Motion due to gravity
... The first person to state clearly that all objects on Earth fall with the same acceleration was Galileo (1564 − 1642). He used experimental observation with mathematical argument to arrive at this. This acceleration, denoted by the letter g, is known as the acceleration due to gravity. It has a valu ...
... The first person to state clearly that all objects on Earth fall with the same acceleration was Galileo (1564 − 1642). He used experimental observation with mathematical argument to arrive at this. This acceleration, denoted by the letter g, is known as the acceleration due to gravity. It has a valu ...
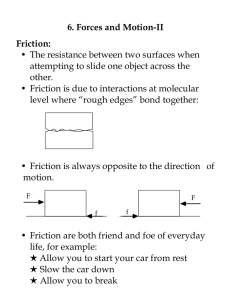
6. Forces and Motion-II Friction: • The resistance between two surfaces when
... A box at 2 m up a ramp (θ = 30°) slides down with an initial velocity of 1 m/s. The ramp has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.6. The box then slides across a 5 m sheet of ice and up a second ramp (θ = 5°). The motion from start to where the box comes to rest took 9 s. What is the coefficient o ...
... A box at 2 m up a ramp (θ = 30°) slides down with an initial velocity of 1 m/s. The ramp has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.6. The box then slides across a 5 m sheet of ice and up a second ramp (θ = 5°). The motion from start to where the box comes to rest took 9 s. What is the coefficient o ...
Introduction to Biomechanics 2001
... contact with other bodies, and the weight of the body c. label all forces and couple moments with proper magnitudes and directions F. Force couple 1. definition: two parallel forces that have the same magnitude, opposite directions, and are separated by a perpendicular distance 2. FR = 0 ...
... contact with other bodies, and the weight of the body c. label all forces and couple moments with proper magnitudes and directions F. Force couple 1. definition: two parallel forces that have the same magnitude, opposite directions, and are separated by a perpendicular distance 2. FR = 0 ...
+Chapter 8 Vectors and Parametric Equations 8.1/8.2 Geometric
... Ex 2: There are 3 forces acting on an object. The 1st force has the magnitude of 7 lbs. and is 90°. The 2nd force has the magnitude of 5 lbs. and is 38° from force 1. The 3rd force has a magnitude of 11 lbs. and is 48° below the positive x-axis. Find the resultant force and the direction. ...
... Ex 2: There are 3 forces acting on an object. The 1st force has the magnitude of 7 lbs. and is 90°. The 2nd force has the magnitude of 5 lbs. and is 38° from force 1. The 3rd force has a magnitude of 11 lbs. and is 48° below the positive x-axis. Find the resultant force and the direction. ...
12.2 Newton`s 1st and 2nd Laws of Motion
... continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a nonzero net force ...
... continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a nonzero net force ...
File
... an equal and opposite reaction.” More Scientific Version When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second exerts a force on the first that is equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction. ...
... an equal and opposite reaction.” More Scientific Version When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second exerts a force on the first that is equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction. ...
Newton`s 2 nd Law
... rope. If they are pulling on the rope with equal but opposite forces, what will happen to the rope? 1. It will stay in place between the 2 people. 2. It will move towards the right. 3. It will move towards the left. 4. It will fall to the ground. ...
... rope. If they are pulling on the rope with equal but opposite forces, what will happen to the rope? 1. It will stay in place between the 2 people. 2. It will move towards the right. 3. It will move towards the left. 4. It will fall to the ground. ...
presentation source
... An object will have zero angular acceleration if the total torque on the object is zero if ...
... An object will have zero angular acceleration if the total torque on the object is zero if ...
Laws of Motion Powerpoint
... • Gravity is the force of attraction between two objects. • The strength of gravity depends on an object’s mass and distance. • For example, the moon’s gravity is 1/6 of the Earth’s gravity because it is much smaller. • Where would gravity be less, at sea level or on top of a mountain? ...
