun and Moon their distances from the Earth. For example: ...
Chapter 2: The Copernican Revolution
... idea of its complexity. The earth (E) does not simply orbit the sun (S). Rather, E orbits the point OE, which orbits O, which orbits S. Thus three circles are needed. (The diagram is not drawn to scale. In Copernicus’s model the two minor epicycles were very small in comparison to the earth‐s ...
... idea of its complexity. The earth (E) does not simply orbit the sun (S). Rather, E orbits the point OE, which orbits O, which orbits S. Thus three circles are needed. (The diagram is not drawn to scale. In Copernicus’s model the two minor epicycles were very small in comparison to the earth‐s ...
Why do Earth satellites stay up?
... Of course, the answer to why satellites do not crash is known, in the sense that aerospace engineers design orbits that are stable over the expected lifetime of the satellite. Nevertheless the calculations in textbooks on astrodynamics and celestial mechanics do not provide a physical explanation fo ...
... Of course, the answer to why satellites do not crash is known, in the sense that aerospace engineers design orbits that are stable over the expected lifetime of the satellite. Nevertheless the calculations in textbooks on astrodynamics and celestial mechanics do not provide a physical explanation fo ...
Dear Teachers - Jeffrey Bennett
... • There are about 100 billion galaxies in the observable universe, and you can assume that a typical galaxy has about 100 billion stars. Activity. Use the given data to calculate the approximate number of grains of dry sand on all Earth’s beaches combined. Compare to the number of stars in the obser ...
... • There are about 100 billion galaxies in the observable universe, and you can assume that a typical galaxy has about 100 billion stars. Activity. Use the given data to calculate the approximate number of grains of dry sand on all Earth’s beaches combined. Compare to the number of stars in the obser ...
The New Astronomy and Cosmology of the Scientific Revolution
... Celestial and earthly motion was understood in terms of bodies seeking their natural resting places. By the completion of the Scientific Revolution, most Aristotelian notions were overthrown. Space was reconceived as isotropic and non-hierarchical. Matter was seen as compositionally consistent throu ...
... Celestial and earthly motion was understood in terms of bodies seeking their natural resting places. By the completion of the Scientific Revolution, most Aristotelian notions were overthrown. Space was reconceived as isotropic and non-hierarchical. Matter was seen as compositionally consistent throu ...
The New Astronomy and Cosmology of the Scientific Revolution
... Celestial and earthly motion was understood in terms of bodies seeking their natural resting places. By the completion of the Scientific Revolution, most Aristotelian notions were overthrown. Space was reconceived as isotropic and non-hierarchical. Matter was seen as compositionally consistent throu ...
... Celestial and earthly motion was understood in terms of bodies seeking their natural resting places. By the completion of the Scientific Revolution, most Aristotelian notions were overthrown. Space was reconceived as isotropic and non-hierarchical. Matter was seen as compositionally consistent throu ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... every 27.32 days on average. This period, called the sidereal month, represents the time it takes the Moon to make one full pass through the sky with respect to the stars. So if one night we find the Moon in the vicinity of a bright star, a sidereal month must pass before the Moon returns to the sam ...
... every 27.32 days on average. This period, called the sidereal month, represents the time it takes the Moon to make one full pass through the sky with respect to the stars. So if one night we find the Moon in the vicinity of a bright star, a sidereal month must pass before the Moon returns to the sam ...
Dorn_projectF08 - Bowling Green State University
... changing appearance of its surface. The Moon orbits at roughly 380,000 km. distance with a diameter of 3475 km., compared to Earth it is 27% smaller with a reflection magnitude at opposition of -12.7. The best views through a telescope are between the crescent and quarter phases when angled light fr ...
... changing appearance of its surface. The Moon orbits at roughly 380,000 km. distance with a diameter of 3475 km., compared to Earth it is 27% smaller with a reflection magnitude at opposition of -12.7. The best views through a telescope are between the crescent and quarter phases when angled light fr ...
Chapter 3
... In addition, the declinations of the planets and the moon are influenced by the inclinations of their own orbits to the ecliptic. The plane of the moon's orbit, for example, is inclined to the ecliptic by approx. 5° and makes a tumbling movement (precession, see below) with a cycle time of 18.6 year ...
... In addition, the declinations of the planets and the moon are influenced by the inclinations of their own orbits to the ecliptic. The plane of the moon's orbit, for example, is inclined to the ecliptic by approx. 5° and makes a tumbling movement (precession, see below) with a cycle time of 18.6 year ...
basics of astronomy through role play
... This handbook on using role play to communicate basics of astronomy to young children is inspired by Mr Samar Bagchi, who used the technique with great efficacy to explain astronomical concepts not only to children but also adults. His enthusiastic and lively sessions made such a lasting impression ...
... This handbook on using role play to communicate basics of astronomy to young children is inspired by Mr Samar Bagchi, who used the technique with great efficacy to explain astronomical concepts not only to children but also adults. His enthusiastic and lively sessions made such a lasting impression ...
Chapter 13 Problems
... spherical neutron star is twice the mass of the Sun and its radius is 10.0 km. Determine the greatest possible angular speed it can have so that the matter at the surface of the star on its equator is just held in orbit by the gravitational force. ...
... spherical neutron star is twice the mass of the Sun and its radius is 10.0 km. Determine the greatest possible angular speed it can have so that the matter at the surface of the star on its equator is just held in orbit by the gravitational force. ...
1Barycenter Our solar system consists of the Sun and the
... Binary bodies are two celestial bodies held together by mutual gravitational attraction. Gravity is a force of attraction between all objects in the universe. Examples of binary bodies are two stars, a planet and its sun, or a planet and its moon. Binary bodies behave somewhat as if they were connec ...
... Binary bodies are two celestial bodies held together by mutual gravitational attraction. Gravity is a force of attraction between all objects in the universe. Examples of binary bodies are two stars, a planet and its sun, or a planet and its moon. Binary bodies behave somewhat as if they were connec ...
Solar System - HMXEarthScience
... A Newly Discovered Planet Scientists studying a Sun-like star named Ogle-Tr-3 discovered a planet that is, on the average, 3.5 million kilometers away from the star’s surface. The planet was discovered as a result of observing a cyclic decrease in the brightness of Ogle-Tr-3 every 28.5 hours. The ch ...
... A Newly Discovered Planet Scientists studying a Sun-like star named Ogle-Tr-3 discovered a planet that is, on the average, 3.5 million kilometers away from the star’s surface. The planet was discovered as a result of observing a cyclic decrease in the brightness of Ogle-Tr-3 every 28.5 hours. The ch ...