HOMEWORK – DUE FRIDAY, NOVEMBER 22ND NEWTON`S
... Write “1” if Newton’s first law applies to the statement, “2” if Newton’s seconds law applies to the statement, or “3” if Newton’s third law applies to the statement. 1. Forces occur in action-reaction pairs. 2. When the same amount of force is applied to two objects with different masses, the objec ...
... Write “1” if Newton’s first law applies to the statement, “2” if Newton’s seconds law applies to the statement, or “3” if Newton’s third law applies to the statement. 1. Forces occur in action-reaction pairs. 2. When the same amount of force is applied to two objects with different masses, the objec ...
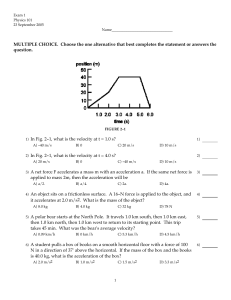
Exam 1
... C) The car is decelerating, and its acceleration is positive. D) A statement cannot be made using the information given. ...
... C) The car is decelerating, and its acceleration is positive. D) A statement cannot be made using the information given. ...
Honors Physics Unit 2 Objectives Newton`s Laws, Statics, and
... 9. Demonstrate an understanding of direct and inverse proportionalities; demonstrate an understanding of the relationships among net force on, mass of, and acceleration of an object 10. Recall from memory Newton’s Second Law of Motion (in words and formula); solve basic acceleration problems using N ...
... 9. Demonstrate an understanding of direct and inverse proportionalities; demonstrate an understanding of the relationships among net force on, mass of, and acceleration of an object 10. Recall from memory Newton’s Second Law of Motion (in words and formula); solve basic acceleration problems using N ...
Work and Kinetic Energy
... position is at x = 0. The work done by spring is positive if: 1) xi = 2cm and xf = 4cm 2) xi = -2 cm and xf = 4cm 3) xi = -2 cm and xf = -4 cm 4) xi = 2 cm and xf = -4 cm 5) xi = -4 cm and xf = -2 cm Q20) A hockey puck sliding on an ice rink is moving at 1 m/s when it slides onto a carpet that someo ...
... position is at x = 0. The work done by spring is positive if: 1) xi = 2cm and xf = 4cm 2) xi = -2 cm and xf = 4cm 3) xi = -2 cm and xf = -4 cm 4) xi = 2 cm and xf = -4 cm 5) xi = -4 cm and xf = -2 cm Q20) A hockey puck sliding on an ice rink is moving at 1 m/s when it slides onto a carpet that someo ...
Document
... Pretend that the wind the blew on the boat’s sail lasts for 2 seconds. We can know find the new velocity of the boat. Using v = a t. vx = ax t: (1.7 m/s2)(2 s) = 3.4 m/s vy = ay t: (1 m/s2)(2 s) = 2 m/s vfx = vix + vx = (2.8 + 3.4) m/s = 6.2 m/s vfy = viy + vy = (2.8 + 2) m/s = 4.8 m/s ...
... Pretend that the wind the blew on the boat’s sail lasts for 2 seconds. We can know find the new velocity of the boat. Using v = a t. vx = ax t: (1.7 m/s2)(2 s) = 3.4 m/s vy = ay t: (1 m/s2)(2 s) = 2 m/s vfx = vix + vx = (2.8 + 3.4) m/s = 6.2 m/s vfy = viy + vy = (2.8 + 2) m/s = 4.8 m/s ...
Dot and Cross Products Dot Product
... a) If a force F = (0, 1, 13) N acts on an object which undergoes a displacement d = (3, 2, 5) m, what work does the force do? b) If a force F = (3, 1, 7) N acts on an object which undergoes a displacement d = (5, 6, -3) m, what work does the force do? c) If a force F = (1, -2, 3) N acts on an object ...
... a) If a force F = (0, 1, 13) N acts on an object which undergoes a displacement d = (3, 2, 5) m, what work does the force do? b) If a force F = (3, 1, 7) N acts on an object which undergoes a displacement d = (5, 6, -3) m, what work does the force do? c) If a force F = (1, -2, 3) N acts on an object ...
Complete the following on a separate sheet of paper
... 7. If a car is able to accelerate at 6.0 m/s2, what acceleration can it attain if it is towing another car of equal mass? Explain your answer. 8. A constant unchanging force of 30.25 N is applied to a 12.02 kg object for exactly 15.00 seconds. What is the final velocity of the object after the 15.00 ...
... 7. If a car is able to accelerate at 6.0 m/s2, what acceleration can it attain if it is towing another car of equal mass? Explain your answer. 8. A constant unchanging force of 30.25 N is applied to a 12.02 kg object for exactly 15.00 seconds. What is the final velocity of the object after the 15.00 ...
Motion - Cloudfront.net
... 1. The motion of an object over a period of time can be shown on a distance-time graph 2. Distance is plotted on the vertical axis (y) ...
... 1. The motion of an object over a period of time can be shown on a distance-time graph 2. Distance is plotted on the vertical axis (y) ...
SHM - ThisIsPhysics
... 1) A body of mass 200 g is executing simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 20 mm. The maximum force which acts upon it is 0.064 N. Calculate: (a) its maximum velocity (b) its period of oscillation ...
... 1) A body of mass 200 g is executing simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 20 mm. The maximum force which acts upon it is 0.064 N. Calculate: (a) its maximum velocity (b) its period of oscillation ...
Force and Motion Force: a push or a pull that causes a change in
... Acceleration: a change in velocity over time. - Acceleration of an object in a free fall on the Earth: = 9.8 m/s2 3 Forces that affect Motion 1) Friction: A force that resists the motion of 2 surfaces/objects touching each other; slows down or prevents motion. Example: car tires on a road surface ...
... Acceleration: a change in velocity over time. - Acceleration of an object in a free fall on the Earth: = 9.8 m/s2 3 Forces that affect Motion 1) Friction: A force that resists the motion of 2 surfaces/objects touching each other; slows down or prevents motion. Example: car tires on a road surface ...
Non-Linear Motion
... bouncing ball, the weight on a pendulum, or such. Period - is the time the object takes to go back and forth. If you spin a weight on a string, you can measure the time it takes to go 1 revolution. Drop a ball and measure the time it takes until it bounces back up. That is its period. Sometimes freq ...
... bouncing ball, the weight on a pendulum, or such. Period - is the time the object takes to go back and forth. If you spin a weight on a string, you can measure the time it takes to go 1 revolution. Drop a ball and measure the time it takes until it bounces back up. That is its period. Sometimes freq ...
Vectors and Newton`s First and Second Laws of Motion
... What two forces are acting on him, i.e., what forces does he feel? How are the strengths of the two forces related to each other? Which one of Newton’s laws applies here? forces: ...
... What two forces are acting on him, i.e., what forces does he feel? How are the strengths of the two forces related to each other? Which one of Newton’s laws applies here? forces: ...