... • Gravity is the force of attraction between two objects. • The strength of gravity depends on an object’s mass and distance. • For example, the moon’s gravity is 1/6 of the Earth’s gravity because it is much smaller. • Where would gravity be less, at sea level or on top of a mountain? ...
Answer, Key – Homework 4 – David McIntyre – 45123 – Mar 25
... of the ball, we need to find the initial velocity of the ball. Let y be the distance above the ground. After the string breaks, the ball has no initial velocity in the vertical direction, so the time spent in the air may be deduced from the kinematic equation, ...
... of the ball, we need to find the initial velocity of the ball. Let y be the distance above the ground. After the string breaks, the ball has no initial velocity in the vertical direction, so the time spent in the air may be deduced from the kinematic equation, ...
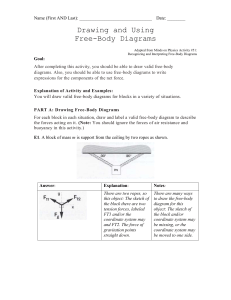
Drawing and Using
... First of all, you should make sure that the directions of all your forces are accurately drawn. This will help you find the components of the forces, which will help you find the net force, and ultimately, the acceleration of the object. Then, if the sizes of the force vectors are also drawn accurat ...
... First of all, you should make sure that the directions of all your forces are accurately drawn. This will help you find the components of the forces, which will help you find the net force, and ultimately, the acceleration of the object. Then, if the sizes of the force vectors are also drawn accurat ...
Powerpoint
... Draw a system schema: • Draw a diagram where you write down the name of each object in the system and then draw a solid circle drawn around it. • Draw two sided arrows like this between the object circles of objects that interact (This illustrates all interactions between the objects in this diagram ...
... Draw a system schema: • Draw a diagram where you write down the name of each object in the system and then draw a solid circle drawn around it. • Draw two sided arrows like this between the object circles of objects that interact (This illustrates all interactions between the objects in this diagram ...
Slide 1
... The net force Fnet acting on a body is equal to the product of the body mass m and its acceleration a Fnet = ma; a= Fnet / m Acceleration component along a given axis is caused only by sum of forces component along that axis ax = Fnet,x /m ; ay = Fnet,y /m ; az = Fnet,z /m SI unit of force New ...
... The net force Fnet acting on a body is equal to the product of the body mass m and its acceleration a Fnet = ma; a= Fnet / m Acceleration component along a given axis is caused only by sum of forces component along that axis ax = Fnet,x /m ; ay = Fnet,y /m ; az = Fnet,z /m SI unit of force New ...
Semester 1 Concept Questions
... For the final, you may use a 8.5”x11” page of notes. This page must be unique, HANDWRITTEN & one-sided. Motion in One & Two Dimensions: 1. A car accelerates from 13 m/s to 25 m/s in 6.0 sec a. What was its acceleration? (2.0m/s2) b. How far did it travel in this time? (114m) 2. What is the equation ...
... For the final, you may use a 8.5”x11” page of notes. This page must be unique, HANDWRITTEN & one-sided. Motion in One & Two Dimensions: 1. A car accelerates from 13 m/s to 25 m/s in 6.0 sec a. What was its acceleration? (2.0m/s2) b. How far did it travel in this time? (114m) 2. What is the equation ...
Physics 50 Sample Midterm Exam #1
... A projectile is fired at time t = 0.0s, from point 0 at the edge of a cliff, with initial velocity components of v0x = 80 m/s and v0y = 600 m/s The projectile rises, then falls into the sea at point P, as shown in the figure. The time of flight of the projectile is 150.0 s. We want to determine the ...
... A projectile is fired at time t = 0.0s, from point 0 at the edge of a cliff, with initial velocity components of v0x = 80 m/s and v0y = 600 m/s The projectile rises, then falls into the sea at point P, as shown in the figure. The time of flight of the projectile is 150.0 s. We want to determine the ...