Contents and Concepts Learning Objectives
... • The solubility of an insoluble salt can be manipulated by adding a species that reacts with either the cation or the anion. • Effect of pH on Solubility • When a salt contains the conjugate base of a weak acid, the pH will affect the solubility of the salt. ...
... • The solubility of an insoluble salt can be manipulated by adding a species that reacts with either the cation or the anion. • Effect of pH on Solubility • When a salt contains the conjugate base of a weak acid, the pH will affect the solubility of the salt. ...
Solvent Denaturation and Stabilization of Globular Proteins?
... where the factor of 1.4 accounts for the difference in dimensions between an amino acid residue and a cubic lattice segment required in the model (Dill, 1985). We neglect here the insignificant difference between Gibbs and Helmholtz free energies. The concentration dependences for individual amino a ...
... where the factor of 1.4 accounts for the difference in dimensions between an amino acid residue and a cubic lattice segment required in the model (Dill, 1985). We neglect here the insignificant difference between Gibbs and Helmholtz free energies. The concentration dependences for individual amino a ...
Chapter 1 - TamAPChemistryHart
... Lewis: emphasize the shared electron pair. • A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor. • A Lewis base is an electron pair donor. • Note: Lewis acids and bases do not need to contain protons. • Therefore, the Lewis definition is the most general definition of acids and bases. For a substance to be a ...
... Lewis: emphasize the shared electron pair. • A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor. • A Lewis base is an electron pair donor. • Note: Lewis acids and bases do not need to contain protons. • Therefore, the Lewis definition is the most general definition of acids and bases. For a substance to be a ...
I have put this in the format of the 1984 exam
... The liquefied hydrogen halides have the normal boiling points given above. The relatively high boiling point of HF can be correctly explained by which of the following? (A) HF gas is more ideal. (B) HF is the strongest acid. (C) HF molecules have a smaller dipole moment. (D) HF is much less soluble ...
... The liquefied hydrogen halides have the normal boiling points given above. The relatively high boiling point of HF can be correctly explained by which of the following? (A) HF gas is more ideal. (B) HF is the strongest acid. (C) HF molecules have a smaller dipole moment. (D) HF is much less soluble ...
Chapter 3 – Stoichiometry of Formulas and Equations This chapter
... of a percent, even though the calculation may be more accurate. This is because percent composition calculations are usually used in the determination of the identity of unknown materials. It is quite difficult to obtain materials more than 99.9% pure and, combined with experimental error in making ...
... of a percent, even though the calculation may be more accurate. This is because percent composition calculations are usually used in the determination of the identity of unknown materials. It is quite difficult to obtain materials more than 99.9% pure and, combined with experimental error in making ...
Chapter 4: Reactions in Aqueous Solution
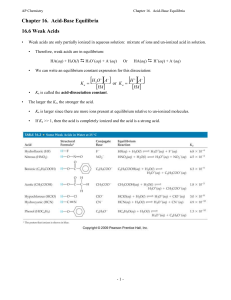
... 1) Water is a very common solvent due to its wide availability and low cost (most of our world is water). 2) Many reactions take place in aqueous solution. The term aqueous means dissolved in water. 3) Hydration of solids in Water A) Solid dissolves (falls apart) through interaction of ions with wat ...
... 1) Water is a very common solvent due to its wide availability and low cost (most of our world is water). 2) Many reactions take place in aqueous solution. The term aqueous means dissolved in water. 3) Hydration of solids in Water A) Solid dissolves (falls apart) through interaction of ions with wat ...
1984 Advanced Placement Exam
... When the concentration of substance B in the re(A) K4[Fe(CN)6] (D) K2[Pt(CN)6] action above is doubled, all other factors being held constant, it is found that the rate of the reac(B) K3[Fe(CN)6] (E) KCN tion remains unchanged. The most probable ex(C) K2[Pt(CN)4] planation for this observation is th ...
... When the concentration of substance B in the re(A) K4[Fe(CN)6] (D) K2[Pt(CN)6] action above is doubled, all other factors being held constant, it is found that the rate of the reac(B) K3[Fe(CN)6] (E) KCN tion remains unchanged. The most probable ex(C) K2[Pt(CN)4] planation for this observation is th ...
Modeling the Solubility of Nitrogen Dioxide in Water Using
... equilibrium with the gases in the vapor phase.4,5 However, the experiments were carried out using an inert background gas, i.e., nitrogen, to dilute NO2 before passing it through the aqueous liquid phase. Though this gas does not participate in the chemical reaction, its presence affects the concentr ...
