Name: Chapter 2 Guided Notes P.S. Teacher: Price Motion and
... 1. ___________________= final velocity - initial velocity over time a = v f – vi / t 2. Units of acceleration – m/s2 3. A speed/time graph tells you if the acceleration is positive or negative • ______________ acceleration – “+” numbers with “+” slope on graph • Negative acceleration –”-” numbers wi ...
... 1. ___________________= final velocity - initial velocity over time a = v f – vi / t 2. Units of acceleration – m/s2 3. A speed/time graph tells you if the acceleration is positive or negative • ______________ acceleration – “+” numbers with “+” slope on graph • Negative acceleration –”-” numbers wi ...
AP Physics – Mechanics – Chapter 7-8
... straight road? Yes because the speed AND direction are constant, meaning constant v, thus: ...
... straight road? Yes because the speed AND direction are constant, meaning constant v, thus: ...
Ppt - AIS Moodle
... 8.2 Centrifugal Force Centrifugal force is not a true force exerted on your body. It is simply your tendency to move in a straight line due to inertia. This is easy to observe by twirling a small object at the end of a string. When the string is released, the object flies off in a straight ...
... 8.2 Centrifugal Force Centrifugal force is not a true force exerted on your body. It is simply your tendency to move in a straight line due to inertia. This is easy to observe by twirling a small object at the end of a string. When the string is released, the object flies off in a straight ...
Motion and Forces Jeopardy
... 1. The property of things to remain at rest if at rest, and in motion if in motion. inertia 2. The distance traveled per time. speed 3. Formula Daily Double: What is the formula for acceleration? A=Vf-Vi/t 4. The speed of an object and direction of motion. velocity 5. A quantity that specifies direc ...
... 1. The property of things to remain at rest if at rest, and in motion if in motion. inertia 2. The distance traveled per time. speed 3. Formula Daily Double: What is the formula for acceleration? A=Vf-Vi/t 4. The speed of an object and direction of motion. velocity 5. A quantity that specifies direc ...
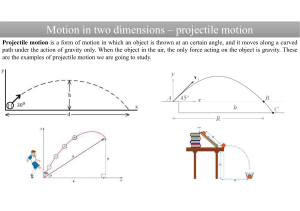
Motion in two dimensions – projectile motion
... In the air the object is under the influence of gravity, which is pulling it down. The acceleration due to gravity is g = 9.8 ms-2 and is downward. Thus ay = g. During an upward motion, a vertical component of the velocity (vy) of an object gradually decreases to zero at the maximum point. On its wa ...
... In the air the object is under the influence of gravity, which is pulling it down. The acceleration due to gravity is g = 9.8 ms-2 and is downward. Thus ay = g. During an upward motion, a vertical component of the velocity (vy) of an object gradually decreases to zero at the maximum point. On its wa ...
Chapter 10.3 Newton`s 1st & 2nd Laws of Motion
... accelerates at 2.0 m/s2. Calculate the net force that causes this acceleration. Read and Understand What information have you been given? Mass of the water-skier (m) = 55 kg Acceleration of the water-skier (a) = 2.0 m/s2 ...
... accelerates at 2.0 m/s2. Calculate the net force that causes this acceleration. Read and Understand What information have you been given? Mass of the water-skier (m) = 55 kg Acceleration of the water-skier (a) = 2.0 m/s2 ...
Name - Spring Branch ISD
... Name _________________________________________________ Date _____________________Period _______ ...
... Name _________________________________________________ Date _____________________Period _______ ...
Newton`s Second Law
... 1. When it is acted on by an unbalanced force, an object will __________________________. 2. When an unbalanced force acts on an object at rest, the object will ___________________________. 3. A change in velocity is called an _____________________________. 4. A large force will cause ______________ ...
... 1. When it is acted on by an unbalanced force, an object will __________________________. 2. When an unbalanced force acts on an object at rest, the object will ___________________________. 3. A change in velocity is called an _____________________________. 4. A large force will cause ______________ ...
06 Objectives
... 10. You should be able to solve problems asking to calculate the net force such as that described on textbook pg. 140. 11. State the three major ideas of Newton’s second law. 12. Tell the relationship between unbalanced forces acting on an object and acceleration of that object. 13. Recognize that c ...
... 10. You should be able to solve problems asking to calculate the net force such as that described on textbook pg. 140. 11. State the three major ideas of Newton’s second law. 12. Tell the relationship between unbalanced forces acting on an object and acceleration of that object. 13. Recognize that c ...
File
... that has run off the end of a runway, without causing injury to passengers. It is solid enough to support a car, but crumbles under the weight of a large airplane. By crumbling, it slows the plane to a safe stop. For example, suppose a 747 jetliner with a mass of 1.75 X 105 kg and an initial speed o ...
... that has run off the end of a runway, without causing injury to passengers. It is solid enough to support a car, but crumbles under the weight of a large airplane. By crumbling, it slows the plane to a safe stop. For example, suppose a 747 jetliner with a mass of 1.75 X 105 kg and an initial speed o ...