... equilibrium with the gases in the vapor phase.4,5 However, the experiments were carried out using an inert background gas, i.e., nitrogen, to dilute NO2 before passing it through the aqueous liquid phase. Though this gas does not participate in the chemical reaction, its presence affects the concentr ...
chemistry I review pwrpt.
... 2. Create reactants table to compare have to need of each reactant ( units: moles or grams). 3. Identify the limiting and excess reactant. 4. Use limiting reactant to calculate theoretical yield of each product. 5. Calculate percent yield by comparing actual yield (from lab) to theoretical yield (ca ...
... 2. Create reactants table to compare have to need of each reactant ( units: moles or grams). 3. Identify the limiting and excess reactant. 4. Use limiting reactant to calculate theoretical yield of each product. 5. Calculate percent yield by comparing actual yield (from lab) to theoretical yield (ca ...
2009 U. S. NATIONAL CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD
... conditions may be caused to occur by increasing the concentration of the reactants and/or decreasing the concentrations of the products. b. ΔHfo values of compounds are relative to their elements in standards states (for which ΔH fo = 0). Depending on the compound, formation may either release energ ...
... conditions may be caused to occur by increasing the concentration of the reactants and/or decreasing the concentrations of the products. b. ΔHfo values of compounds are relative to their elements in standards states (for which ΔH fo = 0). Depending on the compound, formation may either release energ ...
V. Diffusion
... are not easily applied to non-equilibrium systems. However, there sometimes occur so-called quasi-steady states, where the diffusion process does not change in time, where classical results may locally apply. As the name suggests, this process is a not a true equilibrium since the system is still ev ...
... are not easily applied to non-equilibrium systems. However, there sometimes occur so-called quasi-steady states, where the diffusion process does not change in time, where classical results may locally apply. As the name suggests, this process is a not a true equilibrium since the system is still ev ...
File
... Suppose that in one batch of reactants 4.20mol Al was mixed with 1.75mol Fe2O3. Which reactant, if any, was the limiting reactant? Calculate the mass of iron (in grams) that can be formed from this mixture of reactants. How do we approach this question – firstly determine what has been asked of you. ...
... Suppose that in one batch of reactants 4.20mol Al was mixed with 1.75mol Fe2O3. Which reactant, if any, was the limiting reactant? Calculate the mass of iron (in grams) that can be formed from this mixture of reactants. How do we approach this question – firstly determine what has been asked of you. ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... order and illustrate how the reaction conditions above would be changed so that the [I–] would be pseudo first order. e. The activation energy for this reaction was found to be 84 kJ·mol –1 at 25 °C. How much faster would this reaction proceed if the activation energy were lowered by 10 kJ·mol–1 (fo ...
... order and illustrate how the reaction conditions above would be changed so that the [I–] would be pseudo first order. e. The activation energy for this reaction was found to be 84 kJ·mol –1 at 25 °C. How much faster would this reaction proceed if the activation energy were lowered by 10 kJ·mol–1 (fo ...
Acids, Bases and Buffers
... (a) The sharp vertical rise in pH on the pH–volume curve appears at the equivalence point (about 23 mL). Because the acid is monoprotic, the number of moles of acid equals the number of moles of NaOH. That number is the product of the exact volume and the molarity of the NaOH. The molarity of the ac ...
... (a) The sharp vertical rise in pH on the pH–volume curve appears at the equivalence point (about 23 mL). Because the acid is monoprotic, the number of moles of acid equals the number of moles of NaOH. That number is the product of the exact volume and the molarity of the NaOH. The molarity of the ac ...
Final Exam - Dawson College
... c. If the actual vapor pressure measured is 15.2 mm Hg, will the boiling point of this solution be higher or lower than the one expected from Raoult’s law? Explain. ...
... c. If the actual vapor pressure measured is 15.2 mm Hg, will the boiling point of this solution be higher or lower than the one expected from Raoult’s law? Explain. ...
2 - mrstorie
... 1. Give the electron configuration for a neutral atom of manganese, strontium, and iron. 2. Write the short hand notation for the electron configuration of phosphorus, tungsten, and gold. 3. What is the wavelength of light with a frequency of 5.6 x1020 Hz? 4. What is the frequency of light with ener ...
... 1. Give the electron configuration for a neutral atom of manganese, strontium, and iron. 2. Write the short hand notation for the electron configuration of phosphorus, tungsten, and gold. 3. What is the wavelength of light with a frequency of 5.6 x1020 Hz? 4. What is the frequency of light with ener